Ecommerce Fulfillment Services: The Ultimate Guide (2025)
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Understanding E-commerce Fulfillment: A Key to Scaling Your Business
As an e-commerce business owner, you may find yourself overwhelmed with the demands of packing and shipping orders. Managing inventory, processing returns, and ensuring timely delivery can quickly become a logistical nightmare, especially as your sales begin to grow. This is where e-commerce fulfillment comes into play. At its core, fulfillment is the process of getting a product from your warehouse to your customer’s doorstep. It encompasses everything from inventory storage and order processing to shipping and handling returns.
In this guide, we will delve into the various fulfillment models available to growing businesses, helping you navigate the complex world of logistics. We will explore options like Third-Party Logistics (3PL) providers and Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), detailing their unique advantages and challenges. Understanding these models is crucial for making informed decisions that align with your business goals.
Key Components of Fulfillment Services
We will outline the core services that fulfillment partners typically offer. These include inventory management, order processing, shipping solutions, and customer service. By grasping the breadth of services available, you can better assess which solutions will streamline your operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Choosing the Right Partner
Selecting the right fulfillment partner is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and customer experience. We will provide practical tips on what to look for in a fulfillment partner, including technology integration, scalability, and customer support. A well-chosen partner can help you scale your operations without the growing pains associated with logistics.
Understanding Pricing Models
Pricing is often a major concern for e-commerce businesses. We will break down various pricing structures associated with different fulfillment models, including per-item fees, storage costs, and additional charges for returns or special handling. This clarity will empower you to budget effectively and select a fulfillment solution that aligns with your financial goals.
Empowering Your Business
The ultimate goal of this guide is to empower you, the business owner, to make smart, strategic decisions about your logistics. By understanding e-commerce fulfillment in detail, you can focus on what you do best—growing your brand—while leaving the complexities of logistics to the experts. Let’s dive in and explore how effective fulfillment can transform your business operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
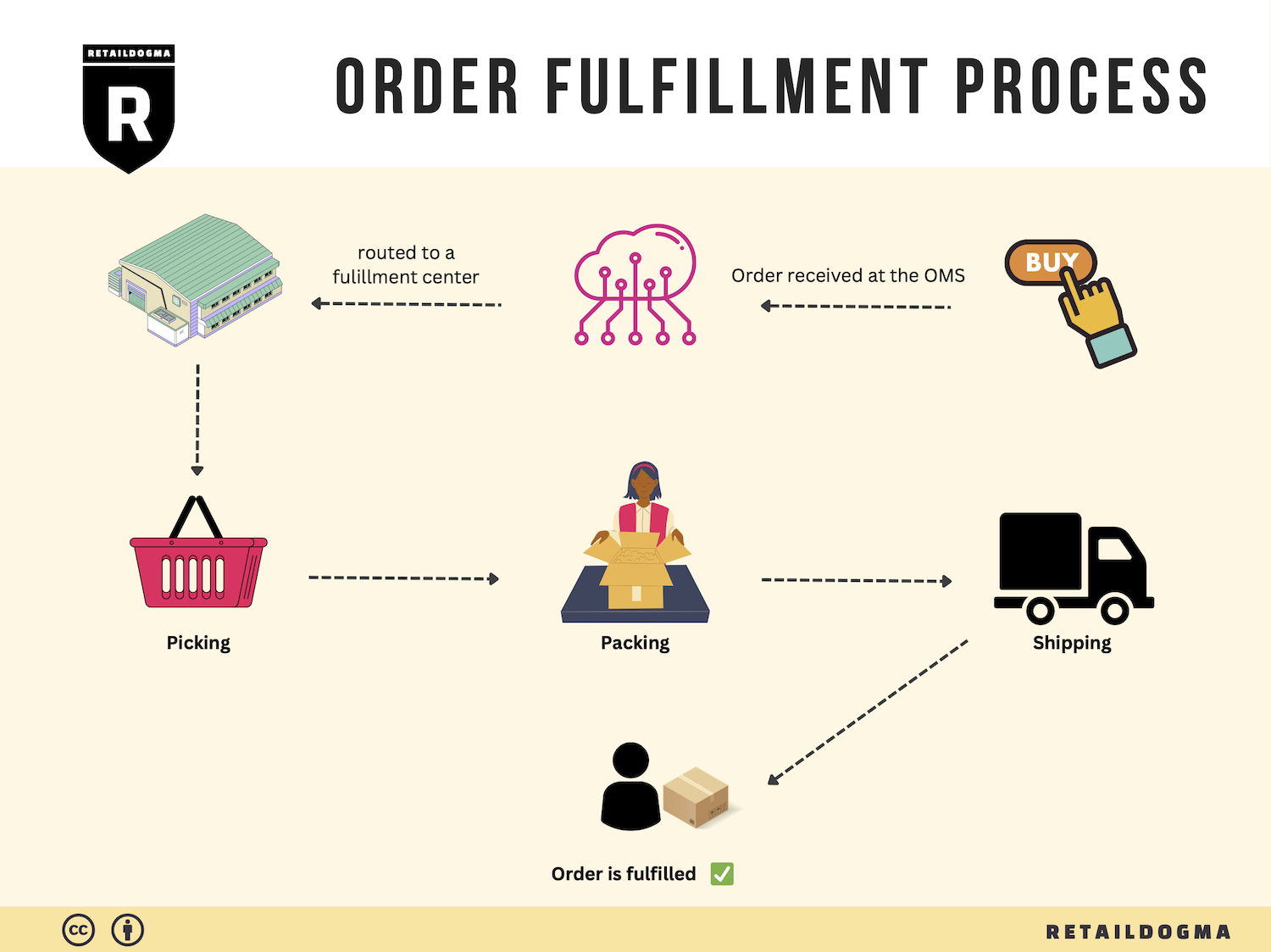
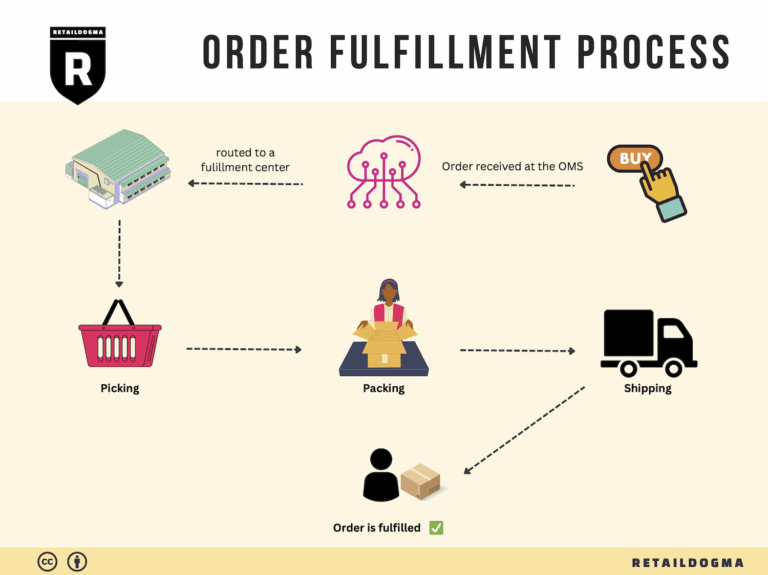
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
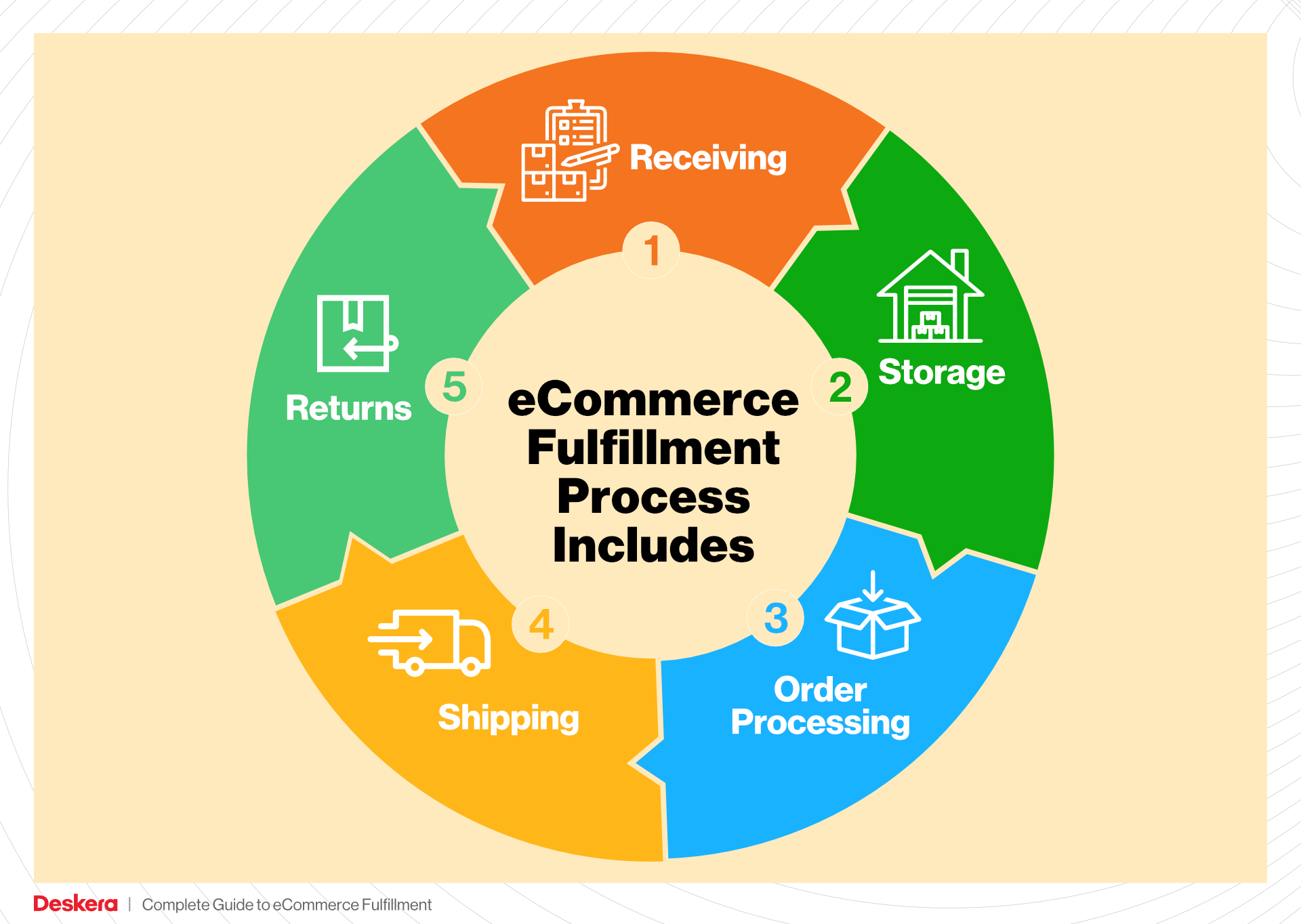
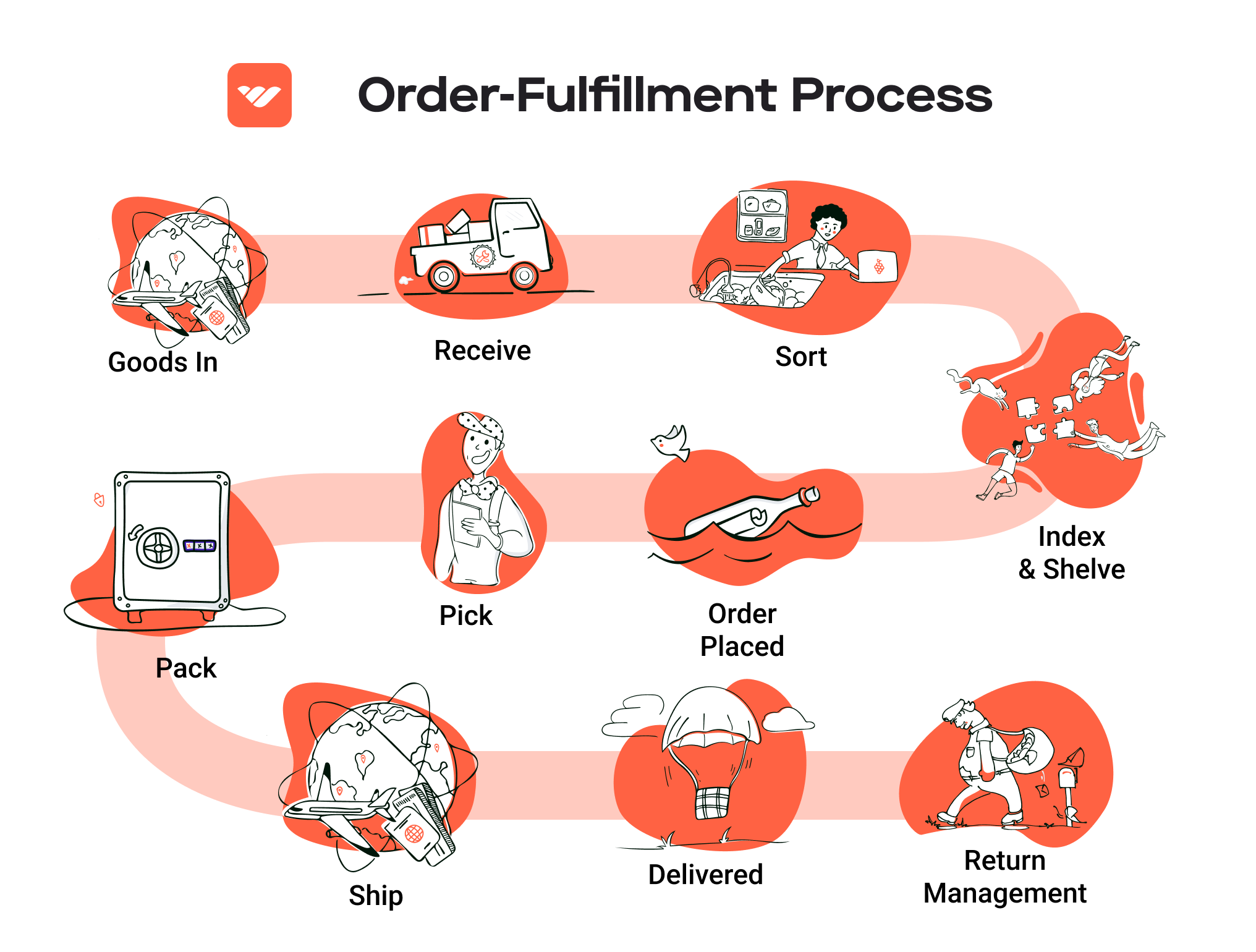
1. Receiving Inventory
The order fulfillment process begins with receiving inventory, a critical step that sets the stage for efficient operations. When products arrive at a fulfillment center, they must be checked for accuracy against purchase orders and quality standards. This involves verifying quantities, inspecting for damage, and ensuring that items match their descriptions.
A key term associated with this step is SKU (Stock Keeping Unit). Each product should have a unique SKU that allows for easy tracking and management within the inventory system. Proper receiving processes not only help in maintaining accurate inventory levels but also prevent costly errors down the line. Efficient receiving can reduce lead times and enhance the overall customer experience, as it ensures that products are available for order fulfillment when needed.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once inventory is received and verified, the next step is warehouse storage. This process involves organizing products within the fulfillment center in a manner that maximizes space and facilitates easy access. Effective warehouse storage utilizes various techniques, such as FIFO (First In, First Out) or LIFO (Last In, First Out), depending on the nature of the products being stored.
Strategic placement of items—grouping similar products and positioning fast-moving items closer to packing areas—can significantly enhance efficiency. Proper storage practices are vital because they not only influence picking speed but also impact inventory accuracy. When items are easily accessible, it reduces the time spent locating products, ultimately speeding up the entire order fulfillment process.
3. Order Picking
Order picking is the next critical step, where items are selected from storage to fulfill customer orders. This process can be manual or automated and often utilizes pick lists—documents that detail the items and quantities needed for each order.
Efficiency in order picking is paramount, as it directly affects order accuracy and fulfillment speed. Businesses can adopt various picking methods, such as single order picking, batch picking, or zone picking, depending on their order volume and product variety. Accurate order picking reduces the risk of errors, which can lead to returns and customer dissatisfaction. By optimizing this step, businesses can improve their fulfillment rates and maintain a positive customer experience.
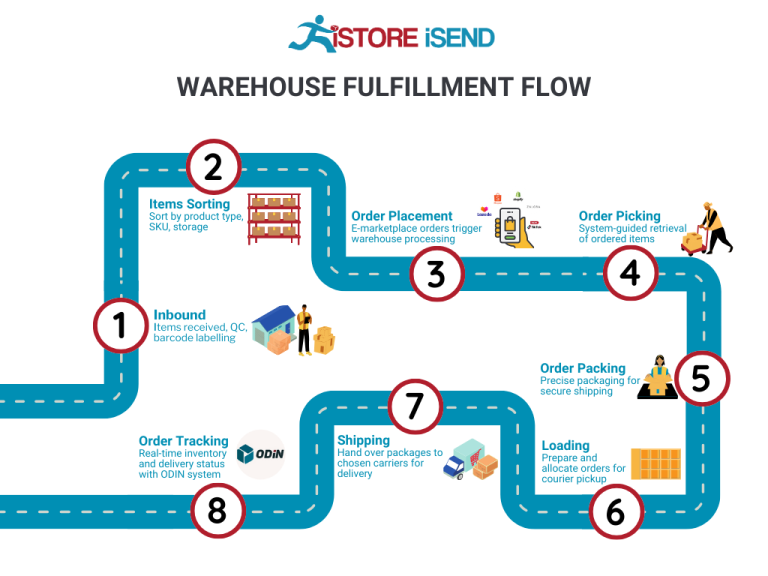
4. Order Packing
After items have been picked, they move to the order packing stage. This step involves securely packing products for shipment to ensure they arrive at the customer’s doorstep in perfect condition. Proper packing includes selecting appropriate packaging materials, such as boxes, bubble wrap, or cushioning, to protect the items during transit.
Key terms associated with this phase include packing slips and shipping labels. A packing slip outlines the contents of the package, while shipping labels provide necessary information for delivery. Efficient packing not only protects products but also contributes to a smoother delivery process. Moreover, well-packed orders can enhance customer satisfaction and encourage repeat business, as customers appreciate receiving their items intact and promptly.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once orders are packed, they are handed off to shipping carriers for delivery to customers. This step involves selecting the right shipping method based on factors such as cost, delivery speed, and destination.
A key term here is shipping carrier, which refers to the company responsible for transporting the package, such as UPS, FedEx, or USPS. Effective shipping strategies can reduce costs and improve delivery times, which are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge in e-commerce. Additionally, businesses should provide tracking information to customers, allowing them to monitor their shipments and enhancing overall satisfaction.
In summary, the order fulfillment process from receiving inventory to shipping and delivery is a complex but essential operation for e-commerce businesses. Each step is interdependent, and optimizing them collectively leads to a more efficient and customer-focused fulfillment strategy. By understanding and refining each aspect of this process, businesses can better scale their operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Fulfillment Model Comparison
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | Business (Own Warehouse) | Established or growing businesses | Complete control over operations | High initial investment and overhead |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | 3PL Provider | Startups to mid-sized businesses | Scalability and expertise in logistics | Less control over fulfillment processes |
| Dropshipping | Supplier/Vendor | New or low-investment businesses | Low upfront investment | Lower profit margins and reliance on suppliers |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment refers to the process where a business manages its own inventory and logistics operations. This model typically involves owning or leasing a warehouse, hiring staff, and investing in the necessary technology and systems to manage order processing, picking, packing, and shipping. In-house fulfillment is best suited for established businesses that have reached a stable level of sales and are looking to scale operations effectively. The primary advantage of this model is the complete control it offers over the entire fulfillment process, allowing businesses to tailor their operations to specific customer needs and preferences. However, it comes with significant challenges, including high initial investment costs, ongoing overhead for staffing and warehousing, and the need for expertise in logistics management. Businesses must weigh these factors carefully, particularly when considering growth strategies.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer businesses an outsourced solution for warehousing, order fulfillment, and shipping. This model is ideal for startups and mid-sized businesses that want to scale quickly without the burden of managing logistics themselves. By partnering with a 3PL, businesses can leverage the provider’s expertise in logistics, access to advanced technology, and established networks for shipping and distribution. This arrangement allows for greater scalability, as businesses can easily increase or decrease their logistics needs based on demand fluctuations. The downside, however, is that businesses relinquish some control over the fulfillment process, which can impact customer experience if not managed properly. Additionally, 3PL fees can vary based on service level and volume, making it essential for businesses to analyze costs carefully to avoid unexpected expenses.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where a retailer does not keep products in stock but instead partners with suppliers who handle inventory and shipping. When a retailer sells a product, the order is sent directly to the supplier, who then ships the product to the customer. This model is particularly attractive for new businesses or those looking to minimize upfront investment, as it eliminates the need for inventory management and warehousing. The primary advantage of dropshipping is the low barrier to entry, allowing entrepreneurs to start an e-commerce business with minimal financial risk. However, dropshipping also has significant drawbacks, including lower profit margins due to reliance on suppliers, limited control over product quality and shipping times, and potential inventory issues if a supplier runs out of stock. As businesses grow, they may find that the dropshipping model becomes less viable, necessitating a shift to in-house fulfillment or partnering with a 3PL for better control and efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment model is crucial for e-commerce businesses aiming to scale effectively. Each model—In-House Fulfillment, Third-Party Logistics, and Dropshipping—offers unique advantages and disadvantages that must be carefully evaluated in the context of the business’s specific needs, growth stage, and long-term strategy. By understanding these dynamics, business owners and operations managers can make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and customer expectations, ultimately leading to more efficient logistics and improved profitability.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service that allows e-commerce sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon then takes care of the logistics involved in storing, packing, and shipping those products directly to customers. The service also handles customer service and returns, making it an attractive option for many sellers looking to streamline their operations and enhance their sales on the platform.
When a customer places an order for a product listed with FBA, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the product on behalf of the seller. The product is eligible for Amazon Prime, which gives it visibility and credibility, potentially increasing sales. Additionally, sellers can track their inventory and manage orders through the Amazon Seller Central platform, making the process more manageable.
How FBA Works
-
Inventory Management: Sellers send their products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Once the items are received, they are stored until sold.
-
Order Fulfillment: When a customer places an order, Amazon’s systems automatically process the order. The product is picked from the warehouse, packed, and shipped directly to the customer.
-
Customer Service: Amazon handles all customer inquiries and issues related to FBA products, including returns and refunds, allowing sellers to focus on their core business activities.
-
Prime Eligibility: Products fulfilled through FBA are eligible for Amazon Prime, providing sellers with access to millions of Prime members who are often more likely to purchase.
-
Multi-Channel Fulfillment: Sellers can also use FBA to fulfill orders from their own websites or other sales channels, streamlining their operations and consolidating logistics.
Pros of Fulfillment by Amazon
Prime Eligibility
One of the most significant advantages of using FBA is the ability to offer products as Prime eligible. This can increase sales, as many customers prefer to shop for Prime items due to the benefits of free two-day shipping.
Customer Trust
Using FBA can enhance customer trust in your products. Amazon’s reputation for fast and reliable shipping can positively influence buyers’ decisions, leading to higher conversion rates.
Multi-Channel Fulfillment
FBA allows sellers to fulfill orders from various platforms, not just Amazon. This means that whether a customer buys from your website or through another marketplace, you can utilize Amazon’s logistics network to deliver the product, simplifying the fulfillment process.
Scalability
FBA can help businesses scale quickly. As demand grows, sellers can rely on Amazon’s infrastructure to handle increasing order volumes without the need for significant investment in warehousing or logistics.
Simplified Logistics
FBA streamlines the logistics process. By outsourcing storage, packing, and shipping to Amazon, sellers can focus on product development, marketing, and other core business activities, reducing the complexity of managing fulfillment.
Cons of Fulfillment by Amazon
High Fees
While FBA can provide many benefits, it’s essential to consider the costs involved. FBA fees can be substantial, often ranging from 24% to over 50% of the sales price when including storage and fulfillment costs. This can significantly affect profit margins, particularly for lower-priced items.
Strict Inventory Rules
Amazon has strict inventory management policies that sellers must adhere to. For example, sellers must maintain a minimum number of units per SKU and comply with labeling and packaging requirements. Failure to meet these requirements can lead to additional fees or inventory being returned.
Commingling Risks
FBA uses a commingled inventory model, meaning that sellers’ products can be mixed with those of other sellers. This can lead to issues such as receiving returns of products that are not yours, which can complicate inventory management and customer service.
Limited Control Over Fulfillment
By using FBA, sellers relinquish control over the fulfillment process. While Amazon’s efficiency is beneficial, it can also lead to issues if the fulfillment process does not meet your expectations, such as longer shipping times or poor handling of products.
Storage Fees for Slow-Moving Inventory
Sellers may incur long-term storage fees for inventory that does not sell quickly. This can be a significant drawback for businesses with seasonal products or those that experience fluctuations in demand.
Who is FBA Best For?
Fulfillment by Amazon is particularly beneficial for small to medium-sized businesses that sell products that are popular with Amazon customers. Sellers who offer lightweight and low-cost items, such as accessories or household goods, can see significant benefits from the reduced fulfillment costs associated with FBA.
Additionally, businesses looking to scale quickly and those that prefer to focus on marketing and product development rather than logistics may find FBA to be an excellent fit. FBA is also suitable for businesses that can maintain a steady flow of inventory and are willing to comply with Amazon’s stringent requirements.
Conversely, sellers with high-value or oversized items may find the fees associated with FBA to be prohibitive. Similarly, businesses that prioritize complete control over their fulfillment process may prefer to handle logistics in-house or through third-party logistics providers.
In summary, FBA offers a range of advantages that can help businesses grow, but it is crucial to weigh these benefits against the associated costs and requirements to determine if it is the right fit for your e-commerce strategy.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Fulfillment centers provide comprehensive inventory management and warehousing services that are critical for e-commerce businesses looking to scale efficiently. This service encompasses the storage, tracking, and management of inventory, allowing sellers to keep their products organized and accessible.
The primary benefit of effective inventory management is the optimization of stock levels. Fulfillment centers utilize advanced software systems that provide real-time inventory tracking, helping businesses avoid stockouts or overstock situations. This is particularly important for e-commerce companies that rely on just-in-time inventory practices to minimize holding costs. By having a clear view of inventory levels, businesses can make informed purchasing decisions, ensuring they have the right amount of stock available to meet customer demand without tying up capital in excess inventory.
Additionally, fulfillment centers often offer climate-controlled storage options for sensitive items, ensuring that products are kept in optimal conditions until they are sold. This level of care can significantly extend product shelf life and quality, particularly for items like cosmetics, electronics, or food products.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services are a cornerstone of fulfillment operations, allowing e-commerce businesses to streamline order processing. In this process, fulfillment center staff pick the ordered items from the warehouse shelves and pack them for shipment.
The efficiency of pick and pack services translates into faster order fulfillment, which is crucial for customer satisfaction in today’s fast-paced e-commerce environment. When customers place an order, they expect prompt delivery, often facilitated by services like Amazon Prime. Fulfillment centers can typically fulfill orders more rapidly than individual sellers managing their own logistics, thereby enhancing the likelihood of repeat business and positive reviews.
Moreover, fulfillment centers often employ automated systems and technologies, such as barcode scanning and conveyor systems, which minimize human error and ensure accurate order fulfillment. This not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces the likelihood of costly returns due to incorrect shipments. In a competitive marketplace, the ability to deliver orders accurately and quickly can be a significant differentiator for e-commerce businesses.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services are particularly beneficial for e-commerce businesses that sell products that require bundling or assembly before shipping. This service involves combining multiple items into a single package or assembling components into a finished product.
For example, a seller might offer a skincare kit that includes several products packaged together or require the assembly of furniture pieces before they are shipped. Fulfillment centers can handle these processes efficiently, allowing businesses to present their products in an appealing and market-ready format.
The advantages of kitting and assembly services extend beyond aesthetics. They can also lead to cost savings in shipping by reducing the number of individual packages sent out, which can lower shipping fees. Additionally, well-packaged kits can enhance the perceived value of a product, potentially leading to higher sales. By outsourcing this function to a fulfillment center, businesses can focus on their core competencies such as product development and marketing, while leaving the logistical complexities to experts.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, is an essential service that fulfillment centers provide to e-commerce businesses. This process involves handling returned merchandise, restocking items, and managing customer refunds or exchanges.
A robust returns management system is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. In e-commerce, the return rate can be significantly higher than in traditional retail, making it essential for businesses to have a streamlined process in place. Fulfillment centers can efficiently manage returns by quickly assessing returned items, processing refunds, and restocking products, which minimizes the impact on cash flow and inventory levels.
Effective returns management can also provide valuable insights into customer behavior and product quality. By analyzing return data, businesses can identify trends, such as which products are frequently returned and why. This information can inform future product development and marketing strategies, helping to reduce return rates over time.
Moreover, a well-executed returns process can enhance a brand’s reputation. Customers are more likely to purchase from a seller that offers a hassle-free return policy, knowing that they can easily return products if they do not meet their expectations. This assurance can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty, making returns management a vital component of a successful e-commerce strategy.
In conclusion, partnering with a fulfillment center that offers these core services allows e-commerce businesses to optimize their operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. By leveraging the expertise and resources of fulfillment centers, businesses can focus on growth and scaling their sales, while ensuring that their logistics are handled efficiently and effectively.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
Choosing a fulfillment partner with the right location and warehouse network is crucial for ensuring timely deliveries and minimizing shipping costs. A partner with strategically located warehouses can help you reach your customers more efficiently, especially if your business operates in multiple regions or countries.
Key Questions to Ask:
– Where are your warehouses located, and how do these locations align with our primary customer base?
– Do you have warehouses in international markets if we plan to expand our reach?
– What are your average shipping times from different warehouses to customers?
Technology & Integrations
In today’s e-commerce landscape, technology plays a pivotal role in streamlining operations. A fulfillment partner with robust technology can automate various processes, from inventory management to order tracking, enhancing overall efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Questions to Ask:
– What technology platforms do you use for inventory management, order processing, and shipping?
– Can your systems integrate with our existing e-commerce platforms (e.g., Shopify, Amazon, eBay)?
– How do you handle real-time inventory updates, and can we access this information easily?
Specializations (e.g., cold storage, oversized items)
Not all fulfillment partners are equipped to handle every type of product. If your business deals with specific categories like perishable goods, oversized items, or hazardous materials, it’s essential to partner with a provider that specializes in those areas. This ensures compliance with regulations and proper handling of your products.
Key Questions to Ask:
– What specializations does your company have, and do you have experience with our specific product types?
– How do you handle storage and shipping for specialized items, such as cold storage or fragile goods?
– Are there any additional fees associated with handling specialty products?
Scalability & Capacity
As your business grows, so will your fulfillment needs. It’s vital to choose a partner that can scale alongside your business, ensuring they can accommodate increased order volumes without compromising service quality.
Key Questions to Ask:
– How do you manage peak seasons or sudden increases in order volume?
– What is your current capacity, and how quickly can you scale up when needed?
– Can you provide examples of how you have successfully scaled operations for other clients?
Pricing and Contracts
Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms is fundamental to making a sound financial decision. Transparent pricing helps you budget effectively and avoid unexpected costs that can eat into your profit margins.
Key Questions to Ask:
– Can you provide a detailed breakdown of your pricing structure, including fulfillment fees, storage fees, and any other costs?
– Are there long-term contracts, and what are the terms for cancellation or changes?
– How do your prices compare to industry standards, and what justifies any premium you may charge?
Customer Support & Reviews
Effective customer support can significantly impact your experience with a fulfillment partner. Look for a provider that offers responsive and knowledgeable support. Additionally, researching reviews and testimonials can provide insights into their reliability and quality of service.
Key Questions to Ask:
– What kind of customer support do you offer, and what are your response times?
– Can you provide references or case studies from current or past clients?
– How do you handle issues or complaints that arise during the fulfillment process?
Conclusion
Selecting the right fulfillment partner is a critical decision that can affect your business’s efficiency and customer satisfaction. By using this checklist, you can systematically evaluate potential partners based on essential criteria that align with your operational needs and growth goals. A well-chosen partner will not only enhance your fulfillment process but also support your overall business strategy as you scale your e-commerce operations.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
When businesses first engage with a fulfillment service, they often encounter initial setup fees. These fees cover the administrative costs associated with onboarding your products into the fulfillment center’s system. The setup process typically includes creating product listings, establishing inventory management systems, and integrating your e-commerce platform with the fulfillment center’s software.
The calculation of initial setup fees can vary significantly between providers, but it usually includes a one-time charge that may range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the complexity of your inventory and the specific services required. Businesses should ensure they understand all components included in the setup fee to avoid unexpected costs.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged when your products arrive at the fulfillment center. These fees account for the labor and resources needed to unload, inspect, and store your items. When products are received, they are typically scanned into the system, and any discrepancies (such as damaged goods or incorrect quantities) are noted.
The calculation of receiving fees can vary based on the volume of items being received and the specific processes involved. Generally, these fees are charged on a per-unit basis and can range from a few cents to several dollars per item, depending on the provider’s pricing structure. It’s crucial to clarify how receiving fees are assessed, particularly if you have a high volume of products.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are incurred for holding your inventory in the fulfillment center. These fees are typically calculated based on the amount of space your products occupy, measured in pallets or bins. Providers often charge a monthly fee for storage, which can vary based on the type of inventory you are storing, the total volume, and the duration of storage.
For example, storage fees might be assessed at a monthly rate per pallet, which can range from $10 to $25, or on a per-bin basis. Long-term storage fees may also apply if inventory remains in the warehouse beyond a certain threshold (often six months), potentially increasing costs significantly. It’s essential to monitor your inventory turnover to avoid excessive storage fees, especially for slow-moving items.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are one of the most significant costs associated with fulfillment services. These fees cover the labor involved in picking your products from the warehouse shelves and packing them for shipment. The calculation of these fees typically depends on the number of items in an order and may include a base fee plus additional charges for each item picked.
For example, a fulfillment center might charge a flat fee of $1.00 per order, plus $0.50 for each item picked. Therefore, an order containing three items would incur a total pick and pack fee of $2.50. Understanding this fee structure is vital for businesses, as it can significantly impact overall fulfillment costs, especially for operations with a high order volume or a diverse product range.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are the costs associated with transporting your products from the fulfillment center to the end customer. These fees can vary widely based on several factors, including the shipping method chosen (e.g., standard, expedited), the weight and dimensions of the package, the destination, and any additional services such as insurance or signature confirmation.
Shipping fees are typically calculated based on weight and distance, with many providers offering tiered pricing based on shipping volume. For instance, a fulfillment center may offer discounted rates for businesses that ship a high volume of packages each month. It’s essential to compare the shipping options available through different fulfillment providers and understand how these fees will impact your overall logistics costs.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
-
Request Detailed Pricing Information: Always ask for a comprehensive breakdown of all fees associated with the fulfillment service. This includes initial setup, receiving, storage, pick and pack, and shipping fees.
-
Understand Volume Discounts: Inquire about potential discounts for high volumes, as many providers offer reduced rates for businesses that ship a larger number of orders.
-
Analyze Your Product Mix: Consider the types of products you will be storing and shipping. Different products may incur different fees, so it’s beneficial to understand how your product mix will influence costs.
-
Factor in Hidden Costs: Be aware of any additional charges that may arise, such as long-term storage fees, returns processing fees, or fees for special packaging.
-
Get Quotes from Multiple Providers: To ensure you’re getting the best deal, compare quotes from several fulfillment centers. This can help you identify the most cost-effective option for your business needs.
By understanding these common fulfillment pricing models and diligently seeking accurate quotes, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their operational efficiency and profitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is Amazon FBA Small and Light (SnL) fulfillment?
Amazon FBA Small and Light (SnL) is a specialized fulfillment service designed for sellers of small, lightweight, and lower-priced items. This service allows these products to be stored in Amazon’s fulfillment centers, where they can benefit from Amazon’s logistics network, while also enjoying reduced fulfillment fees compared to standard FBA.
2. How does SnL fulfillment differ from standard FBA?
The primary difference lies in the target product types and associated fees. SnL is tailored for small, light, and low-cost items, offering approximately 20% lower fulfillment fees than standard FBA for these products. However, SnL items do not qualify for Prime’s same-day or two-day shipping options, which may impact customer appeal.
3. What types of products are best suited for SnL fulfillment?
Products that are ideal for SnL fulfillment typically weigh less than 16 ounces and have a retail price of $15 or less. Examples include small household items, accessories, and low-cost gadgets. These items often face challenges with standard FBA due to high shipping and storage costs relative to their sale price.
4. What are the costs associated with SnL fulfillment?
While costs can vary based on the specific product and fulfillment needs, SnL generally offers lower fees than standard FBA. For example, fulfillment fees for a 2-ounce item priced at $5 might be around $2.90 with SnL, compared to about $3.70 with standard FBA. However, sellers should also account for additional fees such as storage and potential long-term storage fees.
5. What is the minimum inventory requirement for SnL fulfillment?
Sellers must send a minimum of 30 to 50 units per SKU to utilize SnL fulfillment. This requirement ensures that Amazon has enough inventory to manage order fulfillment efficiently, which can be a barrier for some smaller sellers.
6. Can I use SnL fulfillment for products sold on other marketplaces?
Yes, but there is an additional charge for orders fulfilled through SnL to other marketplaces (e.g., eBay, Newegg). Currently, this cost is approximately $5.95 per order, which can impact your overall profitability if you plan to sell across multiple channels.
7. What customer service support does Amazon provide for SnL fulfillment?
Amazon handles customer service for orders fulfilled through the SnL program. While this can be a convenience for sellers, it also means that Amazon will manage all customer interactions, which may not align with some brands’ customer service strategies.
8. What are the potential downsides of using SnL fulfillment?
Some drawbacks include the lack of Prime shipping options (same-day or two-day), the minimum inventory requirements, and the possibility of needing to apply stickers to products that already have barcodes. Additionally, increased long-term storage fees may affect profitability if inventory moves slowly.
9. What is the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse is primarily a storage facility for goods, while a fulfillment center is designed to process orders and ship products directly to customers. Fulfillment centers typically have advanced logistics technology and processes in place to efficiently pick, pack, and ship items, often providing additional services such as inventory management and customer service.
10. What is a Third-Party Logistics Provider (3PL)?
A Third-Party Logistics Provider (3PL) is a company that offers outsourced logistics services, including warehousing, fulfillment, and shipping. Utilizing a 3PL can help businesses streamline their operations, reduce costs, and focus on core activities, especially if they are scaling and require more extensive logistics support beyond what Amazon offers.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Assessing the Benefits of Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a transformative move for e-commerce businesses looking to scale. One of the most significant advantages is the time savings it provides. By entrusting the logistics to a fulfillment service, business owners can redirect their focus toward strategic initiatives such as product development, marketing, and customer engagement. This shift not only enhances operational efficiency but also cultivates a more innovative business environment.
Scalability is another compelling reason to consider outsourcing. As your business grows, so do the complexities of order management, inventory control, and shipping logistics. A proficient fulfillment partner can seamlessly adapt to fluctuations in demand, ensuring that you can meet customer expectations without the burden of managing increased operational demands. This flexibility allows businesses to scale quickly and effectively, capitalizing on new opportunities without the headaches of logistical constraints.
Furthermore, partnering with a fulfillment expert brings invaluable industry knowledge and technology. These providers often have access to advanced systems and practices that can improve order accuracy and speed. By leveraging their expertise, businesses can reduce shipping costs and improve customer satisfaction, ultimately fostering loyalty and repeat purchases.
Choose Your Partner Wisely
However, the success of outsourcing fulfillment hinges on selecting the right partner. It’s essential to evaluate potential providers based on their capabilities, technology, and reputation. A well-aligned partnership can drive significant growth and operational excellence.
Take Action Today
As you contemplate the future of your e-commerce operations, consider conducting an audit of your current shipping processes. Are they meeting your growth ambitions? If not, it may be time to explore whether a fulfillment partner could enhance your business efficiency and customer satisfaction. Take the next step in scaling your business by assessing your logistics strategy today.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.