Ecommerce Fulfillment Services: The Ultimate Guide (2025)
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Understanding E-commerce Fulfillment
As an e-commerce business owner, you may have experienced the overwhelming challenge of managing order packing and shipping. This crucial aspect of your operations can quickly become a bottleneck, diverting your attention from scaling your business and delighting your customers. Fulfillment, in its simplest form, refers to the entire process of getting a product from your inventory to the customer’s doorstep. It encompasses everything from picking and packing to shipping and handling returns.
In today’s fast-paced e-commerce landscape, efficient fulfillment is not just a luxury but a necessity. With the rise of consumer expectations for quick delivery times and seamless service, understanding and optimizing your fulfillment strategy is essential for growth. This guide aims to demystify e-commerce fulfillment, covering various models and services that can help you streamline your logistics.
Key Models of Fulfillment
We will explore different fulfillment models, including Third-Party Logistics (3PL) and Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). Each model has its unique benefits and drawbacks, making it vital for you to understand how they align with your business goals and customer needs.
Core Fulfillment Services
Understanding the core services offered by fulfillment partners is crucial. These typically include inventory management, order processing, packing, shipping, and returns handling. We’ll break down what each service entails and how they can be tailored to suit your specific requirements.
Choosing the Right Partner
Selecting the right fulfillment partner can significantly impact your operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. We will provide practical tips on evaluating potential partners, including questions to ask and key factors to consider, such as technology integration, scalability, and customer service.
Pricing Considerations
Finally, we will delve into pricing structures, helping you understand the various costs associated with fulfillment services. This will empower you to make informed decisions that balance cost-effectiveness with service quality.
Goal of This Guide
The ultimate goal of this guide is to empower you, the growing business owner, with the knowledge needed to make smart decisions about your logistics. By understanding the intricacies of e-commerce fulfillment, you can position your business for sustainable growth, enhance customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive sales. Whether you’re just starting or looking to optimize your existing processes, this guide will serve as a comprehensive resource for navigating the complex world of e-commerce fulfillment.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
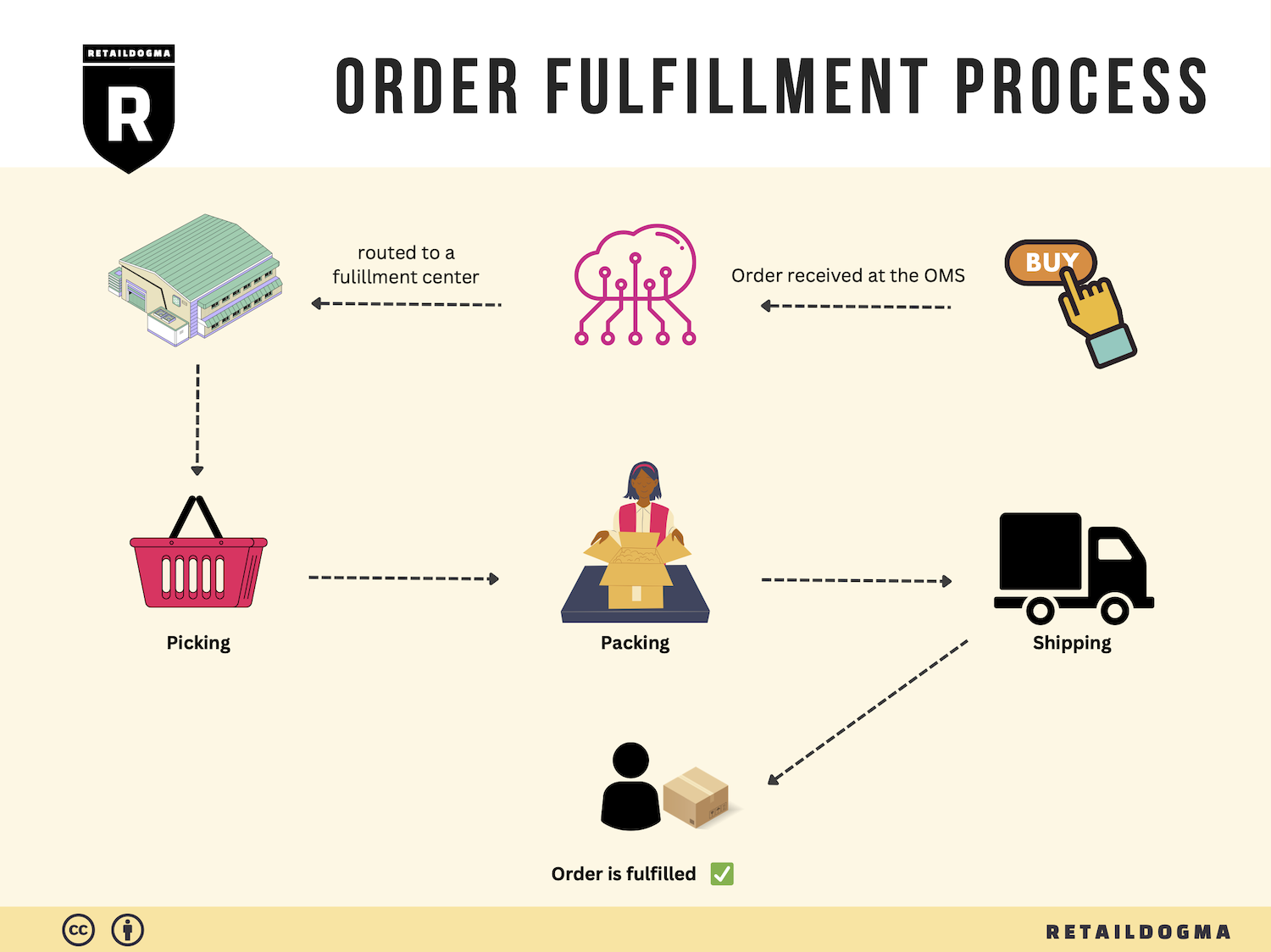
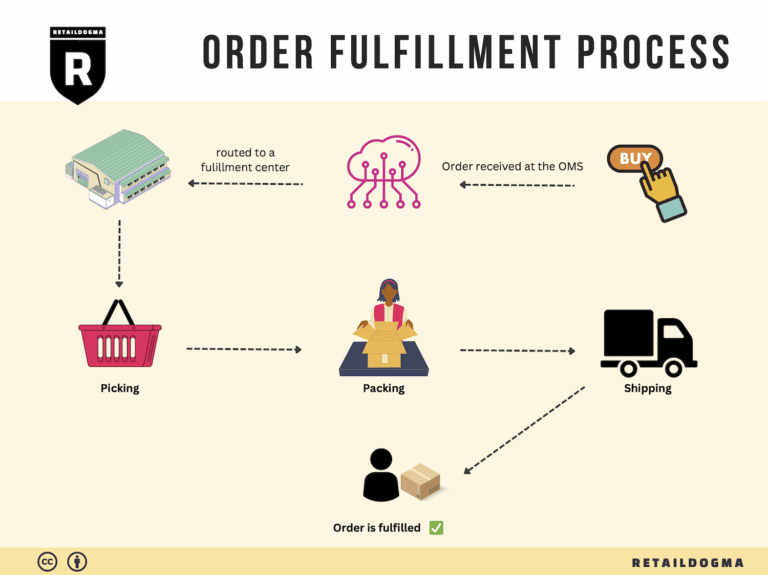
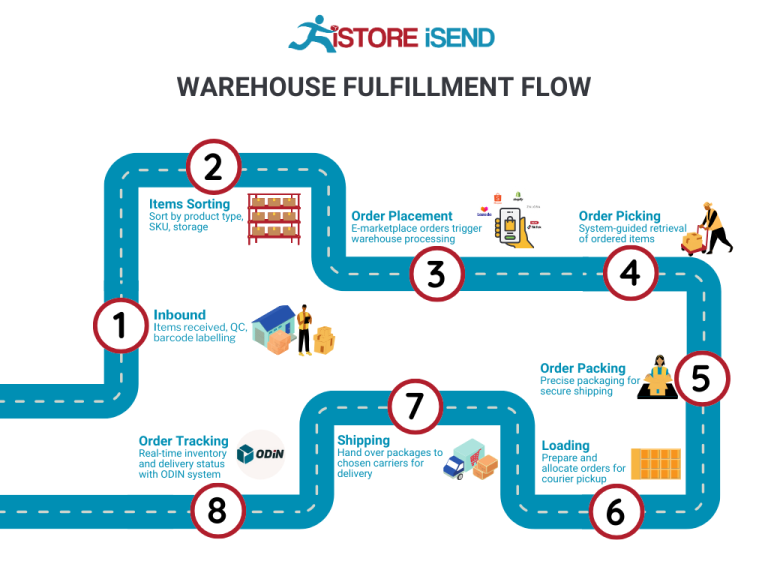
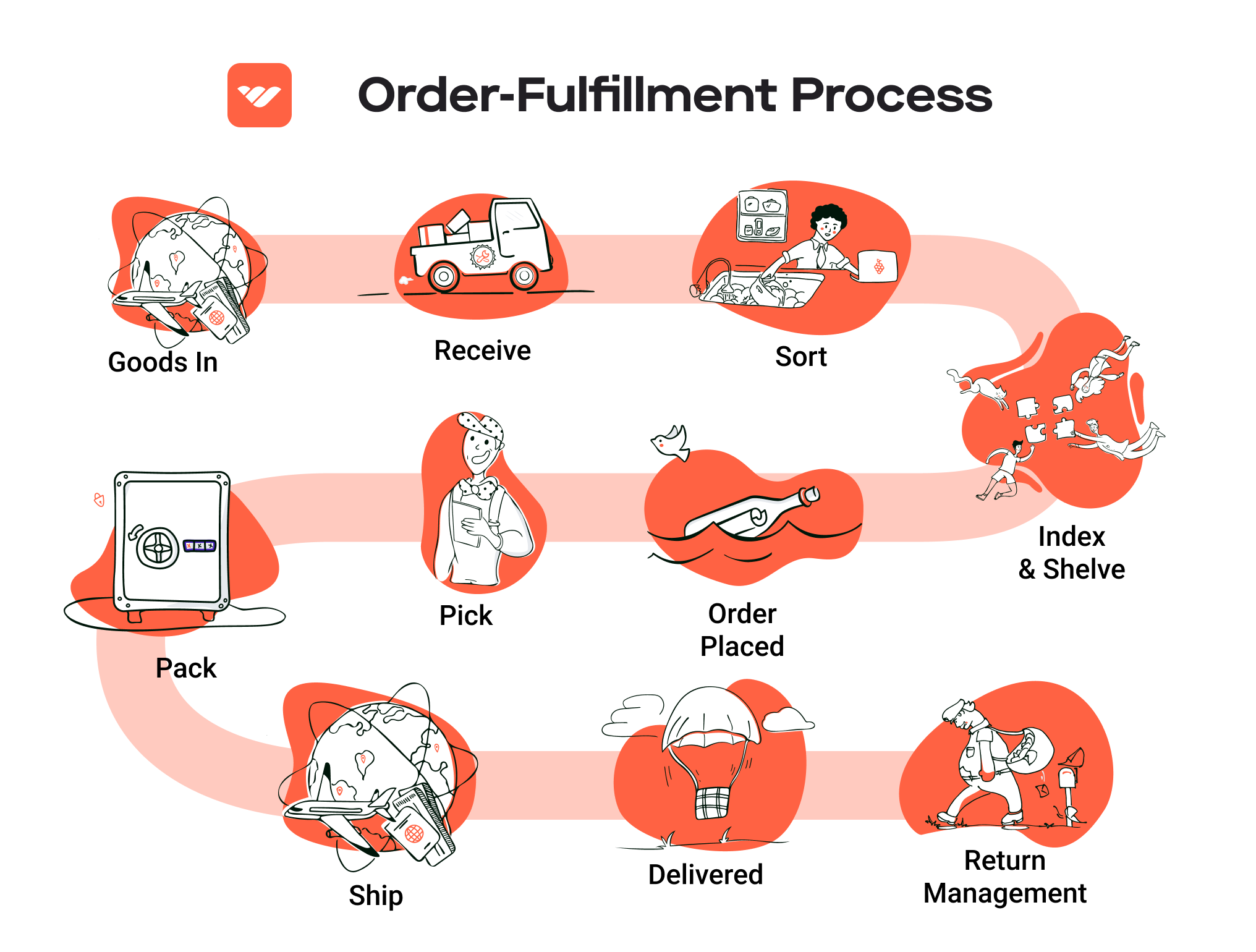
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
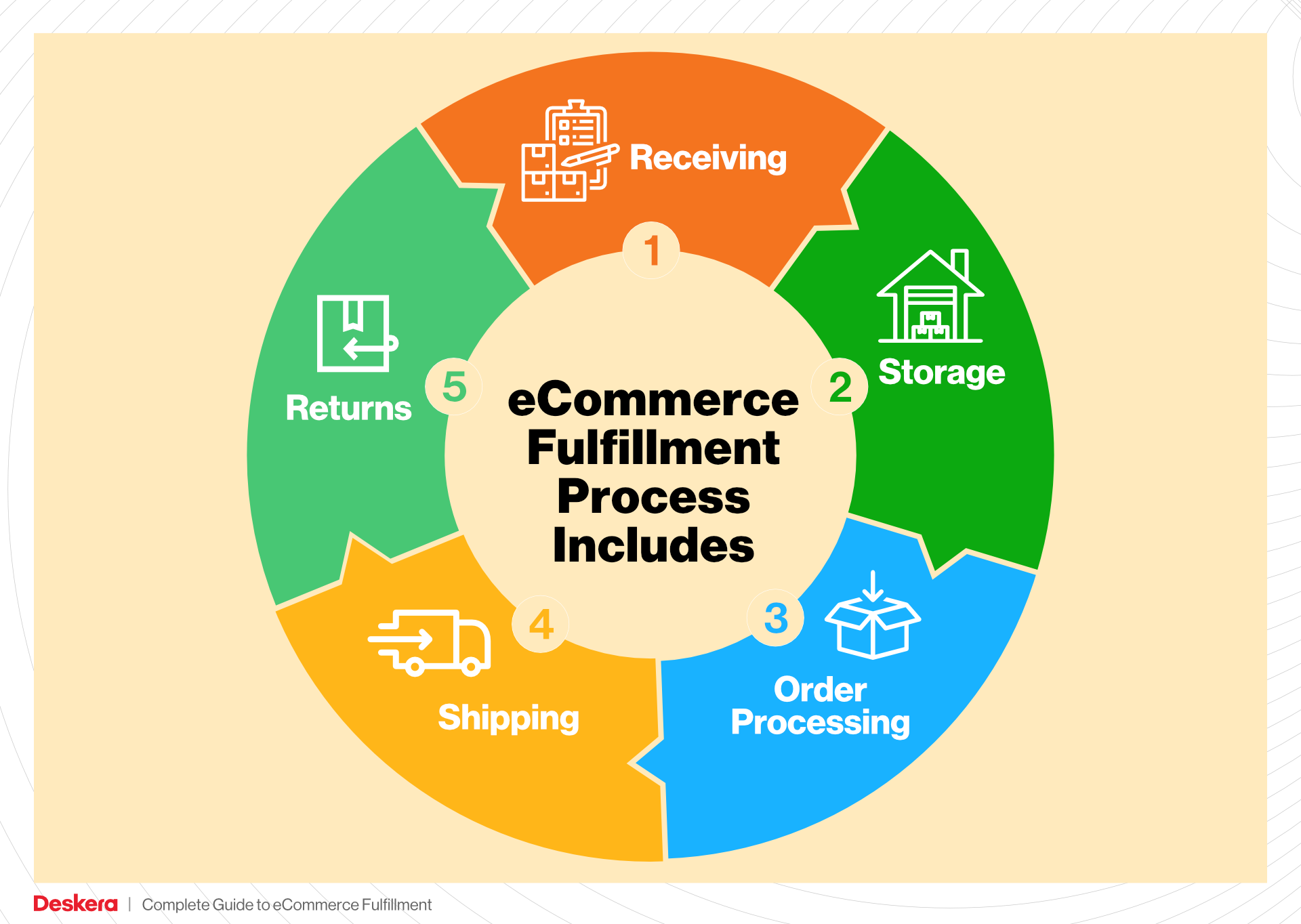
1. Receiving Inventory
The order fulfillment process begins with receiving inventory, a crucial step that sets the foundation for efficient operations. Upon arrival at the micro-fulfillment center (MFC), products are unloaded and checked against purchase orders to ensure accuracy. This process involves verifying quantities, inspecting for damages, and confirming that the right items have been delivered.
This step is vital because it directly impacts inventory accuracy and the overall efficiency of the fulfillment process. Accurate receiving helps prevent stock discrepancies, which can lead to order fulfillment errors and customer dissatisfaction. A key term associated with this stage is SKU (Stock Keeping Unit), which is used to uniquely identify each product and streamline inventory management. Properly managing SKUs from the outset enables businesses to track inventory levels effectively and forecast demand more accurately.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once inventory is received and verified, the next step is warehouse storage. In an MFC, products are stored in a highly organized manner, often utilizing vertical space and compact shelving systems to maximize efficiency. Items are typically categorized based on demand, with fast-moving products placed in easily accessible locations.
Efficient warehouse storage is critical for reducing the time it takes to pick orders later in the process. By strategically organizing inventory, businesses can ensure that the most popular items are readily available, minimizing delays. A key term in this stage is ABC analysis, a method of categorizing inventory based on value and turnover rates. This analysis helps businesses focus on high-demand items, ensuring they are always in stock and easily accessible.
3. Order Picking
The heart of the fulfillment process is order picking, where items are selected from storage to fulfill customer orders. In a micro-fulfillment environment, this process can be highly automated, with robots or advanced picking systems assisting human workers. Pickers use pick lists—documents or digital displays that detail the items required for each order—to locate and retrieve products efficiently.
Order picking is crucial because it directly affects order accuracy and speed. An effective picking process ensures that customers receive the correct items in a timely manner, which is essential for maintaining high satisfaction levels. The implementation of technologies such as voice picking or pick-to-light systems can enhance this step, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
4. Order Packing
After items are picked, they move to the order packing stage. This involves securely packaging the selected products to prevent damage during transit. Proper packing not only protects the items but also enhances the customer experience through thoughtful presentation. Businesses should consider using branded packaging materials and including packing slips or promotional items to create a positive unboxing experience.
The importance of this step cannot be overstated, as it directly influences customer perceptions of quality and care. A key term related to packing is dimensional weight, which refers to the space a package occupies in relation to its weight. Understanding dimensional weight is essential for optimizing shipping costs, as it can significantly affect shipping fees. Efficient packing processes can lead to cost savings and improved delivery times.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once orders are packed, they are labeled and dispatched to the appropriate carriers for delivery to customers. In an MFC model, the focus is often on local and same-day delivery options, enabling businesses to meet rising consumer expectations for quick fulfillment.
Effective shipping and delivery strategies are critical for customer satisfaction, as they determine how quickly and reliably products reach customers. A key term here is last mile delivery, which refers to the final leg of the delivery journey from the distribution center to the customer’s doorstep. This stage is often the most expensive part of the shipping process, making it essential for businesses to optimize routes and partner with reliable carriers to ensure timely delivery.
In summary, mastering each step of the order fulfillment process is essential for e-commerce businesses looking to scale. By focusing on efficiency and accuracy at every stage—from receiving inventory to shipping and delivery—companies can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and ultimately drive growth.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Fulfillment Model Comparison
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | The business itself | Established businesses | Full control over inventory and operations | High overhead costs and operational complexity |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | A third-party provider | Growing and scaling businesses | Scalability and reduced operational burden | Less control over inventory and fulfillment speed |
| Dropshipping | Supplier or manufacturer | Startups and small businesses | Low upfront investment and minimal risk | Lower profit margins and reliance on suppliers |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment refers to the practice of managing all aspects of the warehousing and shipping process within the company itself. This model is often favored by established businesses that have the resources and infrastructure to handle inventory management directly. By maintaining control over inventory, businesses can implement tailored processes to optimize order picking, packing, and shipping. The key advantages include the ability to monitor quality control closely, offer personalized customer service, and streamline operations according to specific business needs. However, this model comes with significant disadvantages, including high overhead costs associated with staffing, warehousing, and technology investment. Moreover, as order volumes increase, the complexity of operations can lead to inefficiencies and require constant adjustments to processes and systems.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) providers offer businesses the ability to outsource their fulfillment operations to an external partner. This model is particularly beneficial for growing and scaling businesses that may not have the capacity to manage fulfillment internally. 3PL providers typically have established warehouses, technology, and expertise, enabling them to handle inventory management, order fulfillment, and shipping efficiently. The primary advantage of using a 3PL is the scalability it offers, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations, such as marketing and sales, without the burden of logistics. Additionally, 3PLs can often negotiate better shipping rates due to their volume, resulting in cost savings for the business. However, the main disadvantage lies in the potential loss of control over inventory and fulfillment processes. Businesses may face challenges in communication and coordination with their 3PL partner, which can lead to delays or inaccuracies in order fulfillment.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where the retailer does not hold any inventory. Instead, when a product is sold, the retailer purchases the item from a third-party supplier who then ships it directly to the customer. This model is particularly advantageous for startups and small businesses looking to minimize upfront investment and risk. With dropshipping, businesses can offer a wide variety of products without the need for warehousing space, making it an attractive option for e-commerce entrepreneurs. The primary benefit of dropshipping is the low financial barrier to entry, as there is no need to invest in inventory upfront. However, this model comes with its own set of challenges. Profit margins can be lower compared to in-house fulfillment or 3PL, as retailers must rely on suppliers for pricing and shipping. Additionally, the retailer has little control over inventory levels and fulfillment speed, which can lead to stockouts and customer dissatisfaction. As a result, businesses must carefully select reliable suppliers and maintain open communication to ensure a smooth fulfillment process.
In summary, each fulfillment model presents unique advantages and disadvantages, and the choice largely depends on the specific needs, resources, and growth stage of the business. Understanding these models is essential for e-commerce business owners, operations managers, and entrepreneurs looking to scale their sales and logistics effectively.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service offered by Amazon that allows sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon then takes care of storage, packaging, and shipping of these products directly to customers. Additionally, FBA provides customer service and handles returns, making it an appealing option for e-commerce entrepreneurs looking to streamline their logistics.
How FBA Works
-
Registration and Product Listing: Sellers first need to register for an Amazon seller account and create product listings. They can choose to enroll their products in FBA.
-
Shipping Inventory: Once enrolled, sellers send their inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon provides guidelines on how to package and label the products for efficient handling.
-
Storage and Management: Amazon stores the products in their warehouses. Sellers can track their inventory through the Amazon Seller Central dashboard.
-
Order Fulfillment: When a customer places an order for an FBA product, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the product on behalf of the seller. This process includes providing tracking information to the customer.
-
Customer Service and Returns: Amazon manages customer service inquiries and handles returns for FBA products, allowing sellers to focus on other aspects of their business.
Pros of Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
-
Prime Eligibility: Products fulfilled by Amazon are automatically eligible for Amazon Prime, which can significantly increase visibility and sales. Prime members often prefer products that offer fast, free shipping.
-
Customer Trust: Leveraging Amazon’s established reputation can help build trust with potential customers. Shoppers are more likely to purchase products from sellers using FBA due to Amazon’s reliable shipping and customer service.
-
Multi-Channel Fulfillment: FBA allows sellers to fulfill orders from other sales channels, such as their own websites or other marketplaces. This means sellers can centralize their logistics and benefit from Amazon’s fulfillment capabilities across multiple platforms.
-
Scalability: FBA allows businesses to scale quickly without the need for large warehousing or logistics infrastructure. As demand increases, sellers can easily send more inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers.
-
Time-Saving: By outsourcing logistics to Amazon, sellers can save time on order fulfillment, allowing them to focus on other business activities such as marketing, product development, or customer engagement.
Cons of Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
-
High Fees: FBA fees can accumulate quickly, including storage fees (for holding inventory) and fulfillment fees (for picking, packing, and shipping orders). These costs can significantly impact profit margins, particularly for lower-priced items.
-
Strict Inventory Rules: Amazon has stringent guidelines regarding inventory management, including limits on how much inventory can be sent to their warehouses. Sellers must also adhere to specific packaging and labeling requirements, which can be challenging for some.
-
Commingling Risks: When products are commingled, it means that inventory from multiple sellers is mixed in the same warehouse. This can lead to issues such as receiving a different item than what was ordered or complications with returns and refunds.
-
Loss of Control: By using FBA, sellers relinquish some control over the fulfillment process. They are reliant on Amazon’s systems and policies, which may change without notice.
-
Potential for Stockouts: If a seller’s products are selling well, they may quickly run out of stock. Restocking can take time, and during that period, sales opportunities may be lost.
Who is FBA Best For?
Fulfillment by Amazon is particularly well-suited for:
-
Small to Medium-Sized Sellers: Businesses that do not have the infrastructure to handle logistics can leverage FBA to gain access to Amazon’s resources without significant upfront investment.
-
Brands Looking to Scale: Sellers aiming for rapid growth can benefit from FBA’s scalability, enabling them to expand their product offerings and reach without worrying about warehousing and fulfillment.
-
Sellers of High-Demand Products: Businesses that sell popular or fast-moving items can take advantage of FBA’s efficient logistics to meet customer demand quickly.
-
E-commerce Entrepreneurs Focused on Customer Experience: Those who want to provide a seamless shopping experience with fast shipping and easy returns can benefit from the customer service support that FBA offers.
-
Multi-Channel Sellers: Brands selling through multiple platforms can use FBA to streamline their fulfillment process, providing a consistent experience across all channels.
In conclusion, while Fulfillment by Amazon presents several advantages such as Prime eligibility and customer trust, it also comes with challenges like high fees and strict rules. E-commerce business owners must weigh these pros and cons based on their unique operational needs and growth objectives to determine if FBA is the right fit for their business strategy.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Inventory management and warehousing are foundational services provided by fulfillment centers. This involves the systematic tracking and storage of products in a controlled environment. Fulfillment centers utilize advanced inventory management systems that offer real-time visibility into stock levels, ensuring that e-commerce businesses can monitor their inventory accurately and efficiently.
The primary benefit of effective inventory management is the reduction of stockouts and overstock situations. E-commerce businesses can avoid the costs associated with excess inventory, such as storage fees or markdowns, while also ensuring that they can meet customer demand without delays. Moreover, sophisticated warehousing solutions enable businesses to store a diverse range of products, including seasonal items or limited editions, without the need for large physical spaces. By having a localized inventory through micro-fulfillment centers, businesses can achieve faster delivery times, enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services are critical in the order fulfillment process. This service entails the picking of products from the warehouse shelves based on customer orders and packing them securely for shipment. Fulfillment centers typically employ both manual and automated systems to ensure accuracy and efficiency in this process.
The benefits of pick and pack services for e-commerce businesses include increased order accuracy and faster processing times. With trained staff and advanced technology, fulfillment centers can significantly reduce the likelihood of shipping errors, which can lead to returns and dissatisfied customers. Additionally, streamlined pick and pack operations allow businesses to scale quickly during peak seasons without compromising service quality. By outsourcing this function, e-commerce owners can focus on strategic activities such as marketing and product development, while leaving the logistics to the experts.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services involve the grouping of various products into a single package or kit, ready for sale. This can include assembling components of a product, bundling related items together, or creating promotional packages. Fulfillment centers often provide this service to help businesses offer unique product combinations or special promotions that enhance the customer experience.
The advantage of kitting and assembly lies in its ability to create value-added services for customers. E-commerce businesses can differentiate themselves in a crowded market by offering curated packages that appeal to specific customer segments. Additionally, this service can lead to cost savings in shipping since bundled products often weigh less than individual items shipped separately. By utilizing kitting services, businesses can also streamline their inventory management processes, reducing the complexity of handling multiple SKUs.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, is an essential service that addresses the process of handling returned products. Fulfillment centers manage returns efficiently, inspecting items, restocking them, and processing refunds or exchanges as needed. This service is particularly crucial for e-commerce businesses, where return rates can be significantly higher than in traditional retail.
The benefits of effective returns management are multifaceted. First, it enhances customer satisfaction by simplifying the return process and ensuring that refunds or exchanges are handled promptly. This responsiveness can build trust and encourage repeat business, a vital component for long-term success. Additionally, an efficient returns process can minimize losses by quickly restocking sellable items and identifying defective products for appropriate handling. By partnering with a fulfillment center for returns management, e-commerce businesses can turn a potentially negative experience into a positive one, maintaining their reputation in a competitive market.
By leveraging these core services—inventory management and warehousing, pick and pack services, kitting and assembly, and returns management—e-commerce businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction. As the landscape of online retail continues to evolve, these services are not just beneficial; they are essential for scaling and thriving in a competitive environment.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
Importance:
The location of your fulfillment partner’s warehouses is critical for minimizing shipping times and costs. The closer the fulfillment center is to your customer base, the faster you can deliver products, which is increasingly important in today’s competitive e-commerce landscape.
Questions to Ask:
– Where are your fulfillment centers located? Can you provide a map of your warehouse network?
– How do you determine the optimal locations for new fulfillment centers?
– Are your warehouses situated in urban areas or population centers to enable quick delivery?
Technology & Integrations
Importance:
Modern e-commerce relies heavily on technology to streamline operations, manage inventory, and improve customer experiences. A fulfillment partner should offer robust technology solutions that integrate seamlessly with your e-commerce platform.
Questions to Ask:
– What technology do you use for inventory management, order processing, and shipping?
– Can your systems integrate with my existing e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce)?
– Do you offer real-time tracking for orders, and how is that communicated to customers?
Specializations (e.g., Cold Storage, Oversized Items)
Importance:
Depending on your product range, you may require specific capabilities from your fulfillment partner. For instance, businesses dealing with perishables or oversized items need partners with specialized storage and handling capabilities.
Questions to Ask:
– What types of products do you specialize in handling (e.g., perishables, hazardous materials, oversized items)?
– Do you have temperature-controlled storage options for perishable goods?
– How do you manage products that require special handling or packaging?
Scalability & Capacity
Importance:
As your business grows, your fulfillment needs will change. A good fulfillment partner should be able to scale operations alongside your business, whether you’re experiencing seasonal spikes or long-term growth.
Questions to Ask:
– What is your current capacity for handling orders, and how do you plan to scale that in the future?
– Can you handle peak seasons or unexpected spikes in order volume without compromising service quality?
– What is your process for onboarding new clients or increasing capacity for existing clients?
Pricing and Contracts
Importance:
Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms is essential to ensure that you are making a cost-effective choice. Hidden fees can quickly erode profit margins, so clarity upfront is vital.
Questions to Ask:
– What is your pricing model (e.g., per order, monthly fees, storage fees)?
– Are there any additional fees I should be aware of (e.g., for returns, special handling, or storage)?
– What are the terms for contract cancellation or modifications? Is there flexibility for seasonal adjustments?
Customer Support & Reviews
Importance:
Strong customer support can make a significant difference in your experience with a fulfillment partner. You want a partner who is responsive and reliable, particularly when issues arise.
Questions to Ask:
– What customer support channels do you offer (e.g., phone, email, chat)?
– Can you provide references or case studies from businesses similar to mine?
– How do you handle issues or disputes, and what is your average response time?
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is a crucial step in scaling your e-commerce business efficiently. By using this checklist, you can systematically evaluate potential partners and ensure they align with your operational needs, customer expectations, and growth ambitions. Remember, the right partner not only fulfills orders but also becomes an integral part of your business strategy, helping you deliver an exceptional customer experience.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
When partnering with a micro fulfillment center (MFC), one of the first costs you may encounter is the initial setup fee. This fee is generally a one-time charge that covers the costs associated with onboarding your business to the fulfillment provider’s system. It may include:
- Software Integration: Costs related to connecting your e-commerce platform with the MFC’s inventory and order management systems.
- Training Costs: If you require training for your staff on how to use the new system effectively, this may also be included.
- Infrastructure Adjustments: Any necessary changes or enhancements to the MFC’s physical infrastructure to accommodate your products.
The amount can vary significantly depending on the complexity of your needs and the provider’s capabilities, often ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged when the MFC accepts and processes your inventory. This fee typically covers the labor involved in unloading, inspecting, and entering your products into the inventory management system.
- Calculation Basis: Receiving fees may be calculated per pallet or per item, depending on the provider’s pricing structure. For instance, a provider might charge a flat fee per pallet received, which could range from $10 to $50, or a fee per item that could vary based on the complexity of the item (e.g., bulky items may incur higher charges).
Understanding this fee structure is crucial, especially if you frequently replenish inventory, as it can significantly affect your overall fulfillment costs.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are incurred for keeping your products within the MFC. These fees are calculated based on the space your inventory occupies and can be charged per pallet, bin, or cubic foot.
- Calculation Basis: A common pricing model includes a monthly fee per pallet, which can range from $15 to $30, or a per-bin fee for smaller items. Some providers may also charge based on the amount of cubic space your items occupy, which can be beneficial if you have a diverse range of product sizes.
Keep in mind that overstocking can lead to higher storage costs, so it’s essential to maintain a balanced inventory that aligns with your sales forecasts.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are charged for the labor involved in picking items from storage and packing them for shipment. This fee can vary based on the complexity of the order, including the number of items and the type of packaging required.
- Calculation Basis: Typically, pick and pack fees are calculated per item or per order. For example, a provider might charge $0.50 to $2.00 per item picked and packed. Additionally, if your order requires special packaging or kitting, there may be additional charges.
Understanding this fee is essential, especially for businesses with high order volumes or those that require customized packing solutions, as it can significantly influence overall fulfillment costs.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are one of the most variable costs in the fulfillment process. These charges cover the cost of transporting your products to customers and can vary based on several factors:
- Shipping Method: Costs will differ based on whether you choose standard, expedited, or same-day shipping.
- Destination: Shipping fees can also vary based on the distance from the MFC to the customer’s location. Urban deliveries are typically cheaper than rural ones.
- Carrier Rates: Different carriers (e.g., UPS, FedEx, USPS) have different pricing structures, and the MFC may pass these costs directly to you or offer negotiated rates.
Shipping fees can often be the most significant expense in your fulfillment strategy, so it’s vital to understand the options available to optimize costs.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
- Detail Your Needs: Clearly outline your product types, order volumes, and any specific requirements (e.g., special handling, packaging) to receive a tailored quote.
- Compare Multiple Providers: Engage with several MFCs to compare pricing structures and services. Don’t just focus on the base rates; consider the full scope of services included.
- Ask About Hidden Fees: Inquire about any additional costs that may not be immediately apparent, such as fees for returns, inventory audits, or seasonal surcharges.
- Negotiate Terms: If you expect high order volumes or long-term partnership, negotiate terms that could lead to discounts or reduced fees.
- Review Contracts Carefully: Before signing, review the contract for clarity on all fee structures and ensure you understand the terms.
By being proactive and thorough in your discussions with fulfillment providers, you can secure a pricing structure that supports your business growth effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is a micro fulfillment center (MFC)?
A micro fulfillment center (MFC) is a small-scale warehouse typically ranging from 3,000 to 10,000 square feet, designed to hold a compact inventory of fast-moving products for rapid delivery to customers. MFCs enable businesses to fulfill orders quickly by placing inventory closer to urban populations, significantly reducing last-mile delivery costs and times.
2. How do micro fulfillment centers differ from traditional warehouses?
Micro fulfillment centers are smaller, more strategically located, and focused on high-demand products for quick fulfillment. In contrast, traditional warehouses are larger facilities that often manage bulk inventory and are designed for less frequent order fulfillment. MFCs emphasize speed and efficiency in handling individual orders rather than bulk shipments.
3. What are the benefits of using a micro fulfillment center?
The primary benefits of MFCs include reduced shipping costs, faster delivery times, improved inventory turnover, and the ability to meet customer expectations for quick service. By positioning inventory closer to the consumer, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction while decreasing operational costs.
4. What types of businesses can benefit from micro fulfillment centers?
Both large retailers and small-to-medium-sized e-commerce companies can benefit from MFCs. Industries such as grocery, fashion, health and beauty, and specialty foods often leverage MFCs to offer faster service and maintain brand integrity while managing fulfillment in densely populated areas.
5. How much do micro fulfillment center services cost?
Costs for MFC services can vary widely based on location, technology used, and the scale of operations. Generally, businesses can expect to invest in real estate, technology (like automation systems), and operational expenses. On average, fulfillment services may range from $2 to $10 per order, depending on the complexity and size of the order.
6. What role does technology play in micro fulfillment centers?
Technology is critical in MFC operations, as it enables automation, inventory management, and efficient order processing. Systems such as robotics, AI-driven inventory management, and real-time tracking help streamline operations, reduce errors, and optimize the picking and packing processes, ensuring faster fulfillment.
7. What is a third-party logistics provider (3PL)?
A third-party logistics provider (3PL) is a company that offers outsourced logistics services, including warehousing, transportation, and fulfillment. Many businesses partner with 3PLs to leverage their expertise, technology, and infrastructure, allowing them to focus on core activities while efficiently managing their supply chain.
8. How do micro fulfillment centers impact last-mile delivery?
MFCs significantly improve last-mile delivery by positioning inventory closer to customers, thereby reducing transportation times and costs. This localized approach allows for quicker delivery options, such as same-day or next-day service, which is essential for meeting modern consumer expectations.
9. Can micro fulfillment centers handle specialized products?
Yes, MFCs can be designed to manage specialized products that require unique handling or packaging, such as fresh produce, fragile items, or oversized goods. Many MFCs offer customized services tailored to the specific needs of businesses, ensuring that all products are handled appropriately.
10. What trends are influencing the growth of micro fulfillment centers?
The rise of e-commerce, heightened customer expectations for rapid delivery, and the increasing costs associated with traditional logistics are driving the growth of MFCs. Additionally, advancements in automation and technology are making it easier for companies to implement MFCs and optimize their fulfillment strategies.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Assessing the Value of Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a strategic move for e-commerce businesses aiming to scale effectively. By leveraging a third-party fulfillment service, companies can save significant time and resources. This allows business owners and operations managers to focus on core activities such as product development, marketing, and customer engagement rather than the logistical complexities of warehousing and shipping.
One of the primary benefits of utilizing a fulfillment partner is scalability. As your business grows, so do the demands of order fulfillment. Fulfillment services provide the infrastructure and flexibility necessary to handle increased order volumes without the need for substantial upfront investment in physical space or technology. This adaptability can be especially advantageous during peak shopping seasons or unexpected surges in demand.
Moreover, specialized fulfillment providers bring expertise that can enhance operational efficiency. They are well-versed in best practices, technological advancements, and market trends, which can help streamline your supply chain and improve delivery times. This expertise not only reduces costs but also enhances customer satisfaction—an essential factor in retaining and growing your customer base.
However, the success of outsourcing fulfillment hinges on selecting the right partner. Conducting thorough due diligence to evaluate potential providers based on their capabilities, technology, and service levels is crucial. A misalignment in expectations can lead to operational disruptions and negatively impact your brand’s reputation.
As you consider whether outsourcing fulfillment is the right move for your business, take a moment to audit your current shipping processes. Assess your fulfillment challenges and weigh them against the potential benefits of partnering with a fulfillment service. This strategic reflection could reveal whether a fulfillment partner is indeed the next step for your growth journey.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.