How Order Fulfillment Works: A Step-by-Step Guide for Businesses
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Understanding E-commerce Fulfillment: A Key to Business Growth
As an e-commerce business owner or operations manager, you may find yourself grappling with the logistics of packing and shipping orders. The excitement of increasing sales can quickly turn into a daunting challenge when you realize that fulfilling orders efficiently is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and driving repeat business. The fulfillment process—essentially, the journey of getting a product from your inventory to your customer’s doorstep—can become overwhelming if not managed effectively.
E-commerce fulfillment encompasses a series of steps that include warehousing, inventory management, order processing, packing, and shipping. For growing businesses, choosing the right fulfillment model can make all the difference. Whether it’s in-house fulfillment, partnering with a third-party logistics provider (3PL), or utilizing services like Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), each option has its unique benefits and challenges. Understanding these models is essential for scaling your operations without sacrificing service quality.
In this guide, we will delve into the various fulfillment models available to e-commerce businesses. You’ll learn about core services that these models typically offer, such as inventory storage, order processing, and shipping logistics. We’ll also discuss how to evaluate and choose the right fulfillment partner for your specific needs, taking into account factors like geographic reach, technology integration, and customer service capabilities.
Additionally, we will cover the important aspect of pricing. Understanding the costs associated with different fulfillment options is crucial for budgeting and ensuring that your operations remain profitable as you scale.
The ultimate goal of this guide is to empower you with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about your logistics strategy. By understanding e-commerce fulfillment in-depth, you will be better equipped to streamline your operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and support sustainable growth for your business. Whether you’re just starting or looking to optimize your existing processes, this guide serves as a comprehensive resource to help you navigate the complexities of e-commerce fulfillment effectively.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
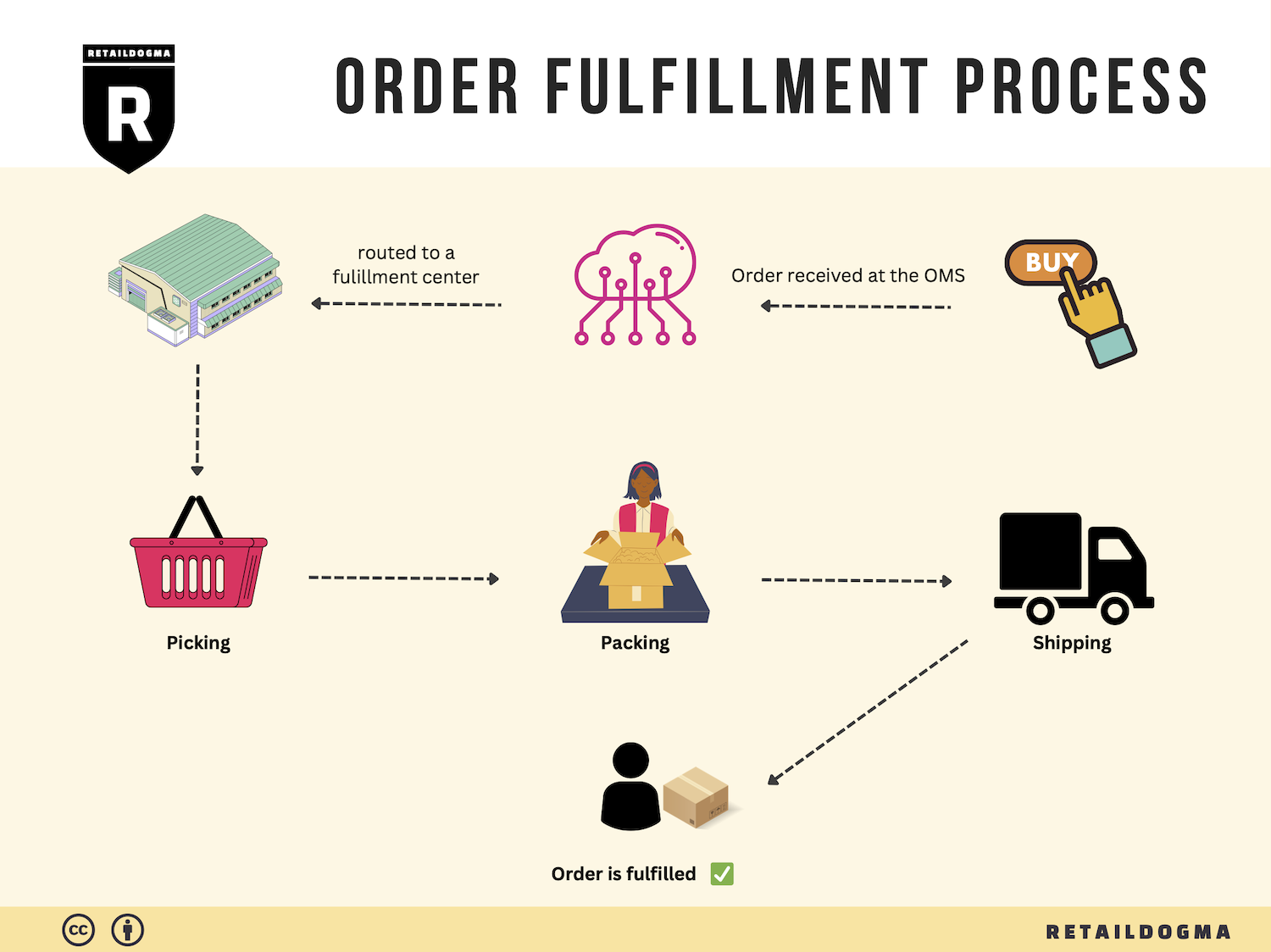
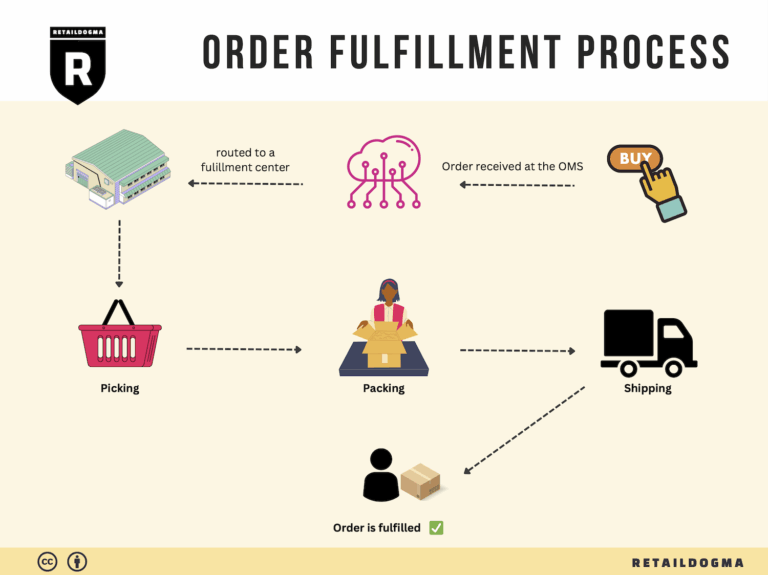
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
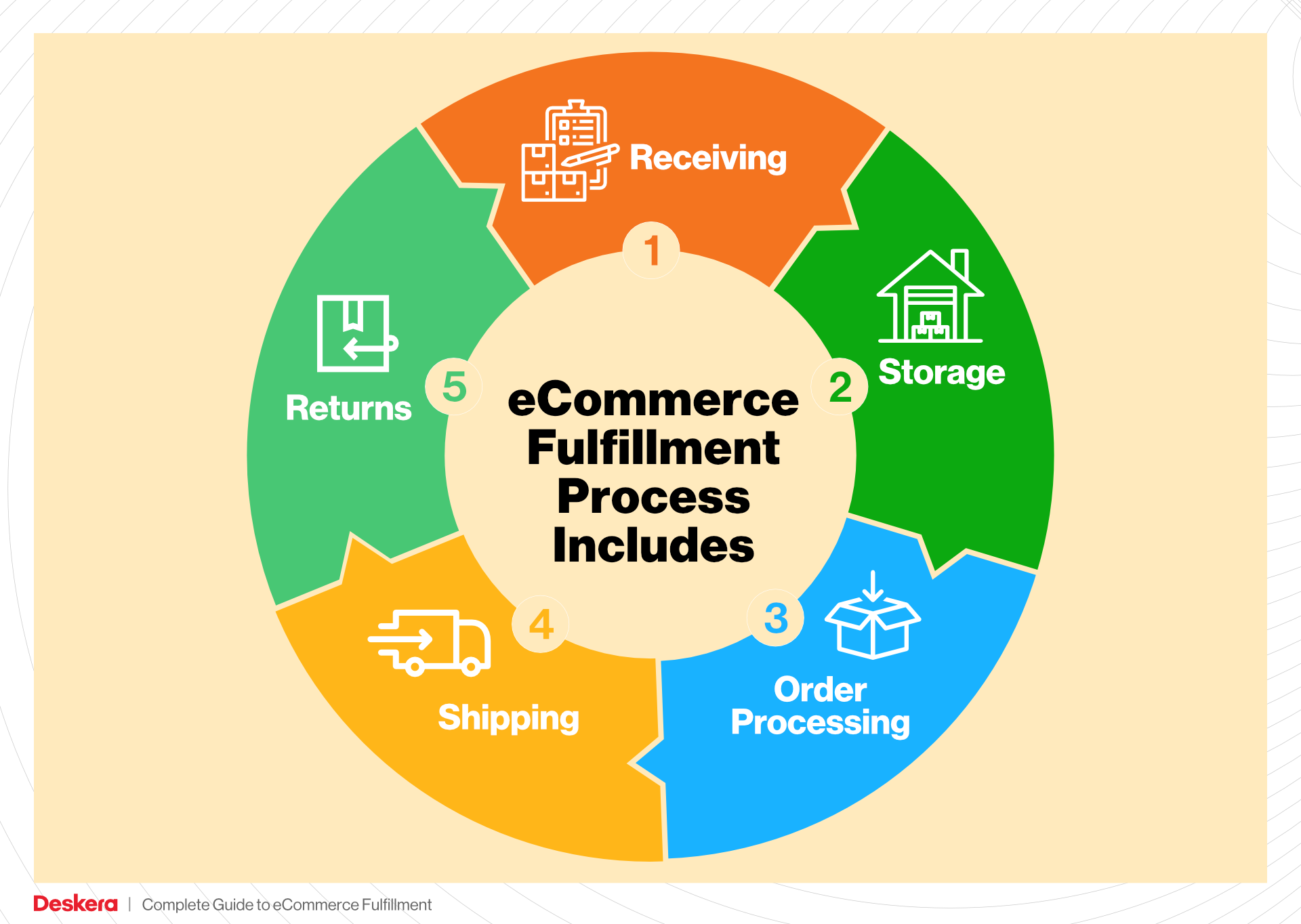
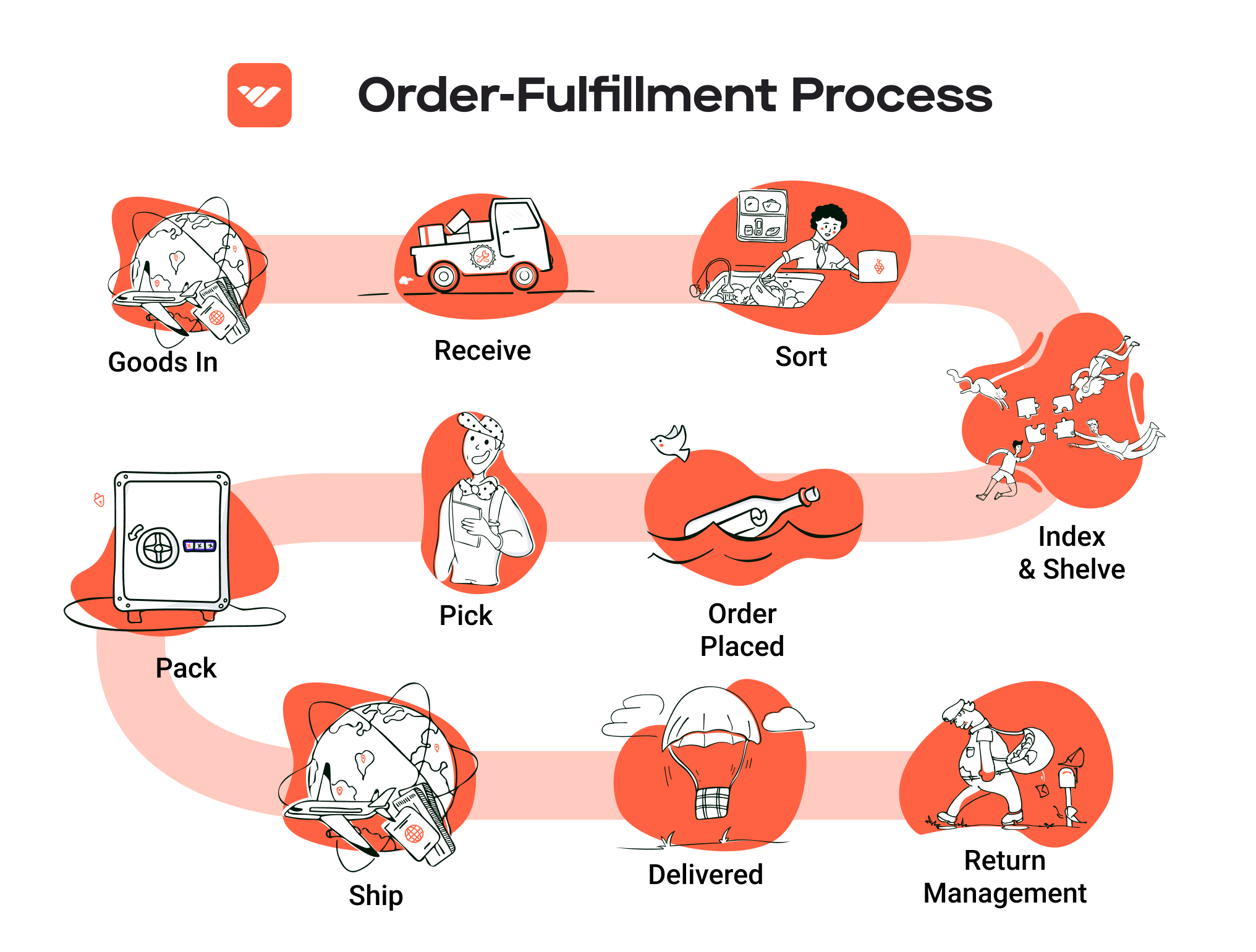
1. Receiving Inventory
The order fulfillment process begins with receiving inventory at the fulfillment center. This step involves the acceptance of goods from suppliers or manufacturers, which are then verified against purchase orders. Key tasks include checking the quantity and quality of the received items, ensuring they meet the necessary standards, and documenting any discrepancies.
Importance: This step is crucial because accurate inventory management starts here. If items are not received correctly, it can lead to stock shortages or excess inventory, both of which can disrupt the supply chain and affect customer satisfaction.
Key Term: SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) – A unique identifier assigned to each product, which helps in tracking inventory levels and sales.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once inventory has been received and verified, it is stored in the warehouse. Proper storage techniques are essential for maximizing space and ensuring that products are easily accessible for future orders. Items are typically organized based on their SKU, size, and demand frequency, often using a system of shelving, bins, or pallets.
Importance: Efficient warehouse storage minimizes the time needed for order picking and reduces the risk of damage to products. A well-organized warehouse also facilitates easier inventory audits and replenishment processes.
Key Term: Bin Location – A designated spot within the warehouse where a specific product is stored, helping to streamline the picking process.
3. Order Picking
When a customer places an order, the next step is order picking, where items are selected from their storage locations. This process can be manual, using pick lists generated by the order management system, or automated through technologies like pick-to-light systems or robotics.
Importance: Order picking is a critical step that directly impacts order accuracy and fulfillment speed. Errors in this stage can lead to incorrect shipments, resulting in returns and dissatisfied customers.
Key Term: Pick List – A document or digital interface that details which items to retrieve for an order, including their quantities and storage locations.
4. Order Packing
After items have been picked, they move to the packing stage. Here, products are carefully packaged to ensure they arrive safely at the customer’s door. This includes selecting appropriate packaging materials, adding packing slips, and sometimes including promotional materials or return labels.
Importance: Proper packing is vital for minimizing damage during transit and enhancing the customer experience. A well-packed order not only protects the items but also reflects positively on the brand.
Key Term: Packing Slip – A document included in the package that lists the items contained in the shipment, serving as a receipt for the customer.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once packed, orders are labeled and dispatched to shipping carriers for delivery to the customer. Companies often have partnerships with various carriers to optimize shipping costs and delivery times.
Importance: This step is the culmination of the entire fulfillment process, directly affecting customer satisfaction. Timely delivery and accurate tracking information can significantly enhance customer loyalty and repeat business.
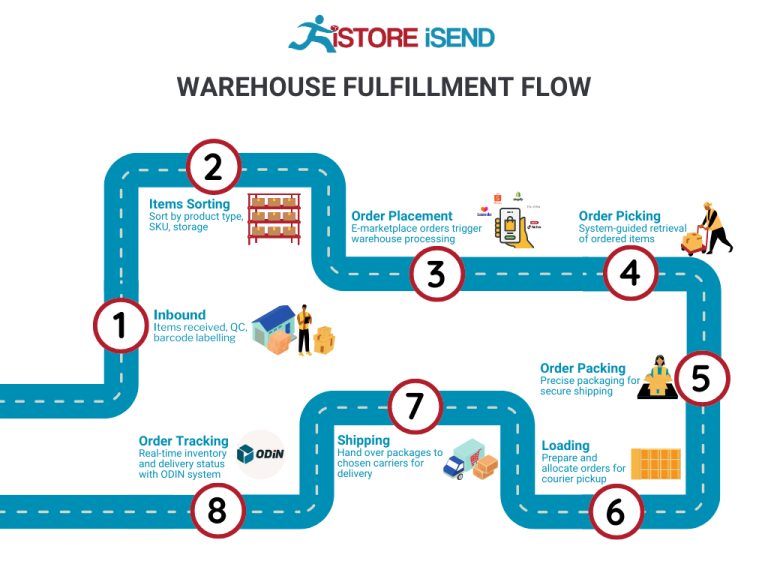
Key Term: Shipping Label – A label attached to the package that contains the recipient’s address, shipping method, and tracking information, facilitating the delivery process.
In summary, each step of the order fulfillment process is interconnected and plays a pivotal role in ensuring customer satisfaction and operational efficiency. By understanding and optimizing these steps, e-commerce businesses can enhance their logistics and scale their operations effectively.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Comparison of Fulfillment Models
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | Business itself | Established businesses | Full control over inventory and processes | High overhead costs and resource-intensive |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | External logistics provider | Growing and scaling businesses | Scalability and reduced operational burden | Less control over inventory and potential service variability |
| Dropshipping | Supplier | Startups and small businesses | Low startup costs and no inventory risk | Lower profit margins and reliance on suppliers’ reliability |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment refers to the model where a business manages its own inventory and fulfillment processes directly. This model is typically best suited for established companies with sufficient resources and a stable order volume. One of the primary advantages of in-house fulfillment is the complete control it offers over inventory management, order processing, and customer service. Businesses can tailor their fulfillment operations to meet specific customer needs and maintain a consistent brand experience. Additionally, having direct oversight can lead to quicker response times and enhanced quality control. However, this model comes with significant disadvantages, such as high overhead costs associated with warehousing, staffing, and equipment, which can burden smaller companies or those still in their growth phase. Moreover, the resource-intensive nature of in-house fulfillment may limit a company’s ability to scale quickly or adapt to changing market conditions.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) involves outsourcing logistics and fulfillment services to specialized providers. This model is particularly advantageous for growing businesses that want to focus on core competencies while leveraging the expertise and infrastructure of a 3PL partner. The key advantage of using a 3PL is scalability; businesses can easily adjust their logistics capabilities in response to fluctuating order volumes without the burden of managing additional warehouse space or hiring more staff. Additionally, 3PL providers often bring advanced technology and logistics expertise, which can enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. However, the reliance on an external partner does come with some downsides. Businesses may experience less control over inventory management and fulfillment processes, which can lead to inconsistencies in service quality. Additionally, the success of this model heavily depends on the chosen 3PL’s reliability and performance, making it crucial to select a partner that aligns with the business’s values and operational goals.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment method where the retailer does not keep goods in stock but instead transfers customer orders directly to a supplier, who then ships the products directly to the customer. This model is ideal for startups and small businesses looking to minimize upfront costs and reduce inventory risk. One of the primary advantages of dropshipping is the low barrier to entry; entrepreneurs can launch an e-commerce business without the need to invest in inventory or warehousing. This flexibility allows businesses to test new products and markets with minimal financial commitment. However, dropshipping comes with significant drawbacks, including lower profit margins due to the reliance on suppliers for fulfillment and shipping. Additionally, businesses face challenges related to inventory management and product quality, as they depend on third parties for these critical aspects of the customer experience. Furthermore, if a supplier fails to deliver on time or provides subpar products, it can directly impact the retailer’s reputation and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment model is a crucial decision for e-commerce businesses as they scale. Each model—In-House Fulfillment, Third-Party Logistics (3PL), and Dropshipping—has its unique advantages and disadvantages, depending on the business stage, resources, and operational goals. In-house fulfillment offers control but at a high cost, while 3PL provides scalability and expertise but may come with less control. Dropshipping allows for low startup costs but can lead to lower profit margins and dependency on suppliers. Understanding these models can help business owners make informed decisions that align with their strategic objectives and operational capabilities.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service offered by Amazon that allows sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon then takes care of storage, packaging, and shipping of these products to customers. This service also includes customer service and returns handling, enabling sellers to focus on other aspects of their business while leveraging Amazon’s extensive logistics network.
How FBA Works
-
Setting Up Your Account: Sellers need to create an Amazon Seller account and enroll in FBA. They can then list their products as FBA items.
-
Shipping Inventory to Amazon: Sellers prepare their products according to Amazon’s guidelines and ship them to designated Amazon fulfillment centers.
-
Storage: Once Amazon receives the inventory, it is stored in their warehouses. Sellers can track their inventory levels through the Seller Central dashboard.
-
Order Processing: When a customer places an order for an FBA product, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the product directly to the customer.
-
Customer Service and Returns: Amazon handles all customer inquiries and manages returns, which can simplify the post-sale process for sellers.
This entire process allows sellers to benefit from Amazon’s infrastructure, including their shipping capabilities and customer service, while also making their products eligible for Amazon Prime, thus enhancing their visibility and appeal to customers.
Pros of Using FBA
-
Prime Eligibility: Products fulfilled by Amazon are eligible for Prime membership, giving sellers access to millions of Prime customers who prefer the fast shipping options that come with their membership.
-
Customer Trust: Amazon’s reputation for reliability and customer service instills confidence in buyers. Products sold via FBA benefit from Amazon’s established trust, which can lead to increased sales and customer loyalty.
-
Multi-Channel Fulfillment: FBA is not limited to just Amazon sales. Sellers can use FBA to fulfill orders from other channels, such as their own websites or other e-commerce platforms. This flexibility can streamline logistics and improve overall efficiency.
-
Scalability: FBA allows sellers to scale their businesses without having to invest heavily in logistics and warehousing. As sales grow, sellers can easily send more inventory to Amazon without worrying about the complexities of fulfillment.
-
Time Savings: By outsourcing logistics to Amazon, sellers can free up time to focus on product development, marketing, and other critical business functions, enhancing their overall operational efficiency.
Cons of Using FBA
-
High Fees: FBA fees can add up quickly, including storage fees for keeping inventory in Amazon’s warehouses and fulfillment fees based on the size and weight of the products. These costs can significantly impact profit margins, especially for low-cost items.
-
Strict Inventory Rules: Amazon has stringent inventory management policies. Sellers need to maintain a certain level of stock and adhere to Amazon’s packaging and labeling standards. Non-compliance can result in penalties or inventory being returned.
-
Commingling Risks: FBA products may be commingled with other sellers’ inventory, which means that a seller’s product may be shipped to a customer from another seller’s stock. This can lead to issues with product quality and customer satisfaction if the other seller’s items do not meet the expected standards.
-
Limited Control Over Fulfillment: Once products are in Amazon’s hands, sellers have limited control over how their products are packaged and shipped. This can affect branding and customer experience, as the packaging may not align with the seller’s brand image.
-
Dependency on Amazon: Relying on Amazon for fulfillment can create vulnerabilities. Changes in Amazon’s policies, fees, or algorithms can directly impact sellers’ businesses, making it crucial for sellers to stay informed and adaptable.
Who is FBA Best For?
Fulfillment by Amazon is particularly advantageous for:
-
Small to Medium-Sized Businesses: These businesses may not have the resources to manage their own warehousing and logistics. FBA allows them to leverage Amazon’s infrastructure without significant upfront investment.
-
E-commerce Entrepreneurs: Sellers who want to quickly scale their operations and reach a large audience can benefit from FBA, especially those focused on growth and market penetration.
-
Retail Arbitrage and Private Label Sellers: Those sourcing products from various suppliers or creating their own branded products can utilize FBA to simplify logistics and reach Amazon’s vast customer base.
-
Sellers with Seasonal Products: Businesses that experience seasonal spikes in demand can use FBA to manage fluctuations in inventory efficiently, ensuring that products are available during peak shopping times.
-
Multi-Channel Sellers: For those selling across multiple platforms, FBA provides a streamlined solution to fulfill orders from various sources, reducing the complexities of logistics management.
In conclusion, while Fulfillment by Amazon offers numerous advantages that can facilitate business growth and streamline operations, it is essential for sellers to weigh these benefits against the associated costs and risks. Understanding the intricacies of FBA can help e-commerce businesses make informed decisions about whether this fulfillment method aligns with their operational goals and customer service standards.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Inventory management is a fundamental service provided by fulfillment centers that enables e-commerce businesses to maintain optimal stock levels while minimizing costs. Fulfillment centers utilize sophisticated inventory management systems that track inventory levels in real-time, allowing businesses to have a clear view of their stock availability. This includes monitoring product quantities, managing reorder points, and forecasting demand based on historical data and trends.
The benefits of effective inventory management are manifold. First, it reduces the risk of stockouts, ensuring that products are available when customers make purchases, which is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty. Second, it minimizes excess inventory, which can tie up capital and lead to increased storage costs. By leveraging the expertise of fulfillment centers, e-commerce businesses can streamline their inventory processes, reduce operational complexities, and focus on strategic growth initiatives rather than day-to-day management of stock levels.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services are at the heart of the fulfillment process. This service involves the selection of ordered items from the warehouse (picking) and then packing them securely for shipment (packing). Fulfillment centers employ trained staff and automated systems to efficiently pick items, ensuring accuracy and speed. They also utilize packaging materials that protect products during transit while optimizing shipping costs.
The primary benefit of pick and pack services for e-commerce businesses is the increased efficiency in order fulfillment. By outsourcing this process to a fulfillment center, businesses can significantly reduce the time it takes to process orders, which is vital in today’s fast-paced e-commerce environment. Quick and accurate order fulfillment enhances customer satisfaction and can lead to repeat business. Additionally, fulfillment centers often have established relationships with shipping carriers, enabling businesses to take advantage of better shipping rates and faster delivery options, further improving the customer experience.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services involve the grouping of various products into a single package or kit, which may also require assembly before shipment. This service is particularly beneficial for businesses that sell bundled products or complex items that require pre-assembly, such as pet supplies that come with accessories or multi-part products. Fulfillment centers have the capabilities to assemble these kits according to specific requirements, ensuring that everything is included and correctly configured.
The benefits of kitting and assembly services are substantial. First, they allow e-commerce businesses to offer unique product bundles that can enhance sales and differentiate their offerings in a competitive market. By providing customers with ready-to-use kits, businesses can improve the perceived value of their products. Second, these services save time and labor costs for businesses, as they do not need to handle the assembly process in-house. This allows them to focus on core business activities such as marketing and customer service while ensuring that their products are shipped correctly and efficiently.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, is a critical service offered by fulfillment centers that deals with the processing of returned items. This service includes receiving returned products, inspecting them for quality, restocking them if applicable, and managing the disposition of unsellable items. Efficient returns management is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand loyalty, as a hassle-free return process can enhance the overall shopping experience.
The primary advantage of effective returns management for e-commerce businesses is the ability to streamline the return process, reducing the time and resources spent on handling returns. Fulfillment centers employ systematic processes to manage returns, ensuring that items are quickly processed and either restocked or disposed of properly. This not only helps recover potential lost revenue but also provides valuable insights into customer behavior and product quality, informing future business decisions. A well-managed returns process can also enhance customer trust, as customers are more likely to make purchases when they know they can return items easily if needed.
In conclusion, leveraging the core services offered by fulfillment centers can significantly enhance the operational efficiency of e-commerce businesses. From inventory management and pick and pack services to kitting and assembly, and returns management, each service plays a vital role in enabling businesses to scale their operations, reduce costs, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction. By partnering with a fulfillment center, e-commerce entrepreneurs can focus on strategic growth while leaving the complexities of logistics to the experts.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
Importance:
The location of your fulfillment partner’s warehouses plays a crucial role in your logistics efficiency. A strategically placed warehouse network can reduce shipping times and costs, significantly impacting customer satisfaction.
Questions to Ask:
– Where are your fulfillment centers located, and how does that impact shipping times to my target markets?
– What is the average shipping time from your warehouses to my customers?
– Do you have plans for expanding your warehouse network in the future?
Technology & Integrations
Importance:
Technology is the backbone of modern fulfillment operations. A partner with robust technology can streamline your order processing, inventory management, and tracking, providing a seamless experience for you and your customers.
Questions to Ask:
– What fulfillment software do you use, and how does it integrate with my existing systems (e.g., e-commerce platforms, ERPs)?
– Can you provide real-time inventory tracking and reporting?
– How often do you update your technology and what innovations are you implementing to enhance operations?
Specializations (e.g., cold storage, oversized items)
Importance:
Different products require different handling and storage solutions. If your business has unique needs—such as perishable items requiring cold storage or bulky items that need special handling—it’s vital to choose a partner that specializes in those areas.
Questions to Ask:
– Do you have experience handling my specific product types, such as perishables or oversized items?
– What special equipment or facilities do you have to accommodate these needs?
– How do you ensure compliance with safety and regulatory standards for specialized items?
Scalability & Capacity
Importance:
As your business grows, your fulfillment needs will change. A partner that can scale with you—whether it’s handling seasonal spikes or expanding your product range—is essential for long-term success.
Questions to Ask:
– How do you handle peak seasons and unexpected surges in order volume?
– What is your capacity for handling increased order volume, and how quickly can you scale?
– Are there any limitations on storage space or order processing capabilities that I should be aware of?
Pricing and Contracts
Importance:
Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms is essential to avoid unexpected costs and ensure that the partnership aligns with your budget. Transparent pricing can help you manage your financial forecasts effectively.
Questions to Ask:
– What is your pricing model (e.g., per order, per item, storage fees), and are there any hidden costs?
– How do you handle pricing adjustments during contract renewals?
– Can you provide a sample contract for review, and what is your policy on contract termination?
Customer Support & Reviews
Importance:
Reliable customer support can make or break your fulfillment experience. A partner that prioritizes customer service will help resolve issues quickly, maintaining smooth operations and protecting your brand reputation.
Questions to Ask:
– What customer support channels do you offer (e.g., phone, email, chat), and what are your response times?
– Can you provide references or case studies from current clients, particularly those in my industry?
– How do you handle operational issues or delays, and what is your protocol for communicating with clients during disruptions?
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is a critical decision that can significantly influence your e-commerce success. By following this checklist and asking the right questions, you can evaluate potential partners effectively, ensuring they align with your business needs and growth goals. Remember, a well-chosen fulfillment partner not only manages your logistics but also enhances your customer experience, allowing you to focus on scaling your business.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
Initial setup fees are typically charged by fulfillment centers to establish your account and get your products ready for storage and shipping. This may include costs associated with onboarding, integration with your e-commerce platform, and initial inventory setup.
The calculation of initial setup fees can vary widely based on the complexity of your operations and the fulfillment center’s pricing model. For instance, if you’re using an advanced inventory management system that requires integration, expect higher fees. It’s important to ask for a detailed breakdown of what these fees cover to avoid surprises.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged when your inventory arrives at the fulfillment center. This fee covers the labor and equipment needed to unload, inspect, and put away your products.
These fees are usually calculated on a per-pallet or per-box basis. For example, if you send a truckload of goods that includes 20 pallets, and the receiving fee is $10 per pallet, your total receiving fee would be $200. It’s crucial to understand how the fulfillment center defines a pallet or box and whether there are any additional charges for oversized or special items.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are ongoing charges for keeping your products in the fulfillment center. These fees are generally calculated based on the volume of space your inventory occupies, often expressed as a fee per pallet or bin, and can be assessed monthly.
For example, if a fulfillment center charges $25 per pallet per month and your inventory takes up 10 pallets, your monthly storage fee would be $250. Some centers may offer tiered pricing where the rate decreases with higher volumes, so it’s beneficial to discuss your expected inventory levels to negotiate the best rate.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are incurred for each order processed by the fulfillment center. This fee encompasses the labor involved in picking items from storage, packing them into boxes, and preparing them for shipment.
Typically, these fees are calculated on a per-item or per-order basis. For instance, if the fee is $1.50 per item and an order includes three items, the total pick and pack fee would be $4.50. Some fulfillment centers may offer a flat fee per order, regardless of the number of items, which can be more economical for larger orders. Understanding the pricing structure is crucial, especially if your business model involves frequent small orders.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are the costs associated with sending your orders to customers. These fees can vary based on the shipping method (standard, expedited, etc.), the destination, and the weight and dimensions of the package.
Shipping fees are typically calculated through carrier rates, which may include additional surcharges for residential delivery or remote locations. Fulfillment centers often have agreements with carriers that can provide discounted rates, so it’s wise to inquire about these options. Make sure to clarify whether the fulfillment center charges a handling fee on top of the carrier rate, as this can significantly impact your overall shipping costs.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
-
Request Detailed Pricing Breakdowns: Always ask for a detailed quote that specifies what each fee includes. This transparency will help you avoid unexpected charges.
-
Understand Pricing Models: Familiarize yourself with the different pricing models used by fulfillment centers. Some may charge per unit, while others may have flat rates or tiered pricing based on volume.
-
Discuss Your Business Needs: Be open about your business model, including expected order volumes and inventory levels. This information can help the fulfillment center provide a more accurate estimate and potentially offer discounts.
-
Negotiate Terms: Don’t hesitate to negotiate fees, especially if you anticipate high volumes or long-term partnerships. Many fulfillment centers are willing to adjust their pricing to secure reliable clients.
-
Review Contracts Carefully: Before signing any agreements, carefully review the terms and conditions regarding fees. Look for clauses related to fee increases or additional charges for services you may require.
By understanding these common fees and how they are calculated, you can make informed decisions that will optimize your fulfillment strategy and improve your bottom line.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is Chewy’s fulfillment center MDT1?
Chewy’s fulfillment center MDT1 is one of the key operational hubs designed to handle the storage, packing, and distribution of pet supplies and medications. Located strategically to optimize shipping times, MDT1 plays a crucial role in ensuring that orders are processed efficiently and delivered promptly to customers.
2. How does Chewy’s fulfillment process work?
The fulfillment process at Chewy typically involves several steps: receiving inventory, storing products in a systematic manner, picking items as orders come in, packing them securely, and finally shipping them to customers. This streamlined approach ensures that orders are fulfilled quickly, often within 1-2 days of being placed.
3. What are the hours of operation for the MDT1 fulfillment center?
Chewy’s MDT1 fulfillment center operates multiple shifts throughout the day to maximize productivity and meet customer demand. While specific hours may vary, the center generally runs 24/7 to ensure that orders can be processed and shipped at any time.
4. What is the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse is primarily a storage facility for goods, while a fulfillment center focuses on the complete process of order fulfillment, including inventory management, order processing, and shipping. Fulfillment centers are designed to handle e-commerce operations more efficiently, ensuring faster delivery times and better customer service.
5. What is a 3PL (Third-Party Logistics)?
A 3PL is a service provider that manages logistics and supply chain operations for businesses. This can include warehousing, fulfillment, transportation, and distribution services. Companies may partner with 3PLs to leverage their expertise and infrastructure, allowing them to focus on core business activities while optimizing logistics.
6. How much do fulfillment services cost?
The cost of fulfillment services can vary significantly based on factors such as order volume, storage requirements, and specific services provided (like packing and shipping). Generally, businesses can expect to pay fees related to storage, picking, packing, and shipping, which may be charged per order or based on monthly volume.
7. What kind of products can be stored and shipped from MDT1?
MDT1 is designed to handle a wide range of pet products, including dry and wet food, toys, grooming supplies, and medications. The fulfillment center is equipped to manage various product types, ensuring safe and efficient storage and handling.
8. How does Chewy ensure the safety of its fulfillment operations?
Chewy prioritizes a safety-first work environment by implementing rigorous safety protocols and training programs for all team members. The company regularly reviews and updates its safety measures to minimize risks and create a secure working environment for its employees.
9. Can businesses partner with Chewy’s fulfillment center for their own products?
While Chewy primarily focuses on its own product lines, businesses interested in partnering for fulfillment services should reach out directly to Chewy’s corporate team to explore potential collaboration opportunities. Chewy’s experience in e-commerce logistics can provide valuable insights for scaling operations.
10. How can I track my order once it has shipped from MDT1?
Once an order is shipped from Chewy’s MDT1 fulfillment center, customers receive a tracking number via email. This allows them to monitor the shipment’s progress in real-time, providing transparency and assurance regarding delivery timelines. Customers can also check their order status through Chewy’s website or mobile app.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Evaluating the Benefits of Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a transformative decision for e-commerce businesses seeking to scale efficiently. One of the primary benefits is time savings. By delegating logistics and order processing to a specialized fulfillment partner, you can focus on core business activities such as marketing, product development, and customer engagement. This shift not only enhances productivity but also allows you to respond more swiftly to market demands.
Scalability is another significant advantage. As your business grows, so do your fulfillment needs. A reliable partner can easily adapt to fluctuations in order volume, whether during peak seasons or promotional campaigns. This flexibility ensures that you can meet customer expectations without overextending your internal resources.
Additionally, partnering with a fulfillment service brings expertise in logistics management. These specialists are equipped with advanced technologies and best practices that can optimize inventory management, reduce shipping costs, and improve delivery times. This level of professionalism can enhance your overall customer experience, fostering loyalty and repeat business.
However, the success of outsourcing fulfillment hinges on selecting the right partner. Not all fulfillment services offer the same level of quality, reliability, and alignment with your business values. Conduct thorough research and evaluate potential partners based on their capabilities, technology, and customer service.
Take Action
If you’re considering whether outsourcing fulfillment is the right next step for your business, start by auditing your current shipping processes. Analyze your order fulfillment times, customer feedback, and operational bottlenecks. This assessment will provide clarity on whether a fulfillment partner could enhance your efficiency and support your growth objectives. Embrace the opportunity to streamline your operations and elevate your customer satisfaction—your future success may depend on it.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.