What Is A Fulfillment Center? A Complete Guide (2025)
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Overcoming the Overwhelm of Packing and Shipping
As an e-commerce business owner, you may find yourself caught in a whirlwind of packing boxes, labeling shipments, and tracking deliveries. The excitement of growing sales can quickly turn into stress when the logistics of fulfilling orders become overwhelming. For many entrepreneurs, the process of getting a product into a customer’s hands can feel like an insurmountable challenge, especially as order volumes increase. This is where understanding e-commerce fulfillment becomes crucial.
Defining Fulfillment
E-commerce fulfillment refers to the entire process of receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders. It encompasses everything from inventory management and order processing to shipping and handling returns. The goal is simple: ensure that customers receive their products quickly and efficiently, which is vital for maintaining satisfaction and loyalty.
What This Guide Covers
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various fulfillment models available to growing businesses, including third-party logistics (3PL), Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), and self-fulfillment. Each model has its own set of advantages and challenges, and we’ll help you determine which option aligns best with your operational capabilities and growth goals.
We will also delve into the core services integral to an effective fulfillment strategy, such as warehousing, inventory management, packing, and shipping. Understanding these components will enable you to streamline your operations and improve customer experiences.
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is another critical aspect we will address. With numerous providers in the market, knowing what to look for—whether it’s technology integration, scalability, or specific service capabilities—can make a significant difference in your logistics efficiency.
Finally, we’ll break down the pricing structures associated with various fulfillment options. From setup and storage fees to shipping costs, having a clear understanding of your potential expenses will empower you to make informed decisions that protect your profit margins.
Empowering Smart Logistics Decisions
The ultimate goal of this guide is to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to navigate the complexities of e-commerce fulfillment. By understanding your options and the intricacies of the fulfillment process, you can make smart decisions that enhance your logistics operations, allowing you to focus on what you do best: growing your business.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
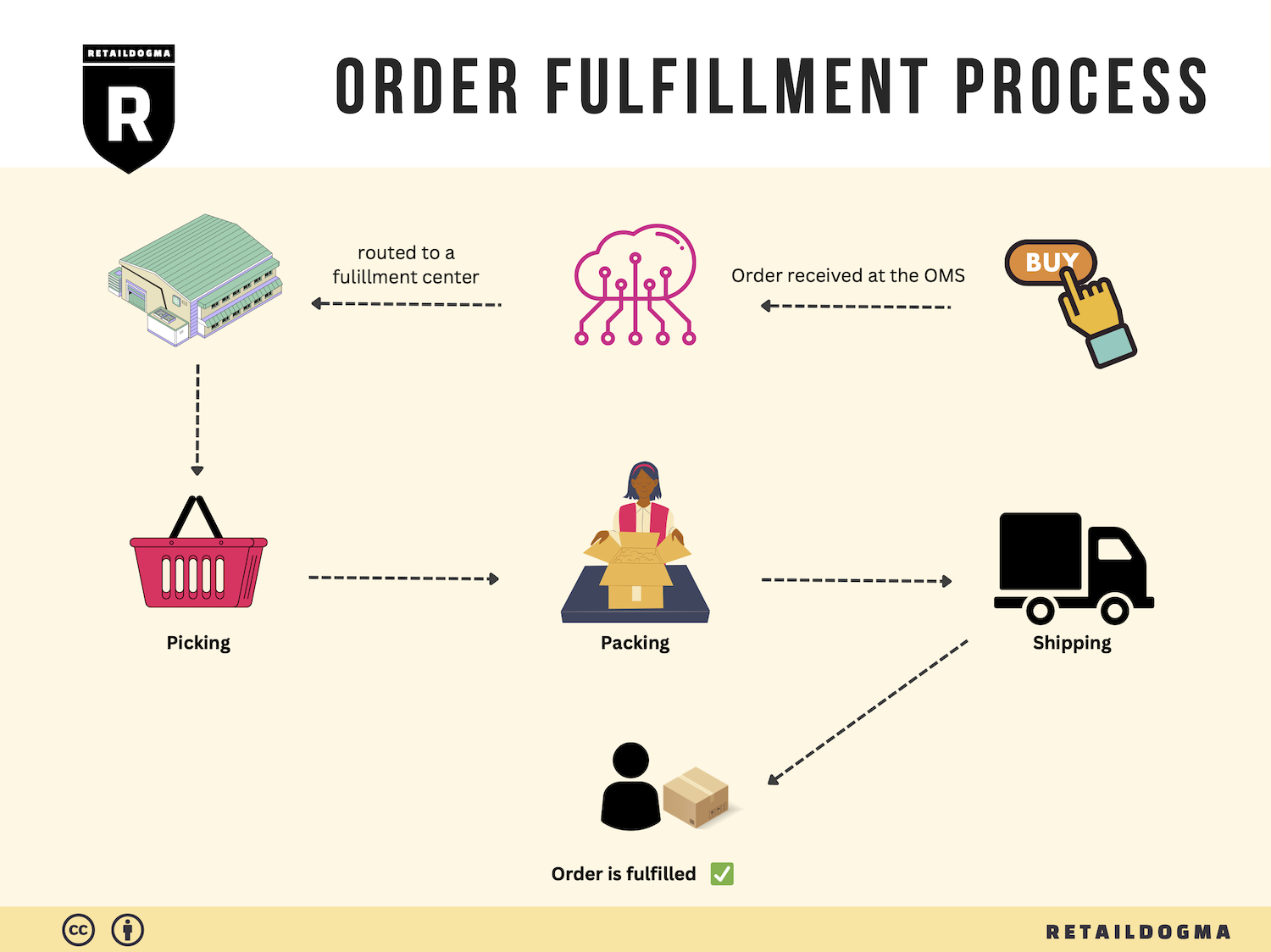
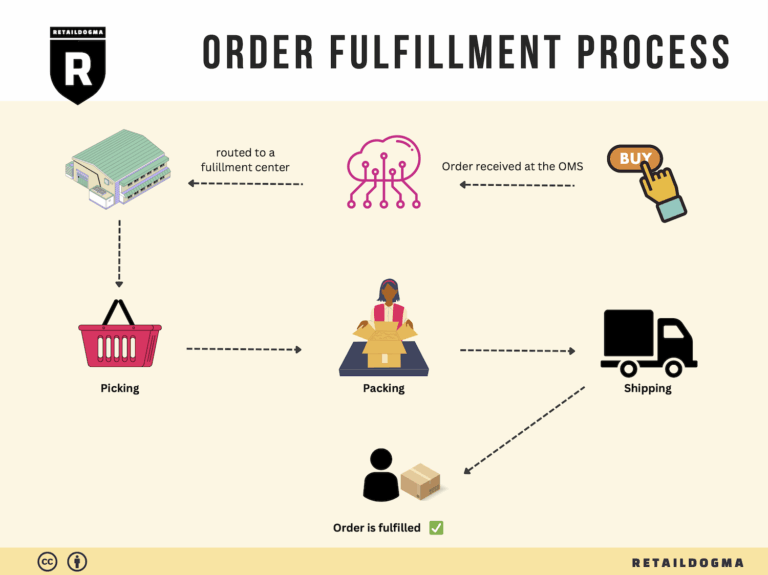
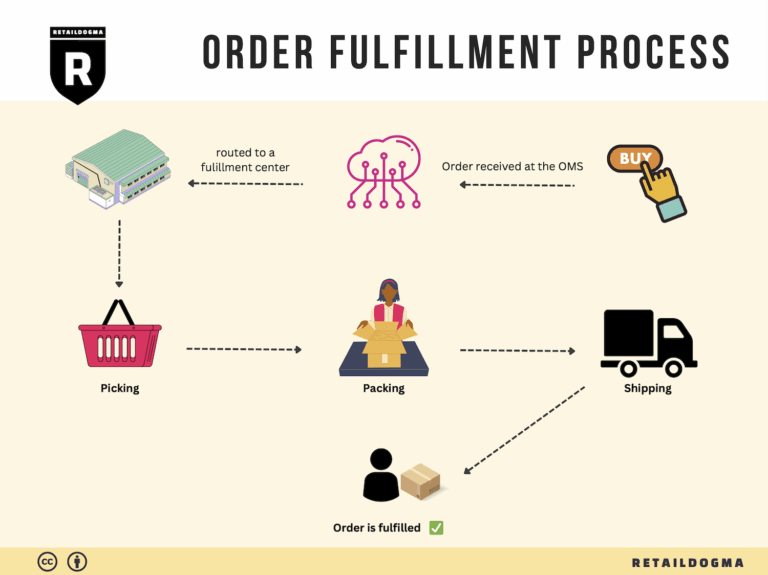
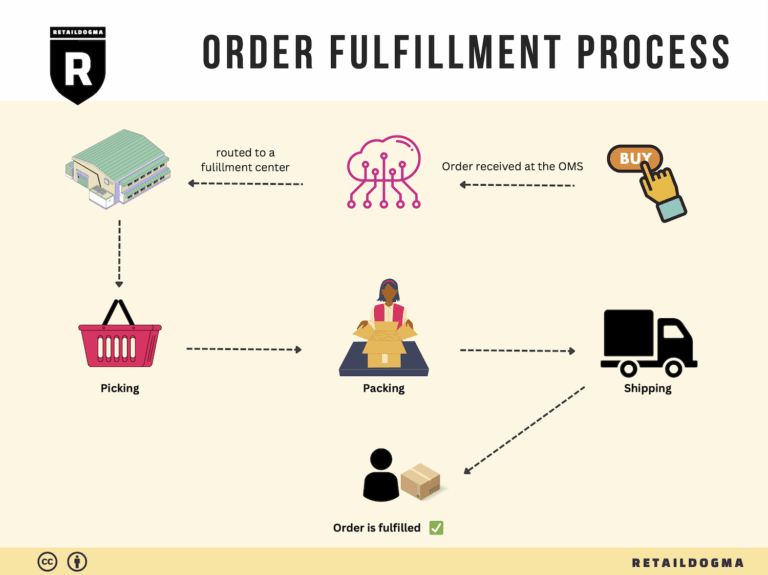
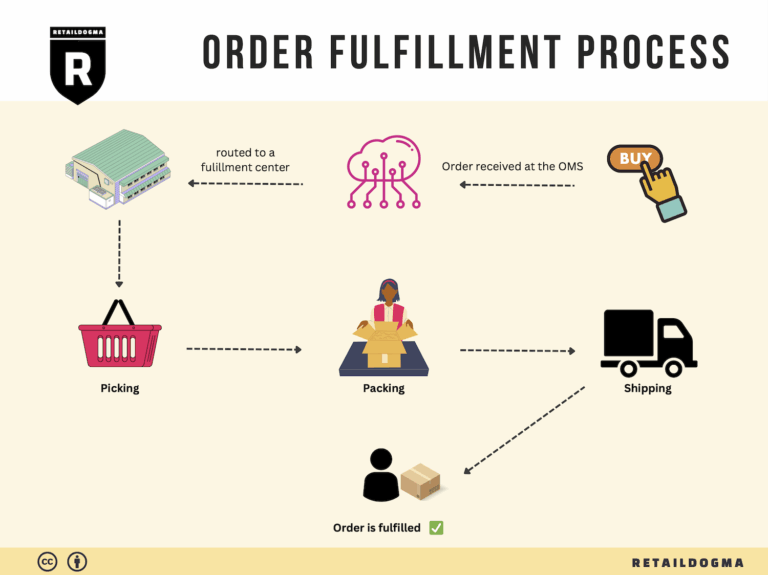
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
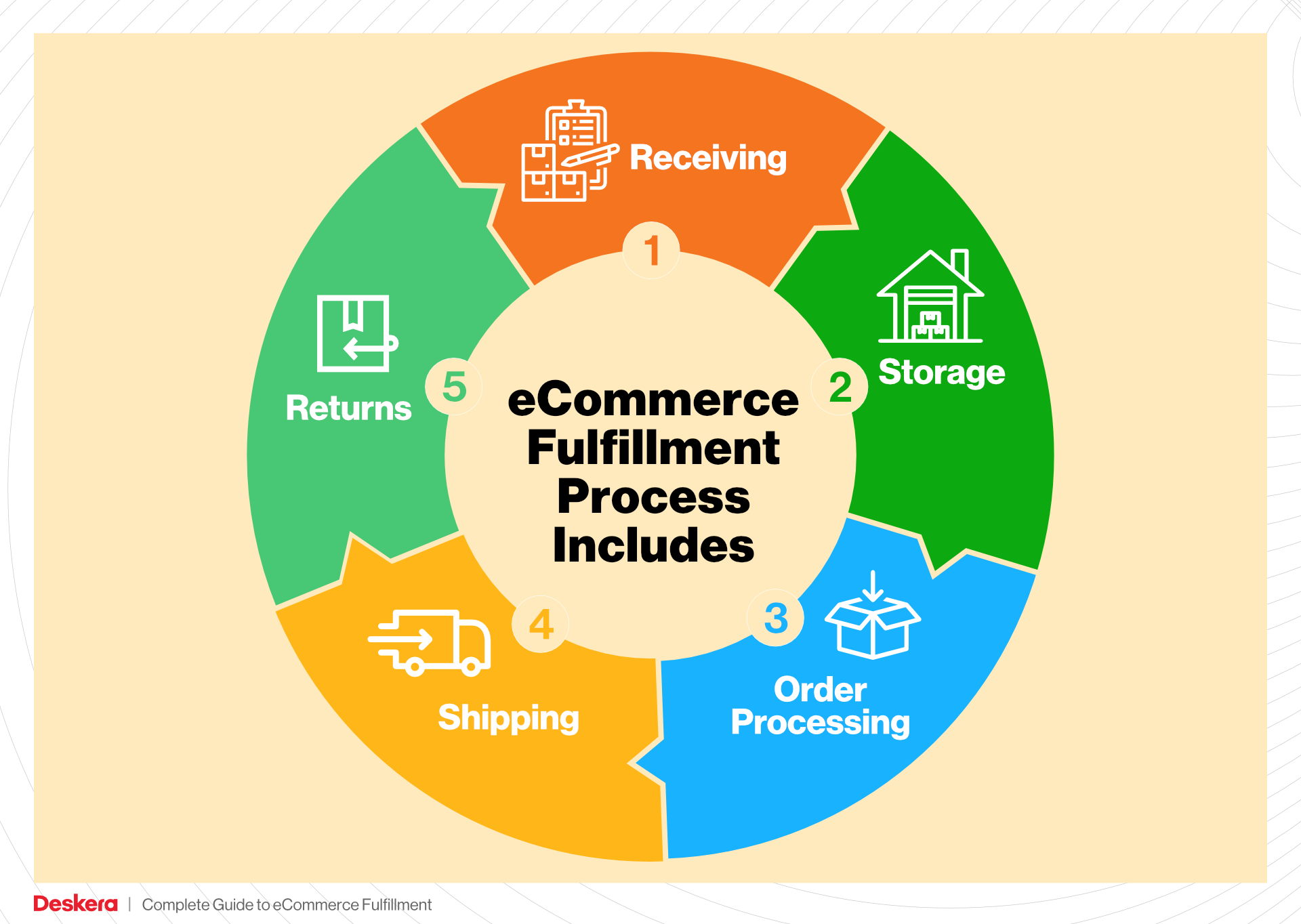
1. Receiving Inventory
The first step in the order fulfillment process is receiving inventory. This involves accepting shipments of products from suppliers and ensuring that they match the purchase orders. Each item is typically tracked using a Stock Keeping Unit (SKU), a unique identifier that helps in managing inventory levels accurately.
Upon arrival, items are inspected for quality and quantity to confirm that they meet specifications. This process is crucial for maintaining inventory accuracy and preventing stock discrepancies. If there are issues with the received goods, such as damage or incorrect quantities, they must be addressed immediately to avoid future complications in order processing.
Efficient inventory receiving helps establish a solid foundation for the entire fulfillment process. By ensuring that all products are accounted for and in good condition, businesses can minimize stockouts and ensure that they can fulfill customer orders promptly.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once the inventory is received, the next step is warehouse storage. This involves strategically placing items in a storage facility based on factors like size, weight, and demand frequency. Proper organization is essential for optimizing space and ensuring that items are easily accessible for order picking.
During this phase, a Warehouse Management System (WMS) is often utilized. This technology helps in tracking inventory locations and movements within the warehouse. The importance of an effective WMS cannot be overstated; it provides real-time data on inventory levels, reducing the chances of overstocking or stockouts.
Effective warehouse storage not only maximizes space but also enhances operational efficiency. By organizing products systematically, businesses can reduce the time taken to locate items, which ultimately speeds up the fulfillment process.
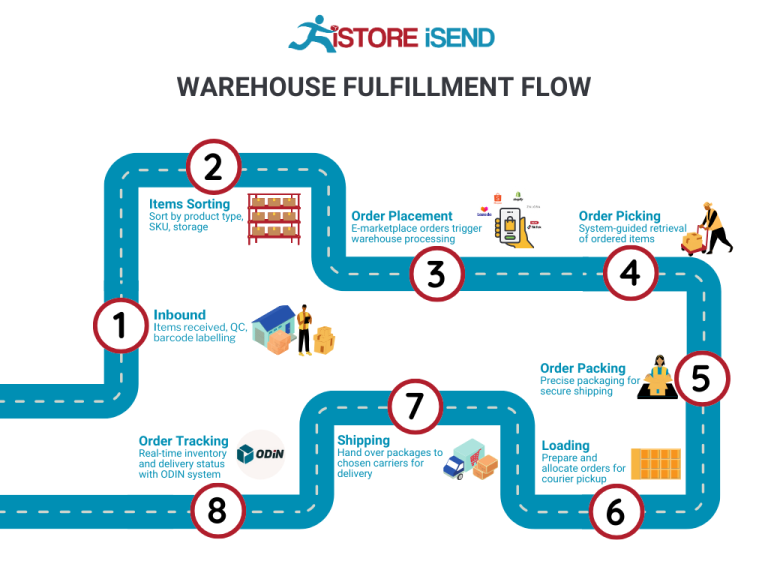
3. Order Picking
The next step in the order fulfillment process is order picking, where staff or automated systems retrieve items from storage to fulfill customer orders. A common tool used in this stage is the pick list, which outlines the items and quantities needed for each order.
Order picking is critical because it directly impacts order accuracy and customer satisfaction. Mistakes during this phase can lead to incorrect orders being shipped, resulting in returns and dissatisfied customers. Therefore, businesses should adopt best practices, such as using barcode scanning technology to verify items during picking.
Efficient order picking can significantly enhance fulfillment speed. By streamlining this process, businesses can ensure that orders are prepared quickly and accurately, leading to improved customer experiences and higher retention rates.
4. Order Packing
Once items are picked, they move to the order packing stage. Here, products are carefully packaged for shipment to ensure they arrive at the customer’s door in excellent condition. Proper packing materials and techniques are essential for protecting items during transit.
A key component of this process is the packing slip, which includes order details and serves as a receipt for the customer. It is important for businesses to ensure that the correct packing slip is included with each order to provide transparency and reinforce trust with the customer.
Effective order packing not only protects products but also enhances the unboxing experience for customers. A well-packed order can lead to positive reviews and repeat business, making this step vital for long-term success in e-commerce.
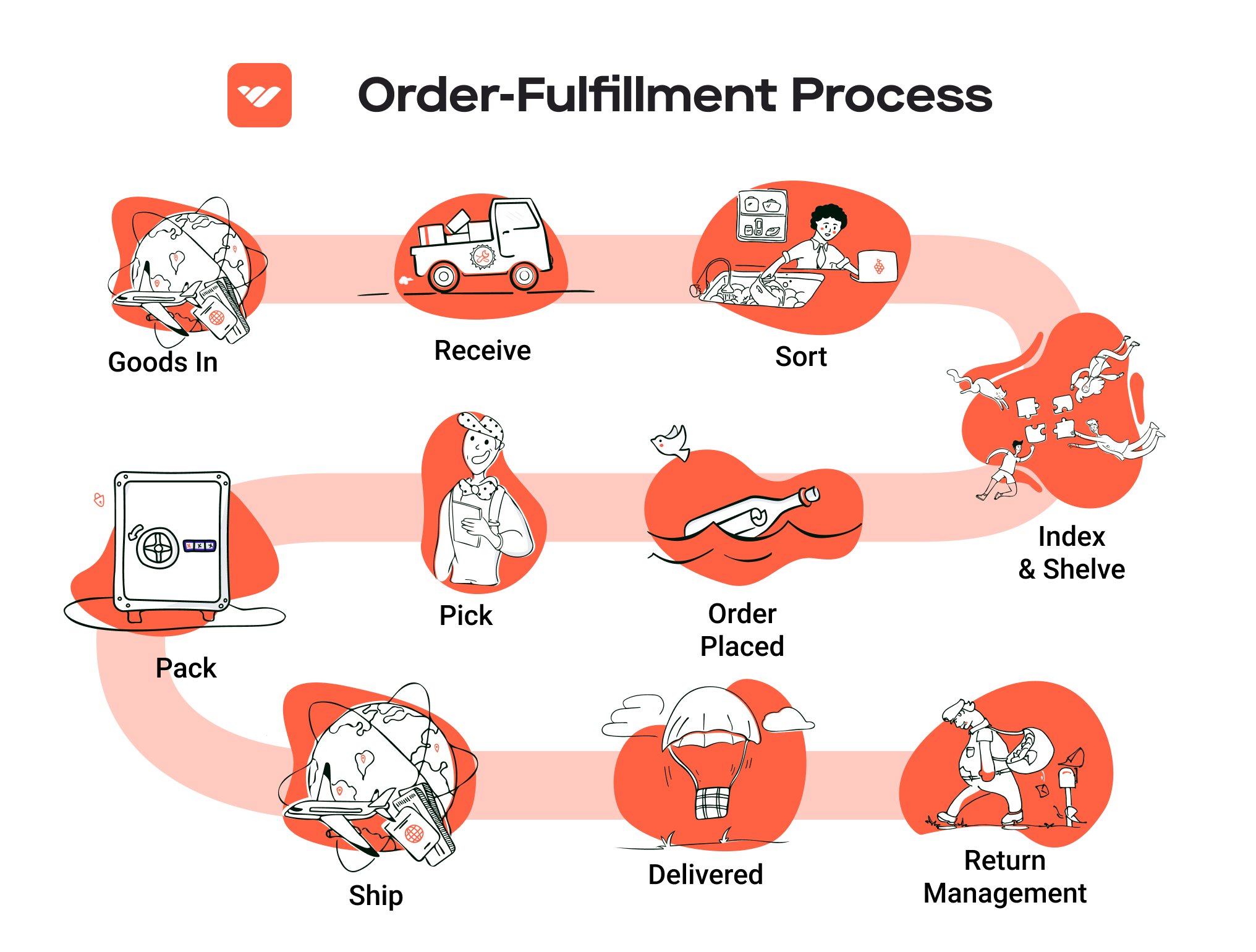
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. This involves selecting a shipping carrier, generating shipping labels, and dispatching the order to the customer. The choice of carrier can significantly affect delivery speed and cost, so businesses should evaluate options carefully.
During this phase, last-mile delivery becomes a crucial focus. This term refers to the final step of the delivery process, where the package is transported from a distribution center to the customer’s doorstep. Efficient last-mile delivery is essential for meeting customer expectations regarding shipping times.
Effective shipping and delivery practices are vital for customer satisfaction. By providing timely updates and tracking information, businesses can keep customers informed about their order status, which enhances their overall experience. A well-executed shipping strategy can lead to repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth referrals, fueling business growth.
In conclusion, understanding and optimizing each step of the order fulfillment process is essential for e-commerce businesses aiming to scale effectively. By focusing on these key areas, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive sales growth.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Fulfillment Model Comparison
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | Business owner/employee | Startups to small businesses | Full control over processes | Resource-intensive and costly |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | Fulfillment service provider | Growing businesses scaling up | Scalability and operational efficiency | Less control over fulfillment process |
| Dropshipping | Supplier/vendor | New entrepreneurs and small stores | Low overhead and inventory risk | Lack of control and potential delays |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment means that the e-commerce business handles every aspect of order processing, from receiving orders to picking, packing, and shipping products. This model is particularly suitable for startups and small businesses that want to maintain control over their fulfillment processes. The key advantage of in-house fulfillment is the ability to oversee the quality of packaging and shipping, ensuring that products meet the company’s standards and brand image. This model also provides direct insight into inventory management, allowing businesses to react quickly to stock levels and customer demands.
However, in-house fulfillment comes with significant challenges. It requires substantial resources, including warehousing space, technology for order management, and a team dedicated to logistics. As businesses scale, the costs associated with warehousing, labor, and shipping can increase dramatically—especially in a market where warehouse storage costs have risen sharply. Moreover, handling fulfillment in-house can divert focus from core business activities such as marketing and product development. Therefore, while in-house fulfillment offers control and flexibility, it may not be sustainable as order volumes grow.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers specialize in managing logistics and fulfillment for e-commerce businesses. This model is ideal for growing companies that experience fluctuations in order volume and need to scale operations efficiently without the overhead of managing fulfillment in-house. With 3PL, businesses can outsource warehousing, inventory management, order processing, and shipping to a specialized provider. This allows companies to focus on their core competencies while benefiting from the 3PL’s expertise in logistics.
The primary advantage of using a 3PL is scalability. As demand for products increases, 3PLs can quickly adapt by adjusting warehouse space and logistics processes without requiring significant investment from the business. Additionally, many 3PL providers offer technology solutions that integrate with existing e-commerce platforms, providing real-time inventory tracking and order updates. However, the key disadvantage lies in the potential loss of control over the fulfillment process. Businesses may find it challenging to maintain their desired quality standards if they do not have a direct hand in how products are packed and shipped. Moreover, aligning processes and communication with a third-party provider can sometimes lead to misunderstandings or delays.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where the e-commerce business does not hold any inventory. Instead, when a customer places an order, the business purchases the item from a third-party supplier who then ships it directly to the customer. This model is particularly attractive for new entrepreneurs and small businesses that want to minimize financial risk and inventory management concerns. With dropshipping, businesses can offer a wide range of products without the need for upfront investment in inventory.
The most significant advantage of dropshipping is its low overhead. Since there is no need to invest in inventory, warehousing, or fulfillment personnel, businesses can allocate resources to marketing and customer acquisition. Additionally, dropshipping can provide flexibility in product offerings, allowing businesses to test new items without significant financial commitment. However, the downsides are substantial. The primary concern is the lack of control over inventory and fulfillment processes. Businesses may encounter issues with product quality, shipping times, and stock availability, which can negatively impact customer satisfaction. Furthermore, the margins in dropshipping can be thin, as businesses must compete on price with suppliers and may face additional fees from dropshipping platforms.
In conclusion, choosing the right fulfillment model is critical for e-commerce businesses looking to scale their operations effectively. Each model—whether in-house, 3PL, or dropshipping—has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the decision should align with the business’s current stage, resources, and long-term goals. Understanding these models allows entrepreneurs to make informed decisions that can optimize their fulfillment processes and enhance customer satisfaction.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service that allows e-commerce sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon then takes care of storage, packaging, and shipping directly to customers. This means that sellers can leverage Amazon’s extensive logistics and distribution network, along with its customer service, to enhance their sales potential without having to manage the fulfillment process themselves.
When a customer orders a product listed by an FBA seller, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the order on behalf of the seller. This service also includes handling returns and customer inquiries, allowing sellers to focus on other aspects of their business, such as product development and marketing.
How FBA Works
-
Setup and Inventory: Sellers sign up for FBA and create a listing for their products on Amazon. They then send their inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, where it is stored until sold.
-
Order Management: Once a customer places an order, Amazon’s system automatically processes it. The item is picked from the inventory, packed, and shipped directly to the customer.
-
Customer Service and Returns: Amazon manages all customer service inquiries related to the FBA products, including handling returns and refunds, which is a significant advantage for sellers.
-
Sales Channels: FBA products can be listed on Amazon’s marketplace, and sellers can also utilize Amazon’s multi-channel fulfillment service to ship orders from other sales channels, such as their own websites.
Pros of Using FBA
1. Prime Eligibility
One of the standout benefits of FBA is that products fulfilled by Amazon are eligible for Amazon Prime. This can significantly boost sales as Prime members tend to prefer Prime-eligible products due to the free and fast shipping options. Being part of the Prime program not only increases visibility but also enhances the likelihood of conversion.
2. Customer Trust
Amazon is synonymous with reliability and customer service. By using FBA, sellers can leverage Amazon’s brand trust, which can lead to higher sales. Customers often feel more secure purchasing from sellers who use FBA, knowing that they will receive their orders promptly and have access to Amazon’s robust return policy.
3. Multi-Channel Fulfillment
FBA allows sellers to fulfill orders from various platforms, not just Amazon. This means that if a seller has their own website or sells on other marketplaces, they can still use Amazon’s fulfillment services to manage those orders. This centralizes inventory management and logistics under one roof, simplifying operations.
4. Scale with Ease
FBA allows sellers to scale their operations without the need for significant investment in their own warehousing and logistics. As sales increase, sellers can simply send more inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers without worrying about the logistics of storage and shipping.
Cons of Using FBA
1. High Fees
While FBA offers many advantages, it comes with a cost. Sellers are charged various fees, including storage fees for keeping inventory in Amazon’s warehouses and fulfillment fees for picking, packing, and shipping orders. These fees can quickly add up, particularly for low-margin products, which can significantly impact profitability.
2. Strict Inventory Rules
Amazon has strict guidelines regarding inventory management. Sellers must ensure that their products meet Amazon’s standards, including packaging and labeling requirements. Failure to comply can result in additional fees or even the suspension of selling privileges. Additionally, Amazon regularly audits inventory levels, and sellers may incur long-term storage fees for unsold items.
3. Commingling Risks
With FBA, products from different sellers can be stored in the same location, a process known as commingling. While this can streamline the shipping process, it poses risks for sellers. If a customer receives a defective item or a return that does not belong to the seller, it can lead to negative reviews and customer dissatisfaction. Sellers have less control over their inventory in this model.
4. Limited Control Over Shipping
Sellers using FBA must accept Amazon’s shipping methods and timelines. This can be a disadvantage for those who prefer to manage their own shipping processes or who have specific requirements for how their products should be delivered. Any delays or issues in Amazon’s fulfillment process can directly impact the seller’s reputation.
Who is FBA Best For?
FBA is particularly beneficial for e-commerce businesses looking to scale without the overhead of managing their own fulfillment operations. It’s ideal for:
-
Small to Medium-Sized Sellers: Businesses that may not have the resources to invest in warehousing and logistics can benefit from Amazon’s infrastructure.
-
Sellers with High Sales Volume: Those who anticipate high sales volumes, particularly during peak seasons, can leverage Amazon’s logistics capabilities to meet customer demand efficiently.
-
Brands Seeking to Build Trust: Newer sellers or brands looking to establish credibility can benefit from the trust associated with Amazon’s fulfillment services.
-
Multi-Channel Sellers: Businesses that sell on multiple platforms can use FBA to streamline their fulfillment processes across all sales channels.
In conclusion, while FBA offers numerous advantages such as Prime eligibility and customer trust, it also comes with its share of challenges, including high fees and strict inventory requirements. Evaluating these factors against your business model and growth goals is essential in determining whether FBA is the right fulfillment strategy for you.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Inventory management and warehousing are foundational services provided by fulfillment centers. This involves the strategic storage of products in a dedicated facility where businesses can efficiently track and manage their inventory levels. A robust inventory management system allows for real-time visibility of stock levels, enabling businesses to make informed decisions about reordering and stock allocation.
Benefits to E-commerce Businesses:
1. Efficiency in Stock Management: By utilizing a fulfillment center, businesses can streamline their inventory processes. Advanced software integrates with e-commerce platforms to automatically update stock levels, reducing the risk of overselling or stockouts.
2. Space Optimization: Outsourcing warehousing frees up valuable space in your own operations, allowing you to focus on sales and marketing rather than logistics.
3. Scalability: As your business grows, fulfillment centers can easily accommodate increased inventory needs without the need for significant capital investment in additional storage facilities.
4. Cost-Effectiveness: Many fulfillment centers offer competitive storage rates, often reducing the overall cost per unit as inventory levels increase, which can significantly lower operational costs for e-commerce businesses.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services refer to the process of selecting ordered items from inventory and packaging them for shipment. This is a crucial step in the fulfillment process, as it directly impacts order accuracy and delivery speed. Fulfillment centers employ trained staff and advanced technology to ensure that items are picked correctly and packed efficiently.
Benefits to E-commerce Businesses:
1. Accuracy and Speed: With dedicated teams focused on picking and packing, fulfillment centers can achieve high levels of accuracy, minimizing the chances of shipping errors that could lead to customer dissatisfaction.
2. Time Savings: Outsourcing this process allows e-commerce businesses to focus on core activities, such as product development and marketing, rather than the labor-intensive aspects of order fulfillment.
3. Custom Packaging Options: Many fulfillment centers offer customizable packing solutions, allowing businesses to enhance their branding through packaging, which can improve customer experience and retention.
4. Integration with Shipping Solutions: Fulfillment centers often have established relationships with major shipping carriers, enabling them to offer competitive shipping rates and faster delivery options, which can be a significant advantage in today’s fast-paced e-commerce environment.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly involve the process of grouping different products together into a single kit or assembling multiple components into a final product before shipping. This service is particularly beneficial for e-commerce businesses that sell products requiring assembly or those that offer bundled products.
Benefits to E-commerce Businesses:
1. Streamlined Operations: By outsourcing kitting and assembly, businesses can reduce complexity in their supply chain. This allows them to focus on core competencies while ensuring that products are ready for sale without additional handling.
2. Enhanced Product Offerings: Kitting enables businesses to create unique bundled offers, which can increase average order value and improve customer satisfaction by providing convenience.
3. Quality Control: Fulfillment centers often have strict quality control processes in place, ensuring that assembled products meet company standards before they reach the customer, thereby enhancing brand reputation.
4. Inventory Flexibility: Kitting services allow businesses to manage inventory more effectively, as they can assemble kits based on demand rather than holding large quantities of individual items.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, is the process of handling returned products efficiently. A well-structured returns management system is crucial for e-commerce businesses, as returns are an inevitable aspect of online shopping. Fulfillment centers provide a streamlined process for receiving, inspecting, and restocking returned items.
Benefits to E-commerce Businesses:
1. Improved Customer Experience: A hassle-free returns process enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. Fulfillment centers can handle returns quickly, ensuring that customers are refunded or exchanged promptly.
2. Cost Control: Efficient returns management helps businesses minimize losses associated with returned products. Fulfillment centers can assess the condition of returned items and determine whether they can be restocked or need to be discounted.
3. Data Insights: Many fulfillment centers offer analytics on return trends, providing businesses with valuable insights that can inform product development and inventory management strategies.
4. Operational Efficiency: By outsourcing returns management, e-commerce businesses can reduce the operational burden on their teams, allowing them to focus on growth strategies rather than the complexities of handling returns.
In conclusion, fulfillment centers offer a variety of core services that can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of e-commerce businesses. By leveraging these services, business owners can focus on scaling their sales and improving customer satisfaction, ultimately leading to sustained growth in a competitive market.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
Importance:
The geographical location of your fulfillment partner’s warehouses plays a critical role in shipping efficiency and delivery times. A strategically located warehouse network can significantly reduce shipping costs and transit times, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Questions to Ask:
– Where are your warehouses located, and how many do you operate?
– Can you provide coverage maps showing the areas you can serve effectively?
– How do you handle regional shipping and delivery times for different locations?
– What carriers do you partner with for shipping, and how do they influence delivery speed?
Technology & Integrations
Importance:
In today’s digital age, having a fulfillment partner that utilizes advanced technology is essential for seamless operations. Integration with your existing systems (like e-commerce platforms, inventory management, and CRM systems) can streamline order processing, reduce errors, and provide real-time visibility into your inventory and order status.
Questions to Ask:
– What technology do you use for order management and inventory tracking?
– How do you integrate with e-commerce platforms (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce)?
– Can you provide real-time inventory updates, and how is this communicated to us?
– What data analytics capabilities do you offer to help us understand our fulfillment performance?
Specializations (e.g., Cold Storage, Oversized Items)
Importance:
Not all fulfillment centers are equipped to handle every type of product. If your business involves specialized items—such as perishables, oversized products, or fragile items—it’s crucial to ensure your partner has the necessary facilities and expertise to manage these effectively.
Questions to Ask:
– What types of products do you specialize in handling?
– Do you have specific capabilities for cold storage or temperature-sensitive items?
– How do you manage fragile items to prevent damage during storage and shipping?
– Are there any restrictions on the size or weight of products you can fulfill?
Scalability & Capacity
Importance:
As your business grows, your fulfillment needs will change. A partner that can scale with you—whether it’s accommodating seasonal spikes in demand or rapid growth due to a successful marketing campaign—will save you time, money, and stress.
Questions to Ask:
– What is your capacity for handling increased order volumes?
– How quickly can you scale operations in response to our growth?
– What contingency plans do you have in place for unexpected surges in demand?
– Can you provide case studies or examples of how you’ve scaled for other clients?
Pricing and Contracts
Importance:
Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms of a fulfillment partner is essential to ensure that their services fit within your budget. Transparency in pricing helps avoid unexpected costs that could erode profit margins.
Questions to Ask:
– Can you provide a detailed breakdown of your pricing structure (setup fees, storage fees, picking and packing fees, shipping fees)?
– Are there minimum order requirements, and what are the implications if we do not meet them?
– How often do you review your pricing, and what factors could lead to price increases?
– What are the terms for terminating the contract, and are there any penalties for early termination?
Customer Support & Reviews
Importance:
Reliable customer support is crucial when issues arise, whether it’s a shipping delay or a system malfunction. Assessing the quality of customer service and the fulfillment partner’s reputation can help you gauge their reliability and commitment to clients.
Questions to Ask:
– What customer support options do you provide (e.g., phone, email, chat)?
– What are your average response times for customer inquiries?
– Can you share testimonials or case studies from current or former clients?
– How do you handle disputes or issues that arise during the fulfillment process?
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is a strategic decision that can significantly impact your business’s efficiency, customer satisfaction, and overall success. By considering these six key points—Location & Warehouse Network, Technology & Integrations, Specializations, Scalability & Capacity, Pricing and Contracts, and Customer Support & Reviews—you can make an informed choice that aligns with your operational needs and growth ambitions. Taking the time to ask the right questions will help you find a partner that not only meets your current requirements but also supports your future growth.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
When partnering with a fulfillment service, the initial setup fees cover the costs associated with integrating your technology systems, syncing inventory, and preparing the first batch of stock. These fees can vary significantly based on the complexity of your needs and the provider’s capabilities. Generally, this might include:
- Integration Costs: Charges for connecting your e-commerce platform with the fulfillment provider’s systems. This ensures real-time inventory tracking and order management.
- Onboarding Costs: Fees for the time spent training your staff on the new system and processes.
- Initial Inventory Handling: Some providers charge for the initial processing of your inventory, which includes inspecting, labeling, and organizing products.
It’s essential to get a detailed breakdown of these fees upfront, as they can be a significant initial investment.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are incurred when the fulfillment center accepts and organizes your inventory. These costs typically cover the following:
- Unloading and Inspection: Charges for unloading your products from delivery trucks and inspecting them for quality and accuracy.
- Inventory Management: The time and labor involved in updating the system to reflect the new stock levels and organizing items in the warehouse.
These fees can be calculated based on the volume of inventory received or the time taken to process it. Depending on the provider, this might be charged per pallet, box, or hour of labor.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are incurred for keeping your products in the fulfillment center’s warehouse. These fees are usually charged on a monthly basis and can be calculated in a few different ways:
- Per Pallet: Many providers charge a flat rate for each pallet of goods stored. This is common for larger items or bulk inventory.
- Per Cubic Foot: For businesses with smaller items, fees may be calculated based on the amount of space your products occupy in the warehouse. This can be particularly beneficial for businesses with varied product sizes.
Storage fees can fluctuate based on the time of year, especially during peak seasons, so it’s wise to discuss potential changes with your provider.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are charged for the labor involved in picking items from the warehouse and packing them for shipment. This pricing can vary based on several factors:
- Per Item: Some fulfillment centers charge a fee for each item picked and packed. This is common for businesses with high order volumes and numerous SKUs.
- Per Order: Others may have a flat fee for each order, regardless of the number of items. This model can be advantageous for businesses with larger orders.
Additional costs may arise if special packaging materials are required or if there are specific packing instructions. Make sure to clarify these details when negotiating fees with potential fulfillment partners.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees represent the costs associated with transporting your products from the fulfillment center to your customers. These fees can encompass several components:
- Carrier Charges: The base cost charged by shipping carriers (like FedEx, UPS, etc.) based on the weight, dimensions, and destination of the package.
- Labeling and Handling: Some fulfillment providers charge additional fees for creating shipping labels and handling packages for dispatch.
Shipping fees can vary widely based on the provider’s contracts with carriers, so it’s beneficial to compare rates and services. Additionally, you may want to explore options for discounted shipping rates or flat-rate shipping programs.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
- Clarify Your Needs: Be clear about your business model, average order size, and inventory turnover. This will help providers give you a more tailored quote.
- Request Detailed Breakdowns: Ask for a line-item estimate that includes all potential fees. This transparency helps you understand the total cost of fulfillment.
- Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate terms, especially if you have a high order volume or are considering long-term partnerships.
- Evaluate Multiple Providers: Compare quotes from several fulfillment centers to ensure you’re getting competitive pricing and services that meet your business needs.
- Consider Hidden Costs: Be aware of potential hidden fees, such as those associated with returns management or peak season surcharges, and ask about these upfront.
By understanding these common fees and how they are calculated, you can make informed decisions that align with your business goals and budget, ultimately contributing to a smoother fulfillment process as you scale your e-commerce operations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is fulfillment in e-commerce?
Fulfillment in e-commerce refers to the entire process of receiving, processing, and delivering customer orders. This includes managing inventory, picking and packing items, shipping them to customers, and handling returns. A well-optimized fulfillment process is critical for ensuring customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
2. What is the difference between in-house fulfillment and outsourcing?
In-house fulfillment means that your business manages the entire process of order fulfillment internally, from storage to shipping. Outsourcing fulfillment, on the other hand, involves partnering with a third-party logistics (3PL) provider to handle these tasks. In-house fulfillment allows for greater control but requires more resources, while outsourcing can save time and labor costs but may involve a loss of direct oversight.
3. What is a 3PL (Third-Party Logistics)?
A 3PL is a service provider that manages logistics and fulfillment operations on behalf of e-commerce businesses. They typically offer warehousing, inventory management, order processing, and shipping services. Utilizing a 3PL can help businesses scale operations quickly without the need for significant upfront investment in infrastructure.
4. How much do fulfillment services cost?
Fulfillment service costs vary widely depending on several factors, including the provider, the volume of orders, and the specific services required. Costs may include setup fees, storage fees, receiving fees, picking and packing fees, and shipping fees. It’s essential to get a detailed quote from potential providers and understand their pricing structure to ensure it aligns with your budget and expected profit margins.
5. What’s the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse is primarily a storage facility where goods are kept until needed. In contrast, a fulfillment center is a specialized type of warehouse designed for processing and shipping orders. Fulfillment centers are equipped with systems and technology that facilitate quick order processing, packing, and shipping, often integrating directly with e-commerce platforms.
6. What is dropshipping, and how does it relate to fulfillment?
Dropshipping is a fulfillment method where the retailer does not keep products in stock. Instead, when a customer places an order, the retailer purchases the item from a third-party supplier who then ships it directly to the customer. This model minimizes overhead costs but can lead to challenges in quality control and shipping times.
7. How can I optimize my fulfillment process?
To optimize your fulfillment process, consider implementing the following strategies:
– Use inventory management software to keep track of stock levels.
– Partner with a reliable 3PL provider to handle logistics.
– Streamline picking and packing processes by organizing your warehouse layout.
– Implement automation tools to reduce manual errors and improve efficiency.
– Monitor shipping performance and adjust carrier choices based on delivery times and costs.
8. What are the key components of a successful fulfillment system?
A successful fulfillment system typically includes the following key components:
– Warehousing: Adequate space for inventory storage.
– Inventory Management: Tools to track stock levels and movements.
– Order Processing: Systems for efficiently picking, packing, and shipping orders.
– Logistics Management: Solutions for optimizing shipping routes and managing carrier relationships.
– Returns Management: Processes for handling returns and restocking inventory.
9. What challenges do businesses face in fulfillment?
Common challenges in fulfillment include managing inventory levels, ensuring timely shipping, handling returns efficiently, and maintaining quality control. Additionally, businesses may struggle with scaling their operations during peak seasons or unexpected demand surges, which can lead to delays and customer dissatisfaction.
10. How do I choose the right fulfillment partner?
When selecting a fulfillment partner, consider the following factors:
– Scalability: Ensure they can handle your current and future order volumes.
– Technology Integration: Look for partners that can seamlessly integrate with your existing e-commerce platforms.
– Capabilities: Verify they can handle your specific product types and any special requirements.
– Cost Structure: Understand their pricing model and any hidden fees.
– Reputation: Research reviews and testimonials to gauge their reliability and service quality.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Evaluating the Benefits of Outsourcing Fulfillment
In the fast-paced world of e-commerce, the efficiency of your fulfillment process can significantly impact your business’s growth trajectory. Outsourcing fulfillment can offer a range of advantages that are particularly appealing for entrepreneurs and operations managers looking to scale their operations.
One of the most compelling benefits of using a fulfillment service is time savings. By delegating the complexities of warehousing, order processing, and shipping to a third-party logistics (3PL) provider, you free up valuable time to focus on core business activities such as marketing, product development, and customer engagement. This shift allows you to concentrate on what you do best while ensuring that orders are handled efficiently.
Scalability is another key advantage. As your business experiences growth—whether through increased sales volume or seasonal spikes—fulfillment partners can adapt to your changing needs without the need for significant investment in infrastructure. This flexibility ensures that you can meet customer demand without compromising on service quality.
Additionally, fulfillment services bring specialized expertise to the table. Many 3PL providers are equipped with advanced technology and industry knowledge that can enhance your logistics operations. They can implement best practices in inventory management, shipping optimization, and returns processing, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction and retention.
However, it’s crucial to choose the right fulfillment partner. The success of outsourcing hinges on finding a provider whose capabilities align with your business model and growth ambitions. Evaluate potential partners based on their technology integration, cost structure, and service offerings to ensure they can support your objectives.
Take Action
To determine if outsourcing fulfillment is the right move for your business, conduct a thorough audit of your current shipping processes. Identify areas where inefficiencies exist and evaluate whether a fulfillment partner could help streamline operations. Taking this strategic step can position your business for sustained growth and enhanced customer satisfaction.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.