How Order Fulfillment Works: A Step-by-Step Guide for Businesses
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
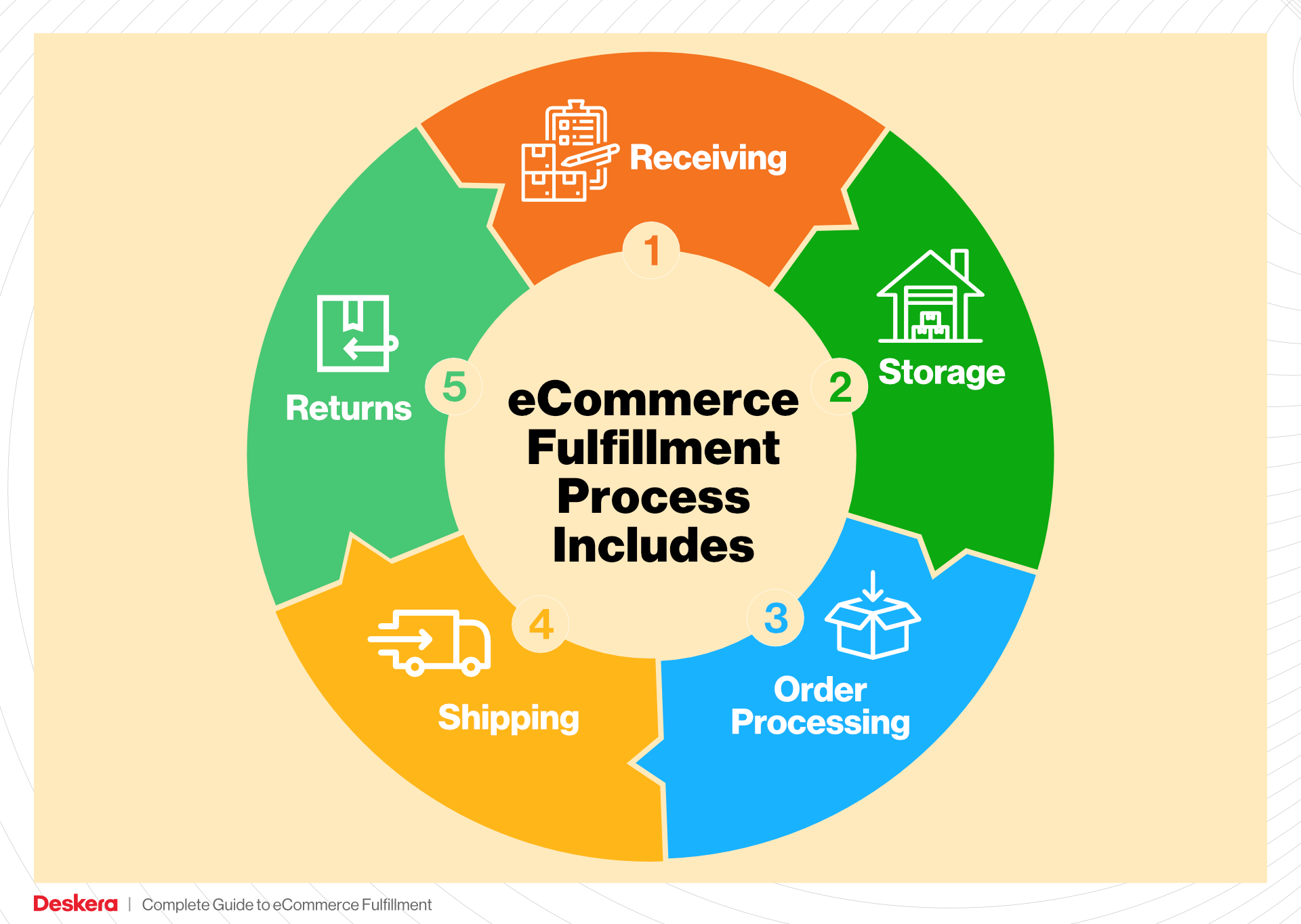
Understanding E-commerce Fulfillment
As your online business begins to flourish, the excitement of increased sales can quickly be overshadowed by the complexities of packing and shipping orders. Many entrepreneurs find themselves overwhelmed with the sheer volume of logistics involved in getting products to customers efficiently. This is where e-commerce fulfillment comes into play—a vital process that ensures your products reach customers in a timely and satisfactory manner.
E-commerce fulfillment is the end-to-end journey of an order from the moment a customer clicks “buy” to when the package arrives at their doorstep. It encompasses everything from receiving inventory and processing orders to packing, shipping, and managing returns. For growing businesses, mastering this process is crucial not only for customer satisfaction but also for maintaining healthy profit margins.
In this guide, we will delve into the various fulfillment models available to e-commerce businesses, including third-party logistics (3PL) and Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). Each model has its unique advantages and considerations, and understanding these options will help you choose the best fit for your business needs.
We will also cover the core services involved in e-commerce fulfillment, such as inventory management, order processing, and shipping logistics. These services are essential for streamlining operations and improving overall efficiency.
Moreover, selecting the right fulfillment partner is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s growth trajectory. We’ll provide practical tips on what to look for in a fulfillment partner, including technology integration, service levels, and scalability.
Finally, pricing is a key aspect that many business owners grapple with. We will break down the costs associated with different fulfillment models and outline how to evaluate pricing structures to ensure they align with your business objectives.
The goal of this guide is to empower you with the knowledge and tools needed to make informed decisions about your logistics strategy. By understanding e-commerce fulfillment, you can position your business for sustained growth while delivering exceptional customer experiences. Let’s embark on this journey together and simplify the complexities of getting your products into the hands of satisfied customers.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
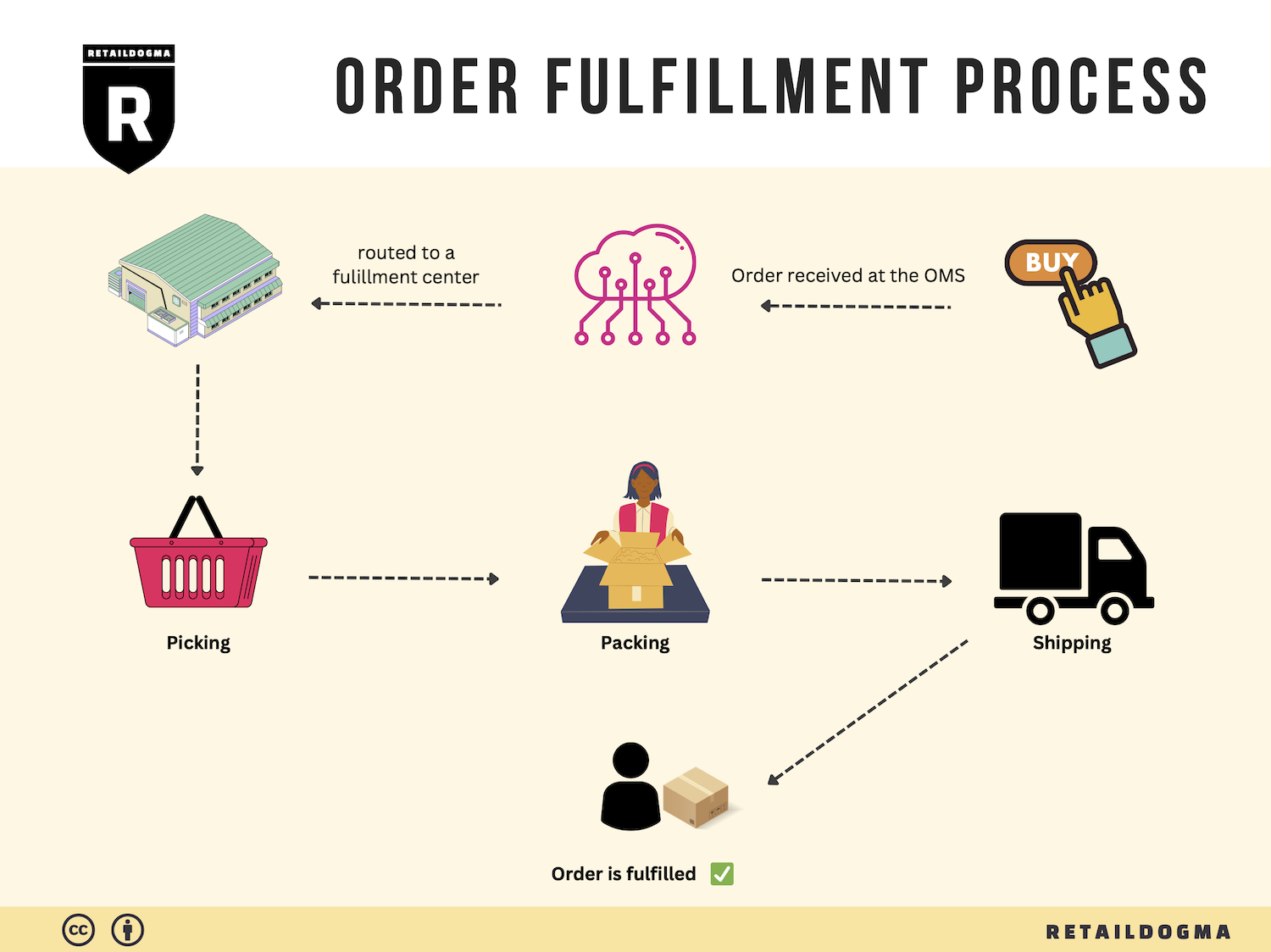
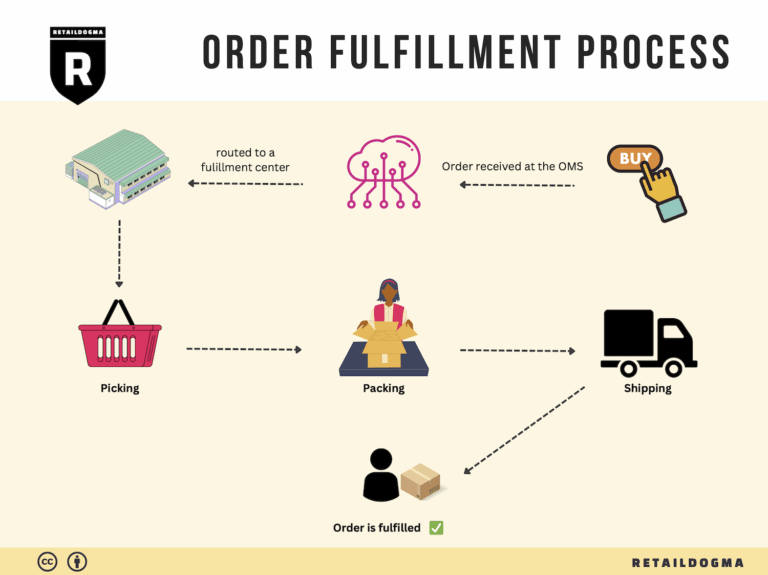
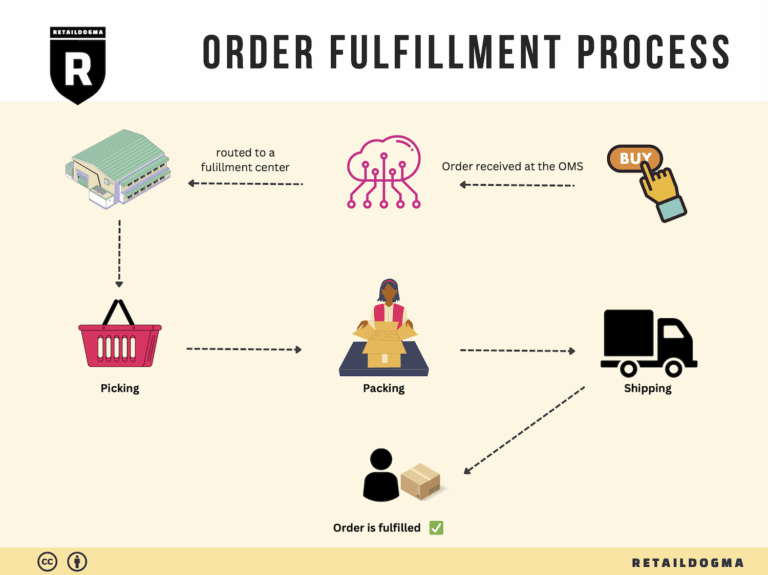
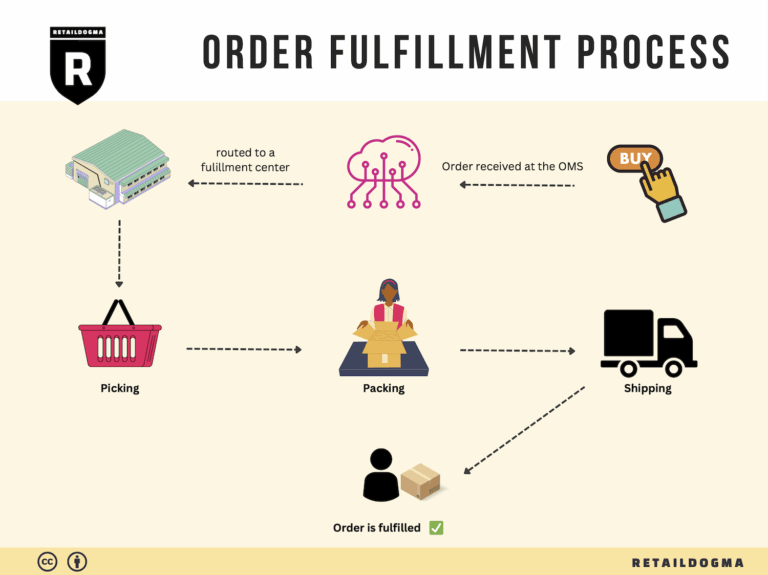
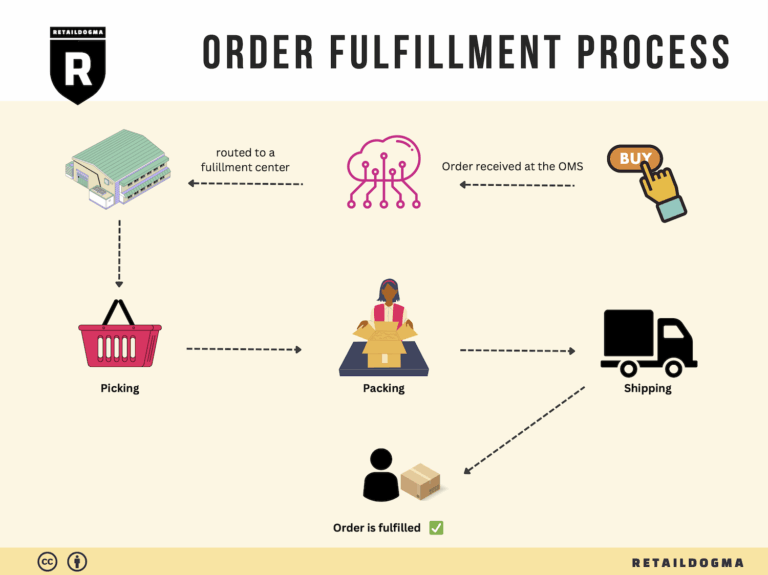
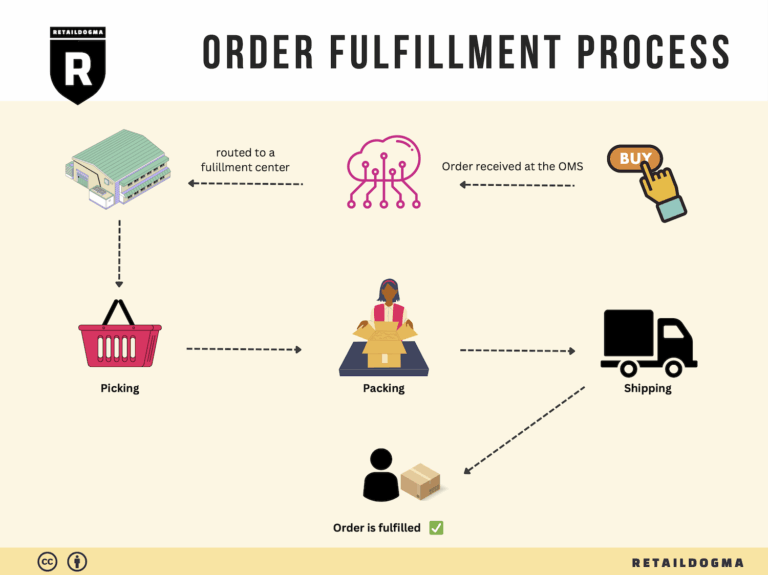
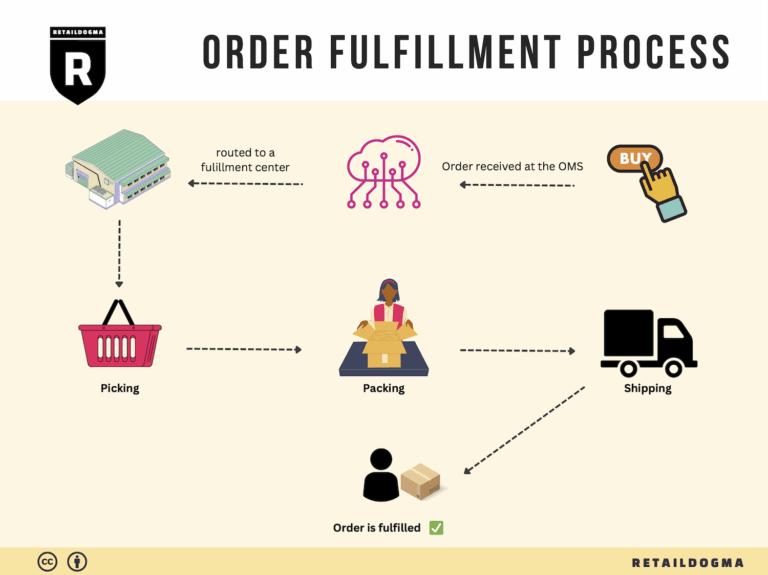
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
1. Receiving Inventory
The order fulfillment process begins with receiving inventory at the fulfillment center. When products arrive from suppliers or manufacturers, they are unloaded and checked for accuracy against the purchase order. This step is crucial because it sets the foundation for efficient operations. Accurate receiving ensures that the right quantities and quality of goods are accounted for, minimizing discrepancies that could lead to stockouts or overstock situations.
Key to this process is the Stock Keeping Unit (SKU), which uniquely identifies each product. By recording SKUs during receiving, businesses can maintain accurate inventory counts and facilitate smoother operations in subsequent steps. If discrepancies are found, they must be addressed immediately to avoid cascading issues throughout the fulfillment process. Effective receiving also involves integrating this information into the warehouse management system (WMS), which is essential for tracking inventory levels and locations within the warehouse.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once inventory is received, the next step is to store it properly within the warehouse. Efficient storage is vital as it influences the speed and accuracy of order fulfillment. Products are organized based on various factors such as size, demand frequency, and handling requirements. Strategic placement can optimize picking routes and reduce labor costs.
Slotting is a key term in this context, referring to the method of organizing products within the warehouse. By analyzing inventory turnover rates and other data, businesses can place high-demand items closer to packing stations, thereby reducing the time it takes to fulfill orders. Accurate storage management not only enhances operational efficiency but also helps prevent stock discrepancies and ensures that inventory levels are readily available for order processing.
3. Order Picking
Once a customer places an order, it triggers the order picking process. This step involves retrieving the items from their storage locations based on the details provided in the order. Efficient picking is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction, as it directly impacts order accuracy and speed of delivery.
Pick lists are generated during this phase, detailing the SKUs and quantities required for each order. There are various picking strategies that can be employed, such as batch picking, where multiple orders are picked simultaneously, or zone picking, where workers are assigned specific areas of the warehouse. The choice of picking method often depends on order volume and the layout of the warehouse. An effective picking process reduces travel time and minimizes errors, which is essential for maintaining a positive customer experience.
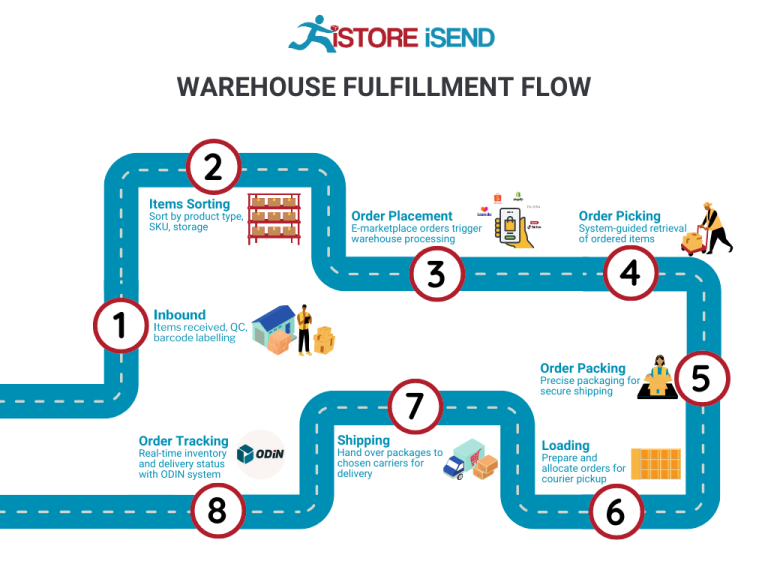
4. Order Packing
After items have been picked, they move to the packing stage. This step is where products are securely packaged for shipment. Proper packing not only protects the items during transit but also enhances the overall customer experience. A well-packaged order can create a positive impression and encourage repeat business.
During packing, items are often scanned to confirm that the correct products have been selected, ensuring accuracy before shipment. Branded packaging is an important aspect here; it can make the unboxing experience memorable for customers. Additionally, the use of eco-friendly materials can resonate well with environmentally conscious consumers. Efficient packing processes can also lead to cost savings by minimizing shipping dimensions and materials, thereby reducing overall logistics expenses.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once the package is packed, it is handed over to a shipping carrier for transport to the customer. This stage is critical as it represents the culmination of all prior efforts and directly affects customer satisfaction.
Carrier selection is a key consideration during this stage. Factors such as delivery speed, cost, and destination play significant roles in determining which carrier will be used. Automated systems can help businesses compare options to choose the most cost-effective and timely solution. Additionally, providing customers with tracking information enhances transparency and trust, allowing them to monitor their order’s progress. Effective shipping and delivery not only fulfill customer expectations but also contribute to brand loyalty and repeat purchases.
In conclusion, mastering the order fulfillment process is essential for e-commerce businesses aiming to scale effectively. By focusing on each of these five steps—receiving inventory, warehouse storage, order picking, order packing, and shipping & delivery—businesses can streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive growth.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Fulfillment Model Comparison
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | The business itself | Startups to small businesses | Control over inventory and processes | Higher overhead costs and scalability issues |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | A third-party provider | Growing to medium-sized businesses | Scalability and expertise in logistics | Less control over fulfillment processes |
| Dropshipping | Supplier or manufacturer | Entrepreneurs and startups | Low initial investment and risk | Lower profit margins and reliance on suppliers |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment refers to the process where businesses manage their order fulfillment operations within their own facilities, utilizing their own staff, systems, and inventory. This model is particularly advantageous for startups and small businesses that are just beginning to establish their brand. The primary benefits of in-house fulfillment include low startup costs, as businesses can start with minimal investment in storage and labor, and direct control over inventory and fulfillment processes. This control allows for tailored customer service experiences and the ability to quickly adapt to changes in demand. However, as the business grows, maintaining in-house fulfillment can lead to higher overhead costs, including labor, storage, and technology expenses. Additionally, scaling can become challenging, particularly during peak sales periods, as businesses may struggle with space, labor capacity, and operational efficiency.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers manage the logistics and fulfillment processes for businesses, allowing them to outsource warehousing, inventory management, and order shipping. This model is ideal for growing to medium-sized businesses that experience increasing order volumes but may not have the infrastructure or expertise to manage fulfillment effectively. One of the key advantages of using a 3PL is scalability; businesses can easily adjust their logistics operations based on changing demand without the need for significant capital investment in facilities or staff. 3PL providers typically possess advanced technology and logistics expertise, which can enhance efficiency and reduce shipping costs. However, the trade-off is a loss of direct control over the fulfillment process, which can lead to inconsistencies in service quality and potential delays if the 3PL does not meet performance expectations. Additionally, businesses may face challenges in integrating their systems with those of the 3PL, which can complicate inventory management and order tracking.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where businesses sell products without holding inventory. Instead, when an order is placed, the retailer purchases the item from a third-party supplier who then ships it directly to the customer. This model is particularly suited for entrepreneurs and startups looking to minimize upfront investment and risk. The primary advantage of dropshipping is the low barrier to entry, as it eliminates the need for inventory storage and management, allowing sellers to focus on marketing and sales. Furthermore, it enables businesses to offer a wide range of products without the financial burden of purchasing inventory upfront. However, dropshipping also has significant disadvantages, including lower profit margins due to reliance on suppliers, potential shipping delays, and quality control issues since businesses have less oversight over the fulfillment process. Additionally, the lack of control can lead to inconsistent customer experiences, which can harm brand reputation and customer loyalty.
Conclusion
Selecting the right fulfillment model is crucial for e-commerce businesses looking to scale effectively. Each model—In-House Fulfillment, Third-Party Logistics, and Dropshipping—offers distinct advantages and challenges that must align with the business’s current stage, operational capabilities, and long-term goals. By understanding these differences, business owners can make informed decisions that will optimize their fulfillment processes and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
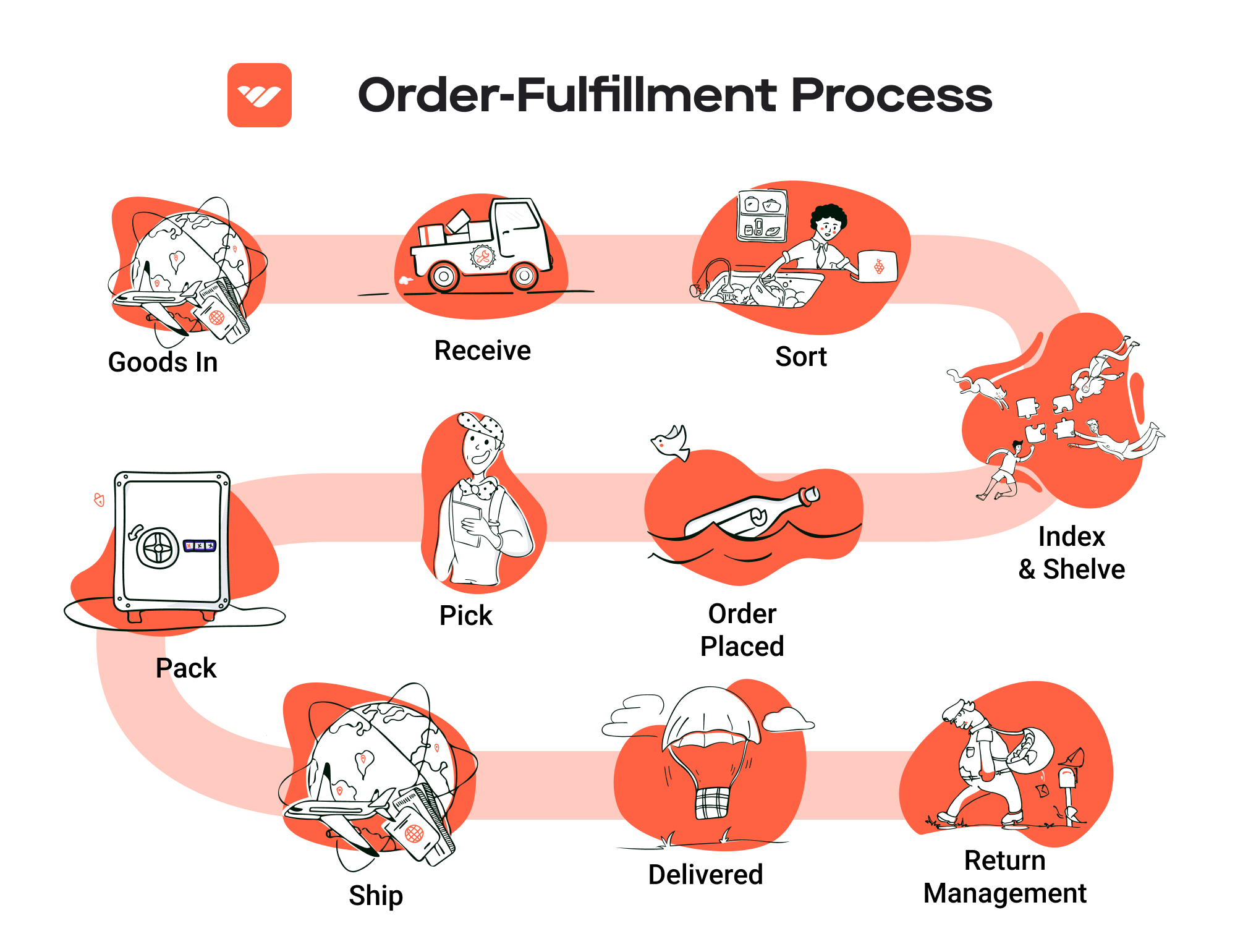
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service provided by Amazon that allows sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. This service not only simplifies the logistics of managing an e-commerce business but also provides sellers with the opportunity to leverage Amazon’s vast distribution network. Once a seller enrolls in FBA, Amazon takes care of storage, packaging, shipping, customer service, and returns on behalf of the seller.
How FBA Works
-
Product Listing: Sellers create product listings on Amazon and select which products they want to fulfill through FBA.
-
Shipping to Amazon: Sellers send their products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon provides guidance on how to prepare and ship products to ensure they meet their standards.
-
Storage: Once received, Amazon stores the products in its warehouses. Sellers can track their inventory through the Amazon Seller Central dashboard.
-
Order Processing: When a customer places an order for a product fulfilled by FBA, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the item directly to the customer. This process is automated and optimized for speed.
-
Customer Service: Amazon handles all customer service inquiries and returns for FBA orders, allowing sellers to focus on other aspects of their business.
-
Returns Management: If a customer returns a product, Amazon processes the return and manages the logistics of restocking or disposing of the item.
Pros of Using FBA
1. Prime Eligibility
One of the standout advantages of FBA is that products fulfilled by Amazon are eligible for Amazon Prime. This means that Prime members can receive their orders with expedited shipping, significantly increasing the likelihood of purchase. Prime eligibility can lead to higher conversion rates, as customers often prefer Prime products for their fast shipping options.
2. Enhanced Customer Trust
By utilizing FBA, sellers can benefit from the trust that comes with the Amazon brand. Customers are more likely to purchase from a seller that uses Amazon’s fulfillment services, as they associate FBA products with reliability and quality customer service. This trust can be a critical differentiator in a crowded marketplace.
3. Multi-Channel Fulfillment
FBA is not limited to Amazon sales alone. Sellers can use FBA for orders from their own websites or other sales channels. This multi-channel fulfillment capability allows sellers to streamline their logistics, manage inventory in one place, and leverage Amazon’s logistics expertise across various platforms.
4. Simplified Logistics
FBA simplifies the logistics process significantly. With Amazon handling warehousing, packing, and shipping, sellers can save time and resources that would otherwise be spent managing these operations. This allows businesses to focus on growth, marketing, and product development.
5. Scalability
As businesses grow, their order volumes can fluctuate. FBA provides a scalable solution that can handle increased demand without the need for significant investment in warehousing and logistics infrastructure. Sellers can easily increase their inventory levels and let Amazon manage the fulfillment.
Cons of Using FBA
1. High Fees
One of the most significant drawbacks of FBA is the cost. Amazon charges various fees for using FBA, including storage fees for inventory stored in their warehouses and fulfillment fees for processing orders. These costs can add up quickly and may eat into profit margins, particularly for low-cost items.
2. Strict Inventory Rules
Amazon has strict guidelines regarding inventory management. Sellers must adhere to specific requirements for packaging, labeling, and shipping. Failure to comply can result in additional fees or penalties, complicating the fulfillment process for sellers who are not familiar with these rules.
3. Commingling Risks
FBA uses a practice called commingling, where products from different sellers are stored together in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. While this can streamline inventory management, it poses a risk for sellers. If a customer receives a damaged or counterfeit item from another seller’s inventory, it can negatively impact the original seller’s reputation. Sellers have limited control over this risk, which can be concerning for brands that prioritize quality assurance.
4. Limited Branding Opportunities
With FBA, sellers lose some control over the unboxing experience. Amazon’s branding dominates the packaging, which can diminish the opportunity for sellers to create a unique brand experience for customers. This may not be a significant issue for some sellers, but for those focused on brand loyalty, it can be a drawback.
Who is FBA Best For?
FBA is particularly well-suited for:
-
Small to Medium-Sized Businesses: Those looking to scale quickly without investing heavily in logistics infrastructure can benefit from FBA’s streamlined processes.
-
Sellers with High Volume: Businesses that anticipate high order volumes can leverage Amazon’s fulfillment network to meet demand efficiently.
-
Brands Seeking Trust: Sellers wanting to capitalize on Amazon’s reputation and customer base will find FBA advantageous in building credibility.
-
Multi-Channel Sellers: Brands that sell on multiple platforms and need a centralized solution for order fulfillment can utilize FBA to manage their logistics effectively.
In conclusion, Fulfillment by Amazon presents an opportunity for e-commerce businesses to enhance their logistics and customer service capabilities. However, sellers must weigh the benefits against the potential costs and limitations. By understanding both the pros and cons, businesses can make informed decisions about whether FBA aligns with their operational goals and growth strategies.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Inventory management and warehousing are foundational services provided by fulfillment centers, serving as the backbone of any e-commerce operation. This service entails receiving, storing, and managing stock in a way that optimizes space and ensures product availability.
Fulfillment centers utilize sophisticated Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) to track inventory levels in real-time, ensuring that e-commerce businesses have accurate data on stock availability across multiple sales channels. This accuracy is critical for preventing overselling and stockouts, which can lead to customer dissatisfaction and lost sales.
The benefits of effective inventory management extend beyond just keeping track of stock. By employing strategic storage solutions—such as slotting SKUs based on turnover rates or using zone-based layouts—fulfillment centers can enhance operational efficiency. This means faster order processing times and reduced labor costs, ultimately leading to improved profit margins for e-commerce businesses.
Additionally, with advanced inventory analytics, fulfillment centers can help businesses forecast demand and optimize their stock levels, ensuring that they are well-prepared for seasonal spikes or promotional events. This proactive approach to inventory management not only safeguards against missed sales opportunities but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely fulfillment.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services are integral to the fulfillment process, where orders are assembled and prepared for shipment. This service involves selecting the ordered items from the warehouse shelves, packing them securely, and labeling them for delivery.
Fulfillment centers employ various picking strategies, such as batch picking, zone picking, or wave picking, to maximize efficiency based on order volume and warehouse layout. By streamlining the picking process, fulfillment centers can significantly reduce the time it takes to get orders ready for shipment.
The benefits of effective pick and pack services are manifold. First, they enhance accuracy; trained staff and automated systems ensure that the right items are picked and packed, minimizing errors that can lead to returns and customer dissatisfaction. Second, by using branded packaging and personalized inserts during the packing process, e-commerce businesses can reinforce their brand identity and improve the overall customer experience.
Moreover, efficient packing not only protects products during transit but can also optimize shipping costs. By using appropriate packaging materials that minimize weight and dimensions, fulfillment centers can help businesses reduce their shipping expenses, which can directly impact profitability.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services involve the grouping of multiple products into a single package or kit, often tailored for specific promotions or bundled offerings. This service is particularly beneficial for e-commerce businesses that sell complementary products or seasonal items that can be marketed as a cohesive package.
Fulfillment centers can manage the entire kitting process, from assembling items together to packaging and labeling them for shipment. This service allows businesses to offer unique product bundles that can enhance customer value and drive sales. For instance, a beauty brand might create a skincare kit that includes several products at a discounted price, appealing to customers looking for a complete solution.
The advantages of kitting and assembly services include increased efficiency and reduced labor costs. By outsourcing this process to fulfillment centers, e-commerce businesses can focus on their core competencies—such as marketing and product development—while relying on experts to handle the logistics of assembly.
Additionally, kitting can lead to higher average order values (AOV) as customers are more likely to purchase bundled products rather than individual items. This not only boosts revenue but also improves customer satisfaction by providing a curated shopping experience.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, is a critical service offered by fulfillment centers that deals with the process of handling returns and exchanges. Given that returns are an inevitable aspect of e-commerce, having a robust returns management system in place can significantly influence customer satisfaction and brand loyalty.
Fulfillment centers streamline the returns process by providing a clear and efficient system for customers to initiate returns. This includes offering easy-to-follow instructions, timely updates, and automated tracking of returned items. Once items are returned to the fulfillment center, they are inspected, restocked if sellable, or set aside for recycling or disposal based on their condition.
The benefits of effective returns management are substantial. A well-organized returns process can enhance customer trust and encourage repeat purchases, as customers are more likely to shop with brands that make returns easy and hassle-free. Moreover, by analyzing return patterns, fulfillment centers can help e-commerce businesses identify issues such as product defects or misrepresentations, enabling them to make necessary improvements upstream in their supply chain.
In summary, robust returns management not only minimizes the costs associated with handling returns but also serves as a valuable feedback loop that can drive better product offerings and customer experiences. By leveraging the expertise of fulfillment centers in managing returns, e-commerce businesses can turn a potentially negative experience into an opportunity for growth and customer retention.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
The geographic location of your fulfillment partner can significantly impact shipping costs and delivery speed. A strategically placed warehouse network can help ensure that your products reach customers quickly and affordably.
Why It Matters:
Proximity to your customer base can reduce shipping times and costs, which is essential for customer satisfaction and retention. Having multiple warehouses can also help you reach a wider audience and provide better service levels.
Questions to Ask:
– How many warehouses do you operate, and where are they located?
– What is your average shipping time to key markets?
– Can you provide options for multiple fulfillment centers to optimize shipping routes?
Technology & Integrations
In today’s e-commerce landscape, technology plays a crucial role in streamlining fulfillment processes. An efficient fulfillment partner should have robust technology solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems.
Why It Matters:
Effective technology enhances order management, inventory tracking, and data analytics. It enables real-time updates, reduces errors, and improves overall operational efficiency.
Questions to Ask:
– What warehouse management system (WMS) do you use, and how does it integrate with my e-commerce platform?
– Can you provide real-time inventory tracking and reporting?
– Do you support automated order processing and shipping label generation?
Specializations (e.g., Cold Storage, Oversized Items)
Depending on your product offerings, you may require a fulfillment partner with specific capabilities. For instance, if you sell perishable goods or oversized items, you need a partner who can handle these special requirements.
Why It Matters:
Choosing a partner with the right specializations ensures that your products are stored and handled correctly, minimizing the risk of damage or spoilage.
Questions to Ask:
– Do you have facilities equipped for specialized storage (e.g., cold storage, climate control)?
– How do you handle items that require special care, such as fragile or oversized products?
– What procedures do you have in place for quality control during storage and shipping?
Scalability & Capacity
As your business grows, your fulfillment needs will likely change. A good fulfillment partner should be able to scale their operations in line with your business growth.
Why It Matters:
A partner that can accommodate increased order volumes, seasonal fluctuations, or new product lines will help you avoid operational bottlenecks and maintain service quality.
Questions to Ask:
– How do you handle scalability during peak seasons or sudden order surges?
– What is your maximum capacity for handling orders, and how quickly can you scale operations?
– Can you provide case studies or examples of how you have successfully scaled for other clients?
Pricing and Contracts
Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms of your fulfillment partner is crucial to maintaining profitability. Transparent pricing allows you to budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs.
Why It Matters:
Fulfillment costs can significantly affect your bottom line. Clear contract terms prevent misunderstandings and ensure you know what to expect in terms of fees, services, and obligations.
Questions to Ask:
– What is your pricing model (e.g., per order, per item, monthly fees)?
– Are there any hidden fees, such as for storage, packaging, or returns?
– What are the terms of the contract, and is there flexibility for renegotiation or cancellation?
Customer Support & Reviews
The level of customer support provided by your fulfillment partner can greatly influence your operational efficiency. Reliable customer service ensures that you can quickly resolve issues as they arise.
Why It Matters:
Effective support can minimize disruptions in your supply chain and enhance your overall business operations. Additionally, reviewing feedback from current or former clients can provide valuable insights into the partner’s reliability and performance.
Questions to Ask:
– What are your customer support hours and channels (e.g., phone, email, chat)?
– Can you provide references or testimonials from other clients in my industry?
– How do you handle issues like order discrepancies, shipping delays, or inventory inaccuracies?
By carefully considering these six key areas when choosing a fulfillment partner, you can position your e-commerce business for success. A well-chosen partner will not only help you meet current demands but also support your growth ambitions in the fast-evolving e-commerce landscape.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
When partnering with a fulfillment provider, the initial setup fees are often the first costs incurred. These fees cover the onboarding process, which may include integrating your systems with theirs, setting up your inventory in their warehouse management system, and customizing their services to meet your needs.
The calculation of setup fees can vary widely based on the complexity of your operations and the provider’s pricing structure. Some providers charge a flat fee, while others may base costs on the number of SKUs, the volume of orders, or the required level of integration. It’s essential to clarify what is included in these fees, as some providers might charge extra for specific services, such as training or additional software features.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged for the process of accepting and storing your inventory at the fulfillment center. This fee typically covers the labor and equipment used to unload, inspect, and stock your products.
Receiving fees can be calculated per pallet or per unit, depending on the fulfillment center’s pricing model. For example, if your shipment consists of 10 pallets, and the receiving fee is $50 per pallet, your total cost would be $500. It’s important to note that some providers may have minimum charges, especially for smaller shipments, so it’s wise to discuss potential costs upfront.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are incurred for the space your inventory occupies within the warehouse. These fees are usually calculated on a monthly basis and can be charged per pallet, per bin, or per cubic foot, depending on how the fulfillment center organizes its space.
For instance, if you have 20 pallets stored at a fulfillment center that charges $25 per pallet per month, your monthly storage fee would amount to $500. Keep in mind that storage fees can fluctuate based on the time of year, with many providers implementing higher rates during peak seasons when space is at a premium. Additionally, some fulfillment centers may also charge for long-term storage if items remain unsold for an extended period, so it’s crucial to monitor your inventory turnover to avoid unexpected costs.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees cover the labor and materials associated with gathering items from storage and preparing them for shipment. These fees are typically calculated on a per-item or per-order basis.
For example, if a fulfillment center charges $1.50 per item and you have an order with three items, the pick and pack fee for that order would be $4.50. Some providers may offer tiered pricing, where the per-item fee decreases as order volume increases, providing an incentive for higher sales. Be sure to understand how fees are structured, especially if you offer multiple product types, as variations in item size or complexity can affect the pick and pack costs.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are one of the most significant expenses in the fulfillment process and are determined by various factors, including the weight and dimensions of the package, the shipping method chosen (standard, expedited, etc.), and the destination.
Shipping fees can be complex, as they may include costs from multiple carriers, negotiated rates, and additional surcharges for special handling or delivery. For instance, if you ship a 5-pound package using a standard shipping method, the cost may be calculated based on the carrier’s pricing structure, which can include base rates, weight breaks, and distance. It’s advisable to compare shipping options and negotiate rates with your fulfillment provider to find the most cost-effective solutions.
Conclusion: Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
To ensure you receive an accurate quote from fulfillment providers, consider the following tips:
-
Be Transparent About Your Needs: Clearly communicate your order volume, product dimensions, and specific requirements. This information helps providers tailor their quotes accurately.
-
Request Itemized Quotes: Ask for detailed breakdowns of all fees, including setup, receiving, storage, pick and pack, and shipping. This transparency allows you to compare providers effectively.
-
Inquire About Additional Fees: Don’t forget to ask about potential hidden fees, such as long-term storage or extra charges for special handling, as these can significantly impact your total costs.
-
Evaluate Flexibility and Scalability: Consider whether the provider can accommodate your growth. A provider that offers scalable solutions can save you money and headaches as your business expands.
-
Negotiate Rates: Don’t hesitate to negotiate fees based on your expected volume and long-term partnership potential. Many providers are willing to offer discounts for larger commitments.
By taking these steps, you can better understand fulfillment pricing and select the right partner to support your e-commerce growth effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is Amazon Fulfillment?
Amazon Fulfillment refers to the process through which Amazon manages storage, packing, and shipping of products sold by third-party sellers on its platform. Sellers send their inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, and Amazon handles the logistics, including picking, packing, shipping, and customer service for those orders.
2. How does Amazon Fulfillment work?
When a customer places an order for a product fulfilled by Amazon, the order details are sent to the nearest fulfillment center. Amazon’s systems automatically select the best location to fulfill the order based on factors like proximity and inventory levels. Warehouse staff then pick the items, pack them securely, and ship them to the customer. Tracking information is provided to both the seller and the buyer.
3. What’s the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse is primarily a storage facility where goods are kept until needed, whereas a fulfillment center is designed specifically for order processing and shipping. Fulfillment centers incorporate advanced logistics technology and processes to efficiently pick, pack, and ship products directly to customers, often including services like returns management.
4. What is a 3PL?
A 3PL, or third-party logistics provider, is a company that offers outsourced logistics services, including warehousing, fulfillment, and shipping. Businesses partner with 3PLs to manage their supply chain and fulfillment processes, allowing them to focus on their core operations while benefiting from the provider’s expertise and infrastructure.
5. How much do fulfillment services cost?
The cost of fulfillment services varies widely based on factors such as order volume, product size and weight, storage requirements, and specific services offered. Typical costs may include storage fees, picking and packing fees, shipping costs, and additional charges for returns or special handling. It’s crucial for businesses to analyze their needs and compare pricing structures from various fulfillment providers.
6. What are the benefits of using Amazon Fulfillment?
Using Amazon Fulfillment can enhance a seller’s operational efficiency by leveraging Amazon’s extensive logistics network, improving delivery speed, and providing customer service support. Additionally, products fulfilled by Amazon are eligible for Prime shipping, which can boost visibility and sales. Sellers also benefit from Amazon’s return management processes, improving customer satisfaction.
7. Can I use Amazon Fulfillment for my own e-commerce website?
Yes, Amazon Fulfillment can be integrated with your own e-commerce platform through programs like Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). This allows you to sell on your website while utilizing Amazon’s logistics capabilities. You can manage your inventory via Amazon’s systems while providing customers a seamless shopping experience.
8. What are the common challenges of Amazon Fulfillment?
Common challenges include managing inventory levels to prevent stockouts or overstocking, understanding Amazon’s policies and fees, and ensuring compliance with shipping requirements. Additionally, sellers must stay informed about changes in Amazon’s algorithms and marketplace dynamics that could affect visibility and sales.
9. How do I get started with Amazon Fulfillment?
To get started, create an Amazon Seller account and enroll in Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). You will need to prepare your products according to Amazon’s guidelines, ship your inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, and set up your listings to indicate that they are fulfilled by Amazon. Familiarize yourself with the fees and policies associated with FBA.
10. What should I consider when choosing a fulfillment provider?
When selecting a fulfillment provider, consider factors such as their location relative to your customers, shipping capabilities, technology integration, scalability, and customer service. Additionally, evaluate the provider’s track record in handling returns and their ability to manage seasonal demand fluctuations. Comparing pricing structures and service offerings will also help ensure you choose a provider that aligns with your business needs.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Evaluating the Benefits of Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a game-changer for e-commerce businesses looking to scale efficiently. By partnering with a dedicated fulfillment service, businesses can save significant time, allowing them to focus on core activities like product development, marketing, and customer engagement. This shift in focus not only enhances productivity but also fosters innovation and growth.
Scalability is another compelling reason to consider outsourcing. As your order volume fluctuates with seasonal demands or promotional campaigns, a fulfillment partner can adjust resources and capabilities accordingly. This flexibility helps you avoid the pitfalls of overextending your internal resources or underestimating peak periods, which can lead to dissatisfied customers and lost sales.
Moreover, fulfillment service providers bring a wealth of expertise and advanced technology to the table. They are well-versed in the complexities of logistics, inventory management, and shipping optimization, enabling them to execute fulfillment processes with precision. This expertise can translate into improved delivery times, reduced shipping costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction—critical factors for maintaining a competitive edge in the e-commerce landscape.
However, the success of outsourcing hinges on selecting the right partner. A thorough assessment of potential providers should consider their track record, technology infrastructure, and alignment with your business goals. A strong partnership can propel your growth, while a poor choice can hinder your operations and customer satisfaction.
Take Action
To determine if outsourcing fulfillment is the right move for your business, conduct an audit of your current shipping and fulfillment processes. Assess your operational efficiency, customer feedback, and scalability challenges. This exercise will help you identify gaps and opportunities, guiding you toward making an informed decision about whether to engage a fulfillment partner. Embrace the potential for growth by exploring how a strategic partnership can enhance your e-commerce operations.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.