Ecommerce Fulfillment Services: The Ultimate Guide (2025)
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Understanding E-commerce Fulfillment: A Key to Growth
As a growing online business, the thrill of increasing sales can quickly be overshadowed by the daunting reality of packing and shipping orders. Many entrepreneurs find themselves inundated with the logistics of fulfillment—managing inventory, processing orders, and ensuring timely delivery—often leading to burnout and operational inefficiencies. This is where understanding e-commerce fulfillment becomes crucial.
In its simplest form, fulfillment is the process of getting a product from your warehouse to your customer’s doorstep. It encompasses everything from inventory management to order processing, packaging, and shipping. While it may seem straightforward, the complexities can multiply as your business scales, making it essential to choose the right fulfillment strategy that aligns with your growth objectives.
This guide will explore various fulfillment models available to e-commerce businesses, including Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM), and Third-Party Logistics (3PL). Each model has its unique advantages and challenges, and understanding these can help you decide which one best suits your needs.
Additionally, we will delve into the core services associated with e-commerce fulfillment. This includes warehousing, order processing, shipping logistics, and customer service. Knowing what services are essential for your operation can streamline your processes and enhance the customer experience.
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is another critical aspect covered in this guide. Whether you decide to handle fulfillment in-house or outsource it to a professional service, the right partner can significantly impact your operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. We’ll provide insights into the factors to consider when selecting a fulfillment partner, such as their reliability, technology capabilities, and service offerings.
Pricing is a significant concern for any business looking to scale. We will outline the different cost structures associated with various fulfillment models, helping you to understand how to budget for fulfillment without compromising service quality.
Ultimately, this guide aims to empower e-commerce businesses to make informed decisions about their logistics. By understanding the nuances of e-commerce fulfillment, you can optimize your operations, reduce stress, and focus on what you do best: growing your business.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
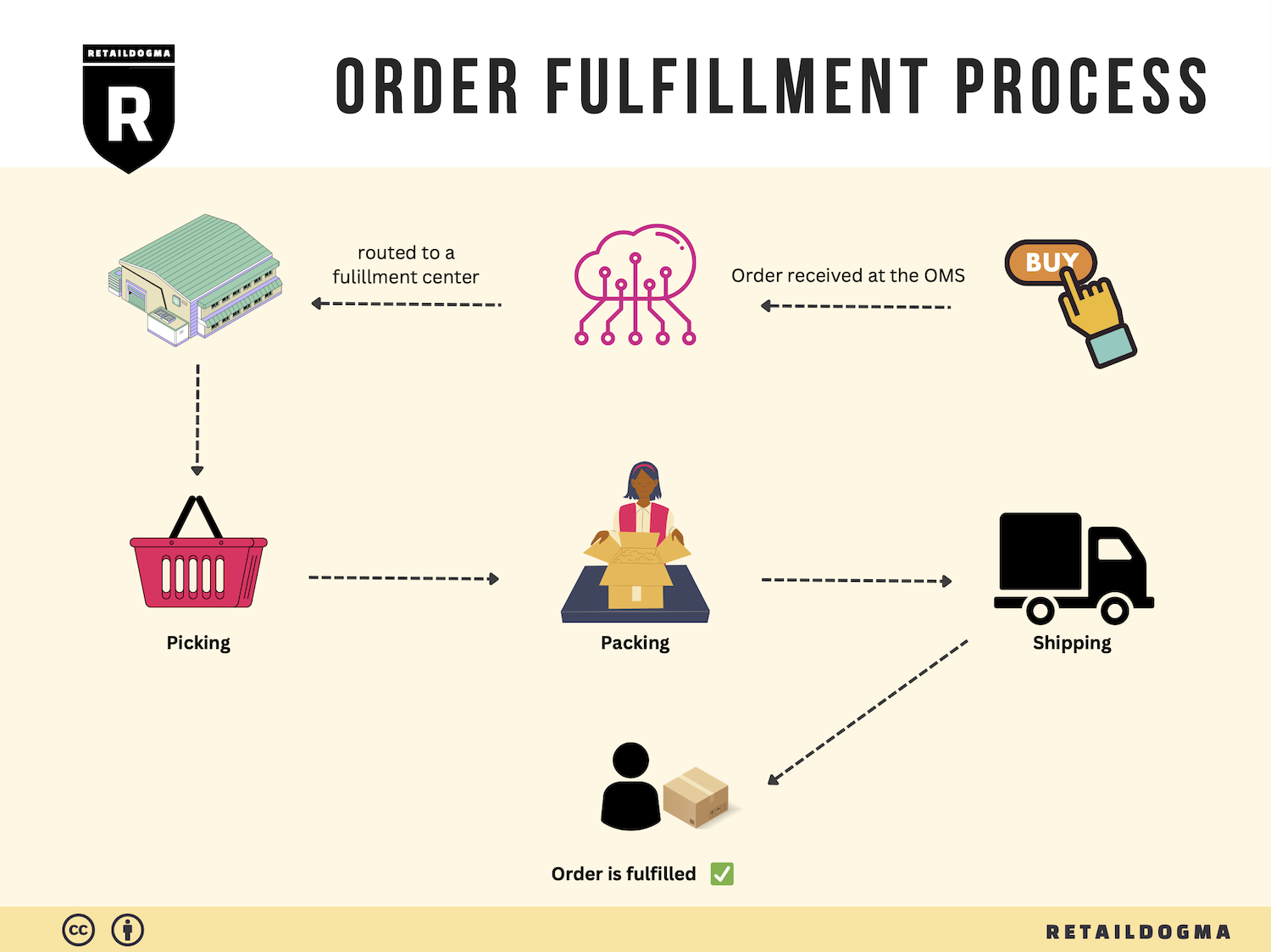
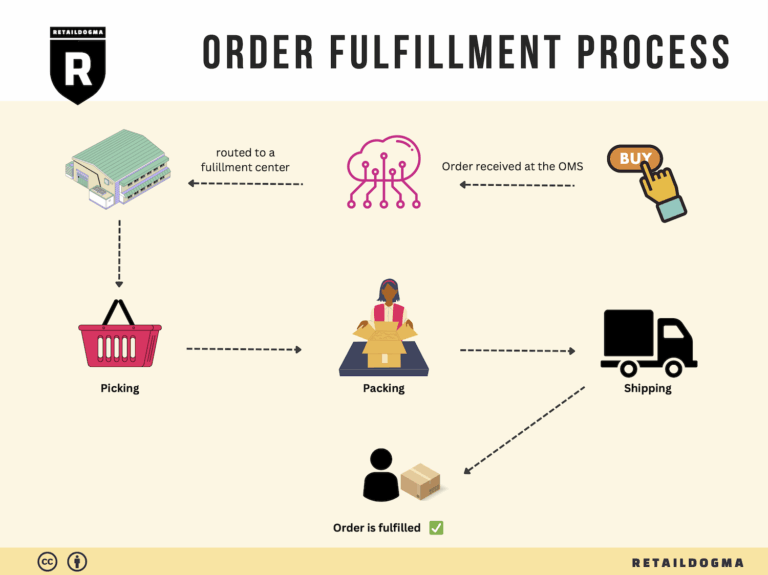
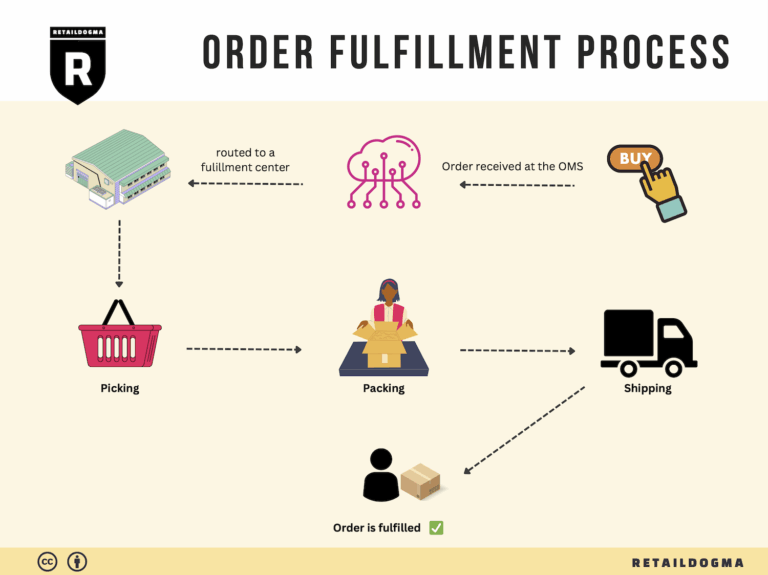
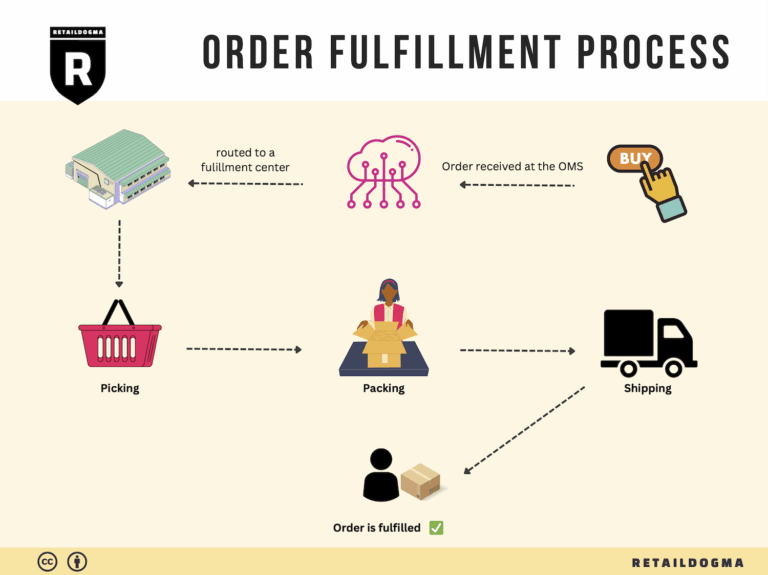
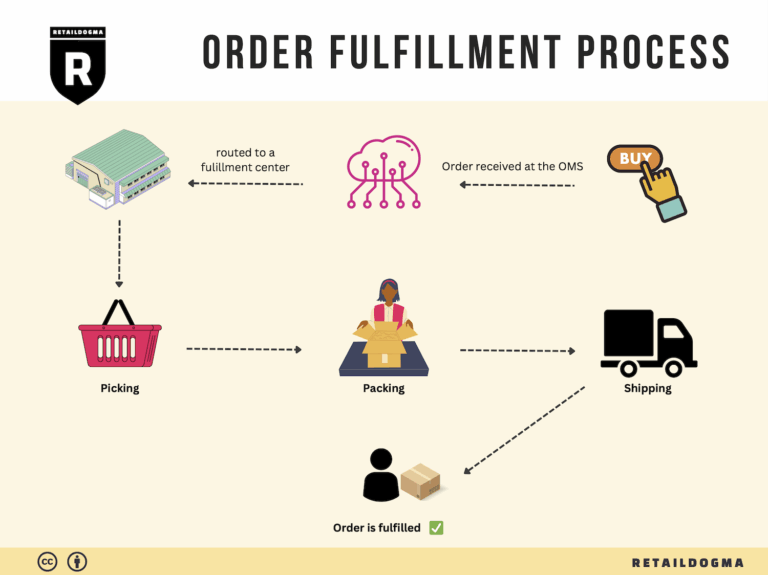
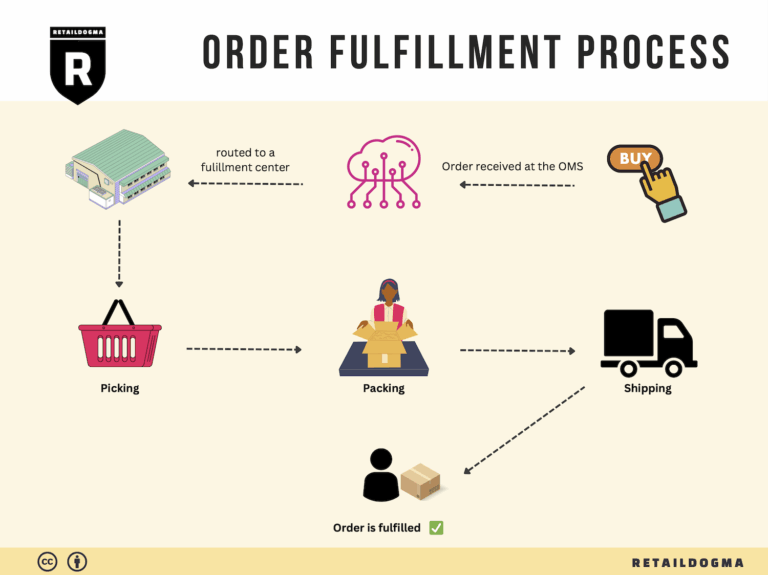
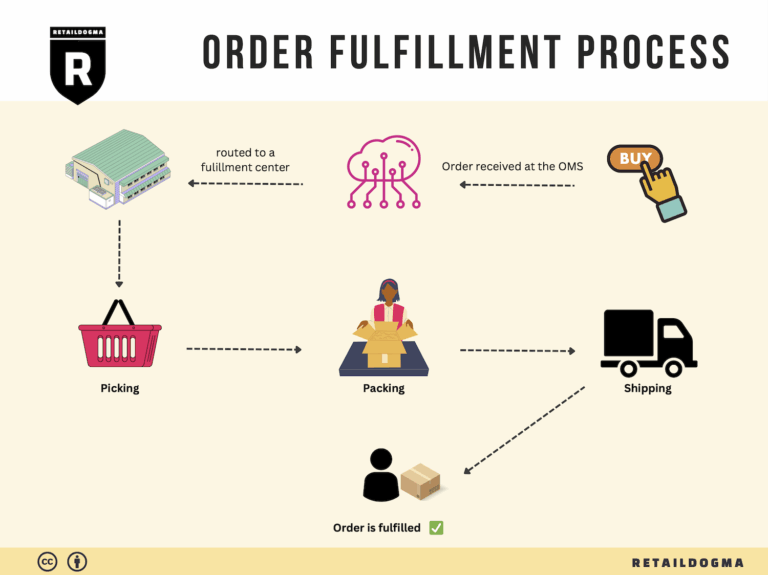
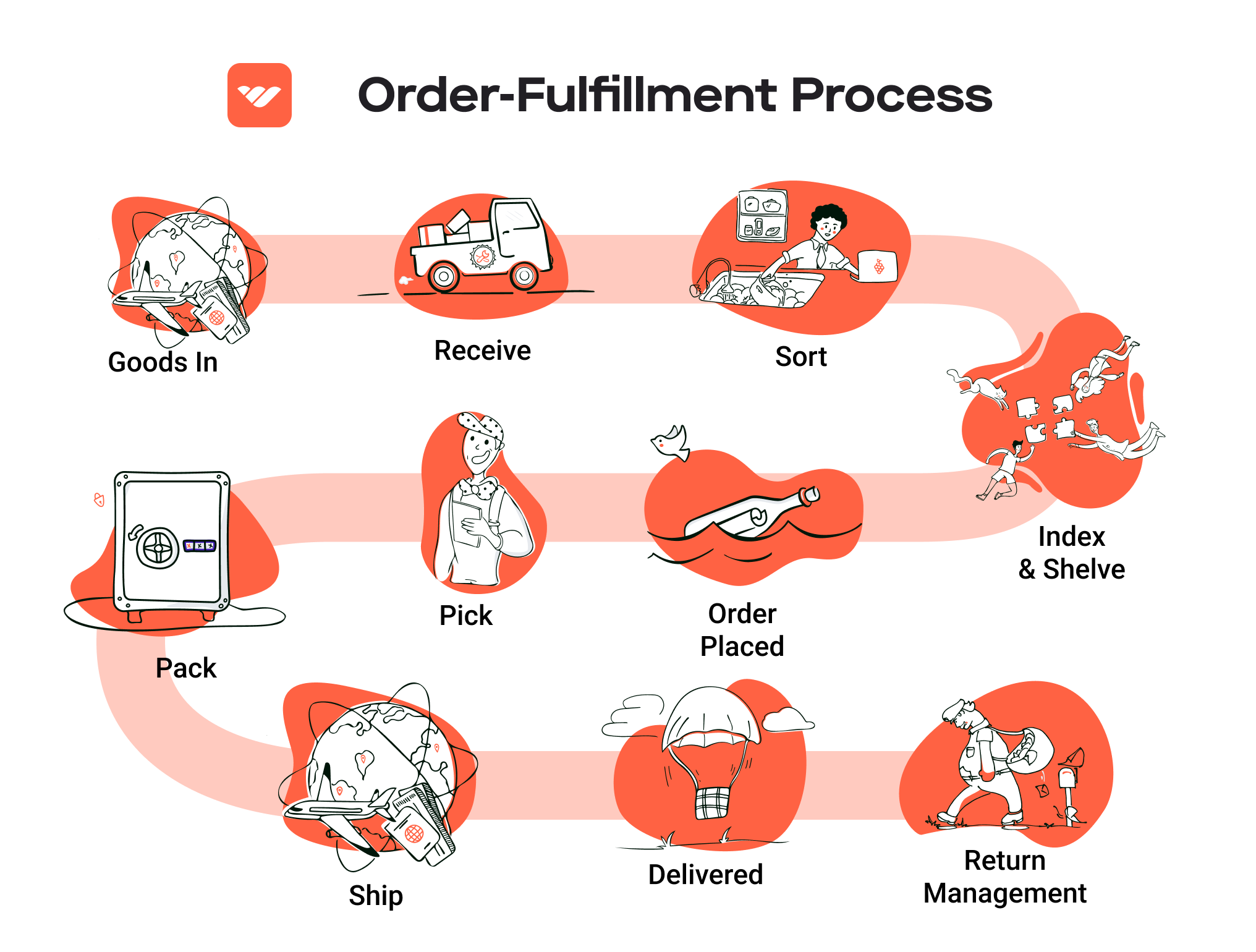
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
1. Receiving Inventory
The first step in the order fulfillment process is receiving inventory. This involves the arrival of products from suppliers or manufacturers to your warehouse or fulfillment center. During this phase, it is essential to check the shipment against the purchase order to ensure that the correct quantity and quality of items have been delivered. This process often involves using Stock Keeping Units (SKUs), which are unique identifiers for each product.
Importance: Efficient inventory receipt is crucial for maintaining accurate stock levels and ensuring that your fulfillment operations can run smoothly. Any discrepancies or damages found during this step can lead to delays in order fulfillment and potential customer dissatisfaction. A well-organized receiving process also sets the stage for effective inventory management and helps prevent stockouts or overstock situations.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once the inventory is received and verified, the next step is warehouse storage. This involves placing products in designated areas within the warehouse for easy access during order picking. Effective warehouse layout and management are vital here, and utilizing a systematic approach—like the use of bins, shelves, or pallet racks—can significantly enhance efficiency.
Importance: Proper storage minimizes the time and effort required to locate products during the picking process. It also prevents damage to items, as well-organized storage reduces the likelihood of accidents. Additionally, implementing a warehouse management system (WMS) can help track inventory levels and locations, facilitating better inventory control and optimizing space utilization.
3. Order Picking
Order picking is the process of retrieving items from storage to fulfill a customer order. When an order is placed, a pick list is generated, detailing the items and their respective locations in the warehouse. This list guides employees (or automated systems) in gathering the products required for shipment.
Importance: Efficient picking is critical for ensuring that orders are fulfilled accurately and on time. The quicker and more accurate the picking process, the higher the customer satisfaction. Moreover, optimizing picking methods—such as batch picking, wave picking, or zone picking—can significantly reduce labor costs and improve order turnaround times.
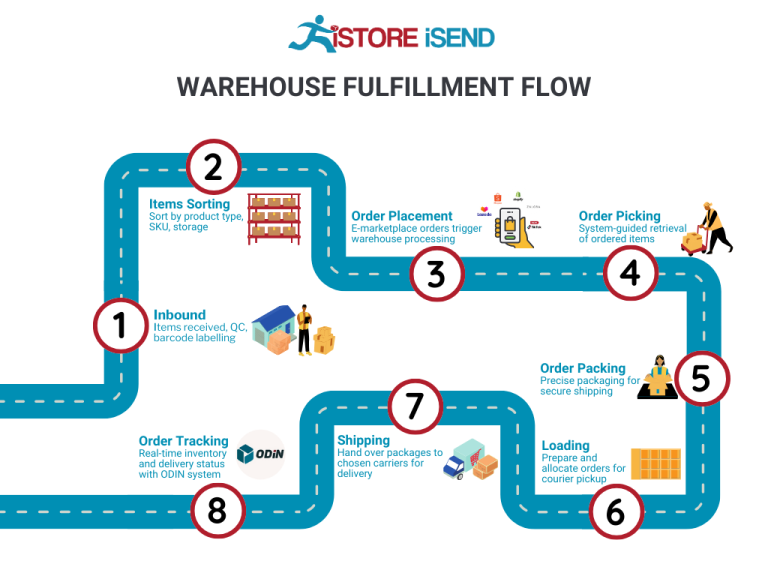
4. Order Packing
After the items are picked, they are taken to the packing station, where they are prepared for shipment. This step involves checking the items against the order for accuracy, securely packaging them to prevent damage during transit, and labeling the packages with shipping information. The use of packing slips, which outline the contents of the package, is standard practice here.
Importance: Proper packing is essential to ensure that products arrive at the customer’s location in pristine condition. Effective packing also reduces the chances of returns due to damages, which can be costly. Moreover, an aesthetically pleasing and branded packaging can enhance the customer experience and foster brand loyalty.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once the orders are packed, they are handed over to a shipping carrier (like USPS, FedEx, or UPS) for delivery. This step includes generating shipping labels, providing tracking information to customers, and ensuring that packages are dispatched promptly based on the selected shipping method.
Importance: Timely delivery is a critical factor in customer satisfaction. The shipping process directly impacts the overall customer experience, influencing repeat purchases and brand reputation. Additionally, utilizing shipping software can help streamline the shipping process, allowing for better rate comparisons and tracking capabilities, which are essential for managing costs and ensuring customer transparency.
In summary, each step of the order fulfillment process plays a vital role in ensuring that products move efficiently from the moment a customer clicks the ‘Buy’ button until they arrive at the customer’s door. By focusing on optimizing each of these steps, e-commerce businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive sales growth.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Fulfillment Model Comparison
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | The business owner or internal team | Established businesses with stable sales | Full control over inventory and fulfillment process | High overhead costs and operational complexity |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | A specialized logistics provider | Growing businesses looking to scale | Access to expertise, technology, and scalable resources | Less control over inventory and fulfillment operations |
| Dropshipping | Supplier or manufacturer | Startups and small businesses | Low upfront investment and no inventory risk | Lower profit margins and reliance on supplier performance |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment involves managing the entire logistics process internally, from inventory storage to order processing and shipping. This model is typically favored by established businesses that have a consistent sales volume and sufficient resources to manage their operations. One of the primary advantages of in-house fulfillment is the complete control it provides over inventory management, order accuracy, and customer service. Businesses can implement their branding and packaging, enhancing the customer experience and fostering brand loyalty.
However, this model comes with significant challenges. The overhead costs associated with warehousing, staffing, and technology can be substantial. Additionally, managing fulfillment in-house can divert attention from core business activities, such as marketing and product development. As order volumes fluctuate, businesses may struggle with scalability, leading to inefficiencies during peak seasons or slow periods. Therefore, while in-house fulfillment offers control, it requires a careful assessment of resource allocation and operational capacity.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer a comprehensive solution for businesses looking to outsource their fulfillment operations. By partnering with a 3PL, businesses can leverage the provider’s expertise, technology, and infrastructure, allowing them to focus on growth and customer engagement. This model is particularly beneficial for growing businesses that may not have the resources or desire to manage logistics internally.
One of the key advantages of 3PL is scalability. As businesses grow, 3PLs can adjust their services to accommodate increased order volumes without the need for significant investment in infrastructure. Additionally, 3PL providers often have established shipping networks and relationships with carriers, which can result in cost savings and faster delivery times. However, the trade-off is a potential loss of control over inventory and the fulfillment process. Businesses must rely on their 3PL partner to maintain service levels, which can be a concern if the provider does not meet expectations. Clear communication and service level agreements (SLAs) are crucial to ensuring a successful partnership.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where the retailer does not hold inventory but instead transfers customer orders directly to a supplier or manufacturer, who then ships the products directly to the customer. This model is particularly appealing to startups and small businesses due to its low upfront investment and minimal risk. Since there is no need to purchase inventory upfront, businesses can offer a wide range of products without the financial burden of stock.
The primary advantage of dropshipping is the reduced overhead costs, making it easier for new entrants to enter the market. Moreover, dropshipping allows for flexibility in product offerings, as businesses can quickly adapt to market trends without being tied to unsold inventory. However, dropshipping also has notable disadvantages. Profit margins tend to be lower compared to other models due to the reliance on suppliers, and the success of the business is heavily dependent on the performance and reliability of those suppliers. Shipping times can also be longer, which may negatively impact customer satisfaction. Additionally, businesses have limited control over branding and packaging, which can dilute the brand experience.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment model is a critical decision that can significantly impact an e-commerce business’s operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Each model—In-House Fulfillment, Third-Party Logistics, and Dropshipping—has its unique advantages and disadvantages. Business owners must carefully evaluate their current stage, resources, and long-term goals to determine which model aligns best with their operational strategy. By understanding the nuances of each fulfillment approach, businesses can position themselves for sustainable growth and improved customer experiences.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service provided by Amazon that allows sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon then takes care of storage, packaging, shipping, and customer service for these products. This service enables sellers to leverage Amazon’s vast logistics network and customer base while focusing on their core business operations.
When a customer orders a product listed on Amazon that is fulfilled by FBA, Amazon handles the entire order process—from picking the item from the warehouse to shipping it directly to the customer. This not only simplifies the logistics for sellers but also provides customers with fast and reliable delivery options.
How FBA Works
-
Set Up Your FBA Account: To begin using FBA, sellers need to create an Amazon Seller Central account and enroll in the FBA program.
-
Prepare and Ship Your Inventory: Sellers must prepare their products according to Amazon’s guidelines, which include labeling and packaging requirements. Once prepared, products are shipped to Amazon’s fulfillment centers.
-
Product Listing: Sellers create product listings on Amazon. These listings can be enhanced with images, descriptions, and keywords to improve visibility.
-
Order Processing: When a customer places an order, Amazon handles the entire fulfillment process. This includes picking, packing, and shipping the product, as well as managing returns and customer inquiries.
-
Payment and Fees: After an order is fulfilled, Amazon deducts its fees from the sale before transferring the remaining amount to the seller.
Pros of FBA
-
Prime Eligibility: Products fulfilled through FBA automatically become eligible for Amazon Prime, which is a significant advantage. Prime members are more likely to purchase products that offer free two-day shipping, increasing sales potential.
-
Enhanced Customer Trust: Customers trust Amazon’s logistics and customer service. When they see the FBA badge, they feel assured that their order will be handled professionally, which can lead to increased conversion rates.
-
Multi-Channel Fulfillment: FBA isn’t limited to Amazon sales. Sellers can use FBA to fulfill orders from their own websites or other sales channels, streamlining operations across platforms.
-
Scalability: FBA allows sellers to scale their business without the complexities of managing logistics. As sales increase, sellers can send more inventory to Amazon without needing to invest in their own warehousing or fulfillment infrastructure.
-
Simplified Returns Management: Amazon handles all customer service and returns for FBA products, alleviating sellers from the burden of managing these processes and allowing them to focus on growth.
Cons of FBA
-
High Fees: FBA comes with a range of fees, including storage fees for keeping products in Amazon’s warehouses and fulfillment fees for each order processed. These costs can add up quickly, especially for sellers with low-margin products.
-
Strict Inventory Rules: Amazon has stringent inventory management policies that sellers must adhere to. This includes rules about inventory levels, storage limits, and the condition of items. Failure to comply can result in penalties or account suspension.
-
Commingling Risks: When multiple sellers use FBA for the same product, Amazon may commingle their inventory. This means that a seller’s product could be shipped to a customer from another seller’s stock, which can lead to issues with product quality and brand control.
-
Loss of Control: By using FBA, sellers cede a degree of control over their customer service and fulfillment processes. This can be a concern for brands that prioritize a unique customer experience or branding.
-
Potential for Inventory Stranding: If products do not sell, sellers risk incurring long-term storage fees. Amazon can also remove items from their fulfillment centers if they do not sell within a certain time frame, leading to potential inventory losses.
Who is FBA Best For?
FBA is particularly well-suited for:
-
E-commerce Startups: New sellers can quickly scale their operations without needing a significant investment in logistics infrastructure.
-
High-Volume Sellers: Businesses that anticipate high sales volumes can benefit from the efficiency and speed of Amazon’s fulfillment network.
-
Brands Seeking Trust: Companies looking to enhance their brand reputation and customer trust can leverage the Amazon platform and its customer service.
-
Sellers with Diverse Product Lines: Those offering a wide range of products can utilize FBA to manage inventory and fulfillment across multiple categories.
-
Businesses Aiming for Multi-Channel Sales: Sellers who want to expand beyond Amazon can use FBA for fulfilling orders from their own websites or other marketplaces, streamlining their logistics.
In conclusion, while FBA offers numerous benefits, including access to Amazon’s vast customer base and logistics network, it is essential for sellers to weigh the pros and cons carefully. Understanding the costs, risks, and operational implications will help businesses make an informed decision about whether FBA aligns with their long-term growth strategy.
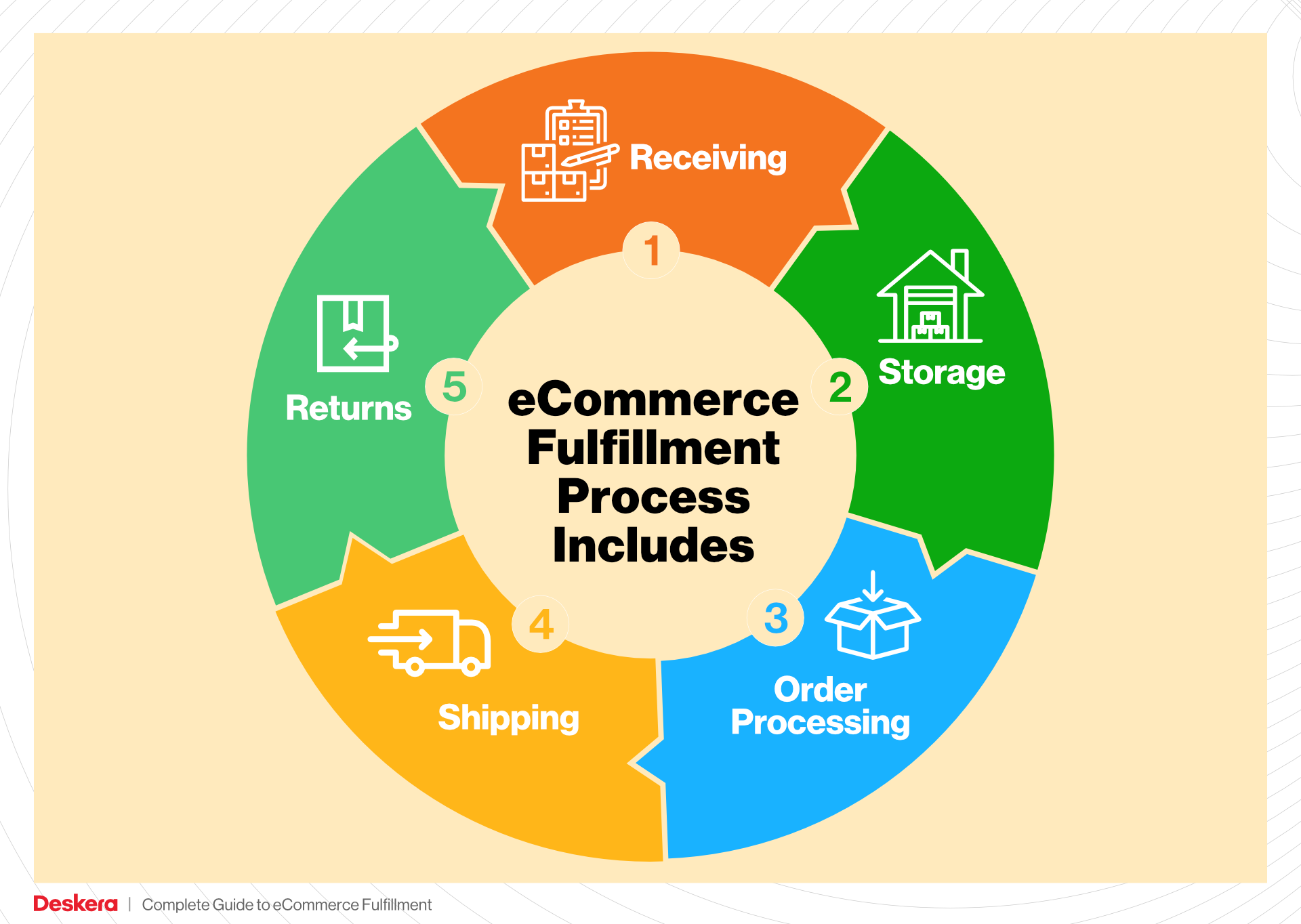
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Inventory management and warehousing form the backbone of any fulfillment operation. Fulfillment centers provide e-commerce businesses with dedicated space to store their products, ensuring that inventory is organized and readily accessible. This service encompasses various aspects, including inventory tracking, stock replenishment, and storage solutions tailored to the specific needs of the business.
Benefits:
-
Optimized Space Utilization: Fulfillment centers are designed to maximize storage efficiency, allowing businesses to store more products in less space. This is particularly advantageous for e-commerce businesses that may not have the capital or need for a large warehouse of their own.
-
Real-Time Inventory Tracking: Advanced inventory management systems employed by fulfillment centers enable real-time tracking of stock levels. This helps businesses avoid stockouts and overstock situations, ensuring that they can meet customer demand without tying up unnecessary capital in unsold inventory.
-
Scalability: As an e-commerce business grows, so do its inventory needs. Fulfillment centers offer scalable solutions that allow businesses to adjust their storage space and inventory management processes without the hassle of relocating or expanding their own facilities.
-
Reduction of Overhead Costs: By outsourcing warehousing and inventory management, businesses can significantly lower their overhead costs associated with renting or maintaining their own storage facilities. This allows them to allocate resources toward marketing, product development, or other growth initiatives.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services are essential for efficiently processing customer orders. This service involves selecting items from inventory, packing them securely for shipment, and preparing them for delivery. Fulfillment centers utilize specialized technology and trained personnel to streamline this process, ensuring accuracy and speed.
Benefits:
-
Increased Order Accuracy: Fulfillment centers employ advanced order management systems that minimize human error during the picking process. This leads to fewer mistakes, reducing the likelihood of returns and enhancing customer satisfaction.
-
Faster Order Processing: With dedicated teams and optimized workflows, fulfillment centers can process orders more quickly than many e-commerce businesses can manage in-house. This enables faster shipping times, a crucial factor in today’s competitive e-commerce landscape.
-
Custom Packaging Options: Many fulfillment centers offer customizable packaging solutions that allow businesses to maintain their brand identity. This includes branded boxes, inserts, and other packaging materials that enhance the unboxing experience for customers.
-
Improved Shipping Rates: Fulfillment centers often have partnerships with shipping carriers that allow them to negotiate better rates. This translates to lower shipping costs for e-commerce businesses, which can improve margins and potentially lead to increased sales through competitive pricing.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services are designed for e-commerce businesses that sell products requiring assembly or bundling. Fulfillment centers can pre-assemble products or create kits containing multiple items, which simplifies the order process for both the business and the customer.
Benefits:
-
Streamlined Operations: By outsourcing kitting and assembly, e-commerce businesses can streamline their operations. This allows them to focus on core activities such as marketing and customer service while leaving the complex assembly tasks to the fulfillment center.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience: Offering pre-assembled products or kits can enhance the customer experience by providing convenience. Customers appreciate receiving ready-to-use products, which can lead to higher satisfaction and repeat business.
-
Inventory Management Efficiency: Kitting can also optimize inventory management by consolidating multiple items into a single SKU. This simplifies stock tracking and can lead to more efficient order fulfillment processes.
-
Flexibility in Product Offerings: Kitting allows businesses to easily create promotional bundles or seasonal offerings without the need for significant changes in inventory. This flexibility can help businesses respond quickly to market demands and trends.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, often referred to as reverse logistics, is a critical service offered by fulfillment centers that deals with the process of handling returned products. Efficient returns management is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and optimizing inventory flow.
Benefits:
-
Simplified Returns Process: Fulfillment centers provide a streamlined process for handling returns, making it easier for customers to send back unwanted items. This includes providing return labels, processing returns quickly, and updating inventory in real time.
-
Cost-Effective Reverse Logistics: Managing returns in-house can be costly and time-consuming. Fulfillment centers leverage their expertise and infrastructure to handle returns more efficiently, reducing the overall costs associated with reverse logistics.
-
Data Insights: A fulfillment center’s returns management process often includes analytics that provide valuable insights into return reasons and patterns. This data can inform product development, marketing strategies, and inventory management, helping businesses reduce future returns.
-
Improved Customer Trust: A smooth returns process can significantly enhance customer trust and loyalty. When customers know they can return items easily, they are more likely to make purchases, leading to higher conversion rates and increased sales.
By utilizing these core services, e-commerce businesses can significantly improve their operational efficiency, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive growth in a competitive marketplace.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
The geographical location of your fulfillment partner’s warehouses is crucial for optimizing shipping times and costs. A partner with strategically placed warehouses can significantly reduce transit times and shipping expenses, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Questions to Ask:
– Where are your warehouses located, and how do these locations benefit my shipping strategy?
– How do you manage shipping logistics in terms of regional distribution?
– Can you provide insights on how your network could scale with my business growth?
Technology & Integrations
In today’s digital landscape, a fulfillment partner’s technology stack can make or break your operations. Efficient order management systems, inventory tracking, and seamless integrations with your e-commerce platform are vital for real-time visibility and operational efficiency.
Questions to Ask:
– What technology do you use for order management and inventory tracking?
– How easily can your systems integrate with my existing e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce)?
– Do you offer real-time tracking for both inventory and orders, and how is this information communicated to me and my customers?
Specializations (e.g., Cold Storage, Oversized Items)
Depending on your product line, you may need a fulfillment partner that specializes in certain types of storage or handling. For instance, if you sell perishable goods, a partner with cold storage capabilities is essential. Similarly, if you deal with oversized items, ensure your partner has the infrastructure to manage such logistics.
Questions to Ask:
– Do you have specialized facilities for my product type (e.g., cold storage, hazardous materials, oversized items)?
– What processes do you have in place for handling these specialized products?
– Can you accommodate seasonal fluctuations in inventory for specialized items?
Scalability & Capacity
As your business grows, your fulfillment partner must be able to scale operations accordingly. This includes not only handling increased volume but also adapting to changes in your product range or market demands. A partner with a flexible approach can save you from the headaches of switching providers down the line.
Questions to Ask:
– How do you handle seasonal spikes in order volume?
– What is your capacity for scaling operations in response to my business growth?
– Can you provide examples of how you’ve successfully scaled with other clients?
Pricing and Contracts
Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms is essential to avoid unexpected costs that could erode your margins. Be clear about what is included in the pricing, such as storage fees, pick and pack fees, and shipping costs.
Questions to Ask:
– Can you provide a detailed breakdown of your pricing model, including any hidden fees?
– What are the terms of the contract, and are there penalties for early termination?
– Do you offer any flexible pricing options based on order volume or frequency?
Customer Support & Reviews
Reliable customer support is a non-negotiable aspect of any partnership. The level of support you receive can impact your operational efficiency and, ultimately, customer satisfaction. Additionally, researching reviews and testimonials can provide insights into the partner’s reliability and service quality.
Questions to Ask:
– What customer support channels do you offer (e.g., phone, email, chat)?
– How quickly can I expect a response to inquiries or issues that arise?
– Can you provide references or case studies from current clients that reflect your service quality?
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is a critical step in scaling your e-commerce operations. By using this checklist, you can make informed decisions that align with your business goals and enhance your logistics capabilities. Remember to prioritize partners that demonstrate flexibility, transparency, and a strong track record in customer service. Your fulfillment partner should not just be a vendor; they should be a strategic ally in your growth journey.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
When partnering with a fulfillment service, businesses often encounter initial setup fees. These fees cover the costs associated with establishing your account and configuring your services. The setup process may involve creating and customizing your online portal, integrating your e-commerce platform with the fulfillment provider’s system, and potentially conducting training sessions for your team.
The calculation of initial setup fees varies widely among fulfillment providers. Some may charge a flat fee, while others might base it on the complexity of your requirements or the volume of products you plan to sell. It’s crucial to clarify what is included in these fees, as additional charges for integrations or customizations can arise.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged when your products arrive at the fulfillment center. This fee typically covers the labor and resources needed to unload, inspect, and log your inventory into the system. The receiving process may also include quality checks to ensure that the items meet the required standards.
Most fulfillment centers calculate receiving fees based on the volume of inventory being received, often charged per pallet or per unit. For instance, if you send a shipment of 100 units, you might incur a fee calculated per unit received. It’s important to check with your provider about any potential minimum fees that may apply, especially for smaller shipments.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are incurred for the space your inventory occupies within the fulfillment center. These fees can be calculated in various ways, commonly based on the number of pallets or bins your products fill, and are typically charged on a monthly basis.
For example, a fulfillment center might charge a monthly fee per pallet, with different rates depending on the time of year. Some providers may have higher fees during peak seasons, such as the holiday period, to account for increased demand and limited space. Understanding the storage fee structure is essential for budgeting, especially for businesses with fluctuating inventory levels.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are associated with the process of selecting items from the warehouse and preparing them for shipment. This fee is generally charged per item or per order, depending on how the fulfillment center structures their pricing.
The calculation of pick and pack fees may vary based on the complexity of the order. For instance, orders with multiple items may incur higher fees due to the additional labor involved in picking each item and packing them together. Some fulfillment centers offer tiered pricing, where the cost per item decreases as order volume increases, incentivizing businesses to scale their operations.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are one of the most significant costs associated with fulfillment. These fees cover the actual transportation of goods from the fulfillment center to the customer. Shipping costs can vary greatly based on factors such as package weight, dimensions, destination, and the chosen shipping carrier.
Most fulfillment providers offer a range of shipping options, from standard to expedited, each with different pricing structures. Some may offer discounted rates through partnerships with carriers, which can help reduce overall shipping costs. It’s vital to understand how your fulfillment partner calculates shipping fees and whether they provide any tools to estimate costs based on your typical order profiles.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
To obtain a precise quote from a fulfillment provider, consider the following tips:
-
Provide Detailed Information: Clearly communicate your product dimensions, weights, and expected order volumes. This information helps providers give more accurate estimates for storage, shipping, and other fees.
-
Ask About Hidden Fees: Inquire about any additional charges that may apply, such as those for returns, packaging, or special handling. Understanding the full scope of fees upfront can prevent budget overruns.
-
Compare Multiple Providers: Don’t settle for the first quote you receive. Compare pricing structures and services from several fulfillment partners to identify the best fit for your business needs.
-
Request a Breakdown of Costs: Ask for a detailed breakdown of all fees associated with your account. This transparency helps you understand how different charges are calculated and allows for more informed budgeting.
-
Review Seasonal Pricing Changes: Be aware that some providers may adjust their pricing during peak seasons. Discuss any potential changes in costs throughout the year to ensure your budget remains accurate.
By understanding these common fees and following these tips, e-commerce businesses can effectively navigate fulfillment pricing and make informed decisions that support their growth and scalability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM)?
Fulfillment by Merchant (FBM) is a method where the seller is responsible for storing, packing, and shipping their products directly to customers. Unlike Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), where Amazon handles these tasks, FBM allows sellers to retain control over their inventory and fulfillment process.
2. How does FBM differ from Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)?
FBM differs from FBA primarily in who handles the fulfillment process. With FBM, the seller manages inventory, shipping, and customer service, while FBA involves Amazon’s warehouses and logistics. FBM sellers can also avoid some of the fees associated with FBA but sacrifice the benefits of the Prime badge and Amazon’s logistical expertise.
3. What are the advantages of using FBM?
FBM offers several advantages, including:
– Cost Efficiency: Lower fees compared to FBA.
– Control: Greater control over branding and customer interactions.
– Flexibility: Ability to handle unique shipping needs or large items better.
– Less Strict Requirements: Fewer restrictions and requirements from Amazon compared to FBA.
4. What are the drawbacks of FBM?
Some drawbacks of FBM include:
– Time-Intensive: Managing fulfillment can take significant time, especially for small businesses.
– No Prime Badge: FBM products do not qualify for Amazon Prime, which may limit visibility and sales.
– Learning Curve: Sellers must learn the intricacies of order fulfillment and customer service.
5. How much do fulfillment services cost?
Fulfillment service costs can vary widely based on factors like order volume, storage space, and shipping methods. Generally, you can expect to pay for:
– Monthly storage fees for inventory.
– Per-order fulfillment fees for picking, packing, and shipping.
– Shipping costs, which can vary based on carrier and delivery speed. It’s advisable to compare multiple providers to find the best fit for your budget.
6. What is a 3PL and how does it relate to FBM?
A 3PL, or third-party logistics provider, is a company that offers logistics services, including warehousing, fulfillment, and shipping. Many FBM sellers partner with 3PLs to outsource the fulfillment process, allowing them to focus on other aspects of their business while leveraging the expertise and resources of the 3PL.
7. What’s the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse is primarily a storage space where goods are kept until needed, while a fulfillment center is designed for the complete process of receiving, storing, picking, packing, and shipping products directly to customers. Fulfillment centers are optimized for quick order processing and shipping.
8. How do I set up FBM on Amazon?
To set up FBM on Amazon:
1. Create an account on Amazon Seller Central.
2. List your products, ensuring to provide detailed descriptions and images.
3. Set up your shipping options and handling times.
4. Manage your inventory and fulfillment process, either through self-fulfillment or by partnering with a 3PL.
9. Can I use FBM for international shipping?
Yes, FBM can be used for international shipping. However, sellers should be aware of the additional complexities, such as customs regulations and international shipping costs. It is crucial to clearly communicate shipping options and delivery times to customers to manage expectations.
10. What customer service responsibilities do FBM sellers have?
FBM sellers are responsible for all aspects of customer service, including handling inquiries, processing returns, and managing feedback. Providing prompt and helpful customer service is vital for maintaining a positive seller rating and ensuring customer satisfaction.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Evaluating the Benefits of Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a transformative decision for e-commerce businesses looking to scale efficiently. The key benefits of utilizing a fulfillment service are multi-faceted, primarily centered around saving time, enhancing scalability, and leveraging specialized expertise.
By delegating the logistics and order fulfillment process to a third-party provider, business owners can reclaim valuable time that can be redirected towards strategic initiatives, such as marketing and product development. This time-saving aspect is crucial in today’s fast-paced e-commerce landscape, where operational efficiency can significantly impact overall profitability.
Scalability is another compelling reason to consider outsourcing fulfillment. As your business grows, so too does the complexity of managing inventory, shipping logistics, and customer service. A professional fulfillment partner can effortlessly scale operations to meet demand fluctuations, ensuring that you can focus on expanding your market reach rather than getting bogged down in logistical challenges.
Moreover, partnering with an experienced fulfillment provider brings specialized knowledge and resources that many e-commerce businesses may lack in-house. From understanding the nuances of shipping regulations to optimizing packaging for cost-effectiveness and branding, a capable partner can enhance your customer experience and operational efficiency.
However, it is vital to choose the right fulfillment partner. Your chosen provider should align with your business goals and understand your unique needs. A thorough audit of your current shipping processes can provide clarity on whether a fulfillment partner is the right next step for your business.
Take Action Now
Consider assessing your current fulfillment strategy. Ask yourself if your operations are scalable, if you have the expertise needed to navigate complex logistics, and whether your time is being utilized effectively. By conducting this audit, you can determine if outsourcing fulfillment is the strategic move that will propel your business growth forward.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.