How Order Fulfillment Works: A Step-by-Step Guide for Businesses
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Growing an online business often brings with it a host of challenges, one of the most pressing being the logistics of packing and shipping orders. As sales increase, so too can the complexity and time commitment required to manage fulfillment. For many e-commerce entrepreneurs, this overwhelming process can detract from the core focus of scaling their business and serving their customers effectively.
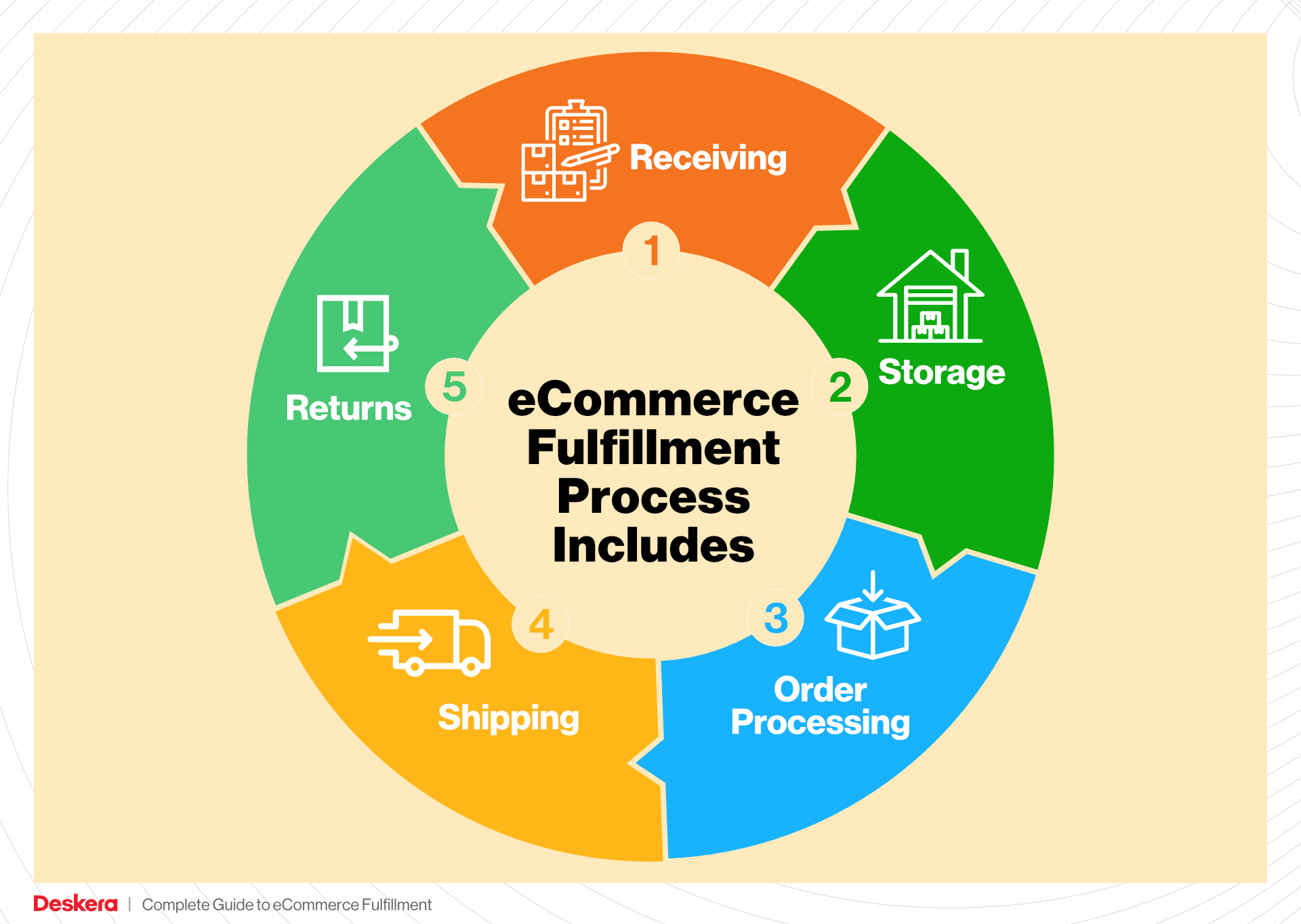
At its essence, e-commerce fulfillment is the process of getting a product from your inventory to your customer’s doorstep. This involves several key steps: receiving inventory, storing products, processing orders, picking and packing items, shipping them out, and managing returns. Understanding this process is crucial for any business looking to grow sustainably in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
In this guide, we will explore the various fulfillment models available to online businesses, including Third-Party Logistics (3PL) and Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). Each model has its own set of advantages and challenges, and we will break these down to help you find the best fit for your operational needs.
We will also cover the core services offered by fulfillment partners, such as inventory management, order processing, and shipping logistics. Knowing what services are available can help you streamline your operations and enhance customer satisfaction.
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is a critical decision that can significantly impact your business’s efficiency and customer experience. We will provide practical tips on how to evaluate potential partners based on factors like scalability, technology, and customer service.
Finally, we will address pricing structures and what to expect in terms of costs associated with different fulfillment options. Understanding the financial implications will empower you to make informed decisions that align with your business goals.
The ultimate goal of this guide is to empower e-commerce business owners and operations managers to make smart, strategic decisions about their logistics. By demystifying the fulfillment process and providing actionable insights, we aim to help you create a seamless experience for your customers while positioning your business for growth.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
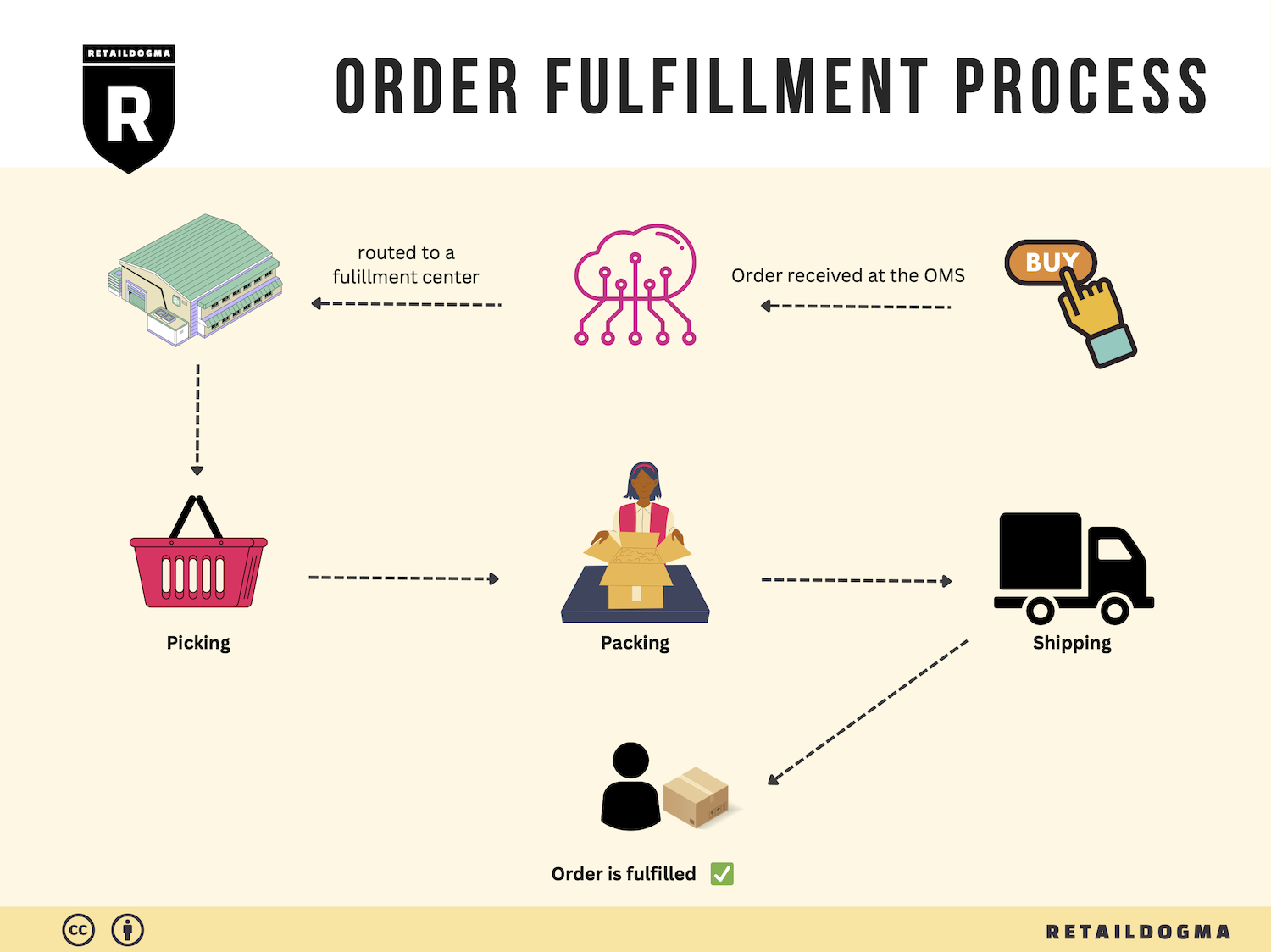
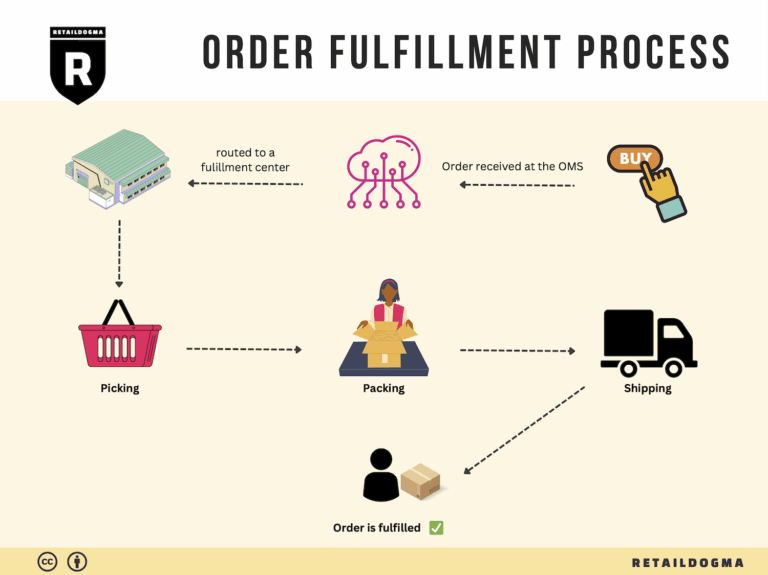
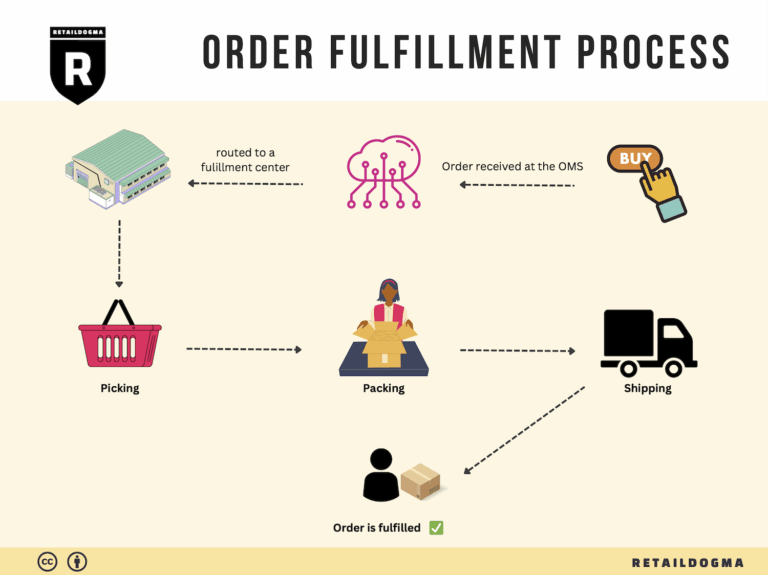
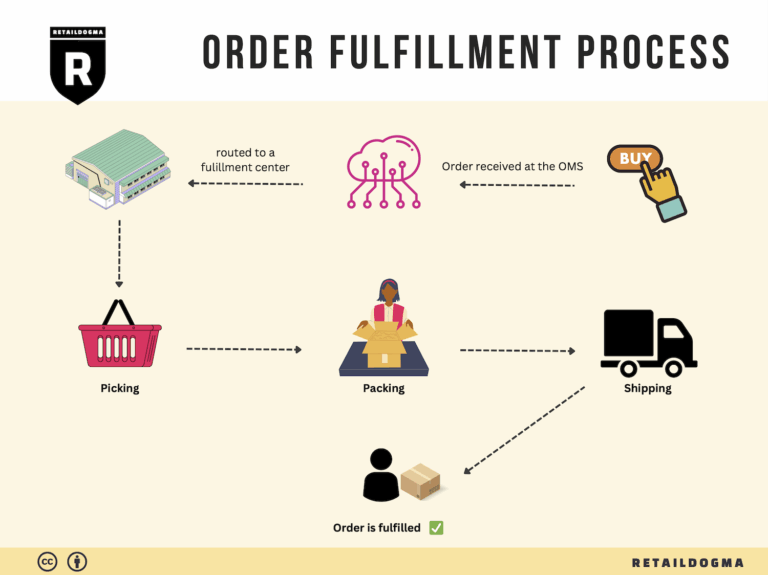
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
1. Receiving Inventory
The order fulfillment process begins with receiving inventory. This step involves the arrival of products from suppliers into your warehouse or fulfillment center. Upon receipt, each item must be checked against purchase orders to ensure accuracy in quantities and specifications. This is crucial for maintaining inventory integrity and preventing stock discrepancies.
Key terms associated with this step include SKU (Stock Keeping Unit), which is used to identify each product uniquely. By utilizing SKUs, businesses can streamline inventory tracking, making it easier to manage stock levels and reorder products when necessary. An effective receiving process minimizes errors and ensures that the subsequent steps in the fulfillment process can proceed smoothly.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once inventory is received, the next step is warehouse storage. This involves organizing products in a systematic manner within the warehouse. Efficient storage solutions, such as shelving, pallet racks, and bins, should be used to maximize space and facilitate easy access to items.
This step is important because it directly impacts the efficiency of order picking later on. A well-organized warehouse reduces the time it takes to locate and retrieve products, which can significantly enhance overall operational efficiency. Key terms for this phase include ABC Analysis, a method for categorizing inventory based on importance and turnover rates, which helps in optimizing storage locations and inventory management.
3. Order Picking
Order picking is the process of retrieving items from storage to fulfill customer orders. When a customer places an order, the fulfillment team generates a pick list that details the items and quantities needed for that specific order. This document guides warehouse staff in efficiently locating and collecting the products.
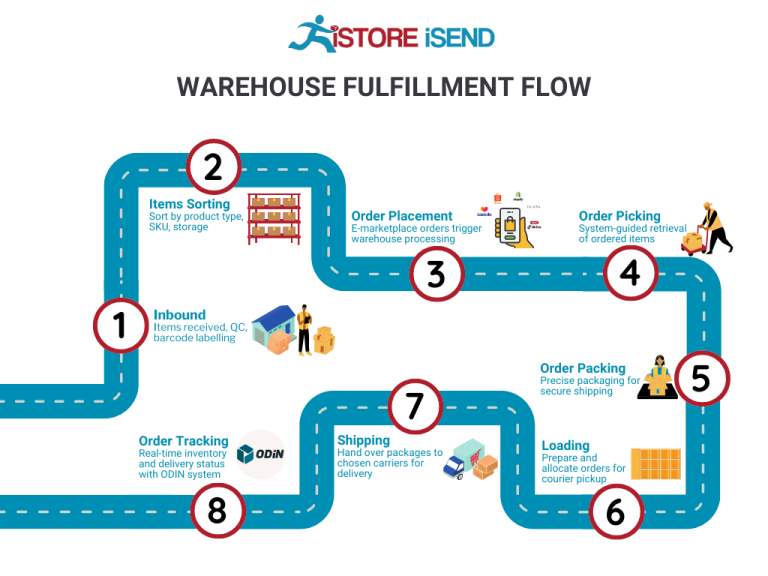
The importance of this step cannot be overstated; accurate picking is essential to ensure customer satisfaction and reduce returns. Errors during picking can lead to incorrect shipments, negatively affecting customer trust and increasing operational costs. Techniques such as batch picking or zone picking can be employed to further enhance efficiency, allowing multiple orders to be picked simultaneously or dividing the warehouse into zones for specialized picking.
4. Order Packing
After items are picked, they move to the packing stage. Here, products are carefully packed into boxes or containers suitable for shipping. This process involves not just placing items in boxes, but also ensuring they are secure and protected to prevent damage during transit. Packing materials such as bubble wrap, packing peanuts, and sturdy boxes are commonly used.
Effective packing is vital because it ensures that products arrive at the customer’s location in perfect condition, thereby enhancing the customer experience. Additionally, proper packing can help reduce shipping costs by optimizing box sizes and weights. Key terms for this step include packaging optimization, which refers to the practice of using the most efficient packaging methods to minimize costs while ensuring product safety.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once orders are packed, they are labeled and prepared for dispatch. Choosing the right shipping carriers and methods is crucial, as it affects delivery speed, cost, and overall customer satisfaction. Businesses can offer multiple shipping options to cater to different customer needs, such as standard shipping or expedited delivery.
This step is significant because it marks the transition of products from the warehouse to the customer’s doorstep. Effective logistics management ensures that orders are shipped on time and tracked throughout their journey. Key terms in this phase include last-mile delivery, which refers to the final step of the delivery process, where the package reaches the customer. Optimizing last-mile delivery can greatly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
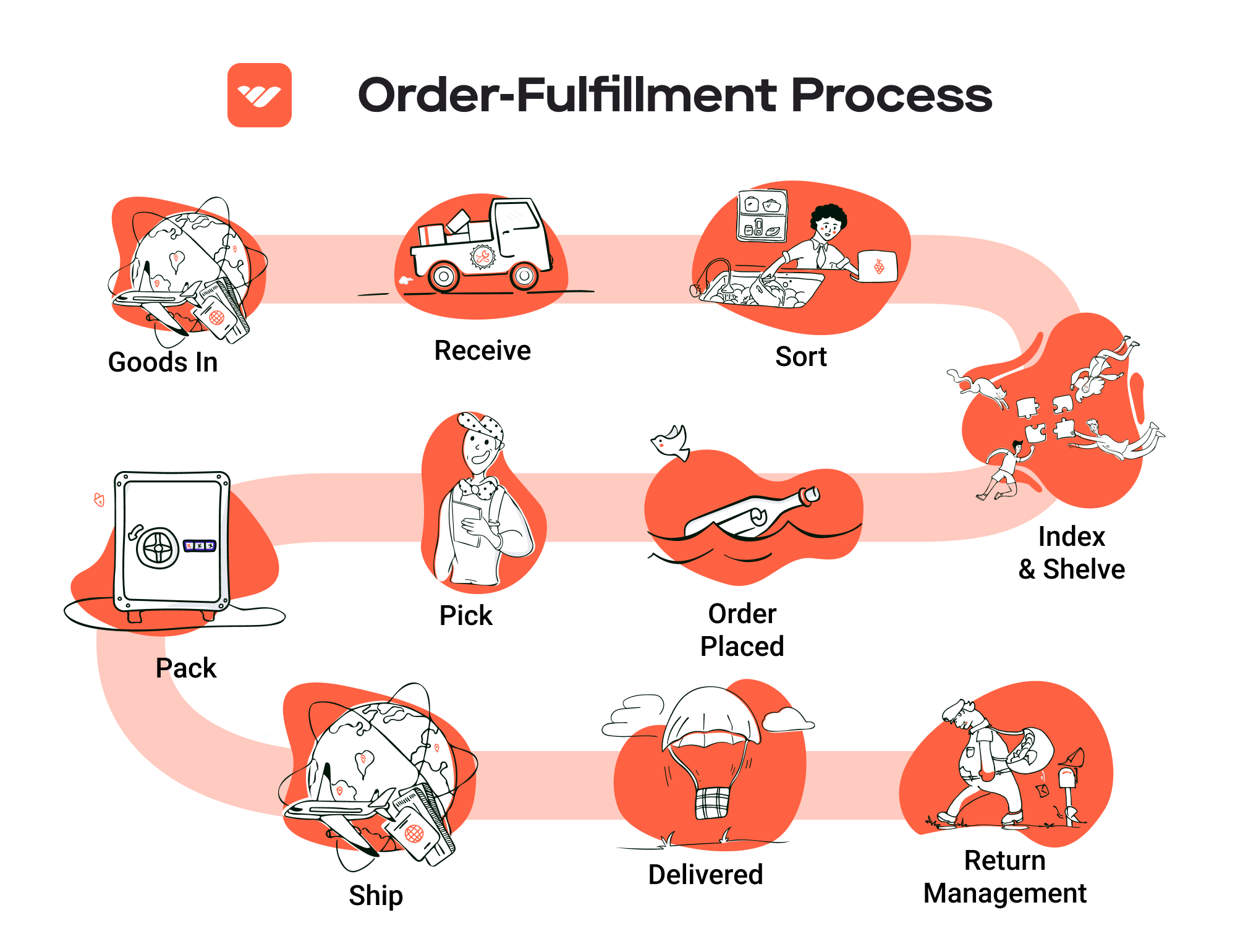
In conclusion, a streamlined order fulfillment process that encompasses these five steps—receiving inventory, warehouse storage, order picking, order packing, and shipping & delivery—can significantly enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By focusing on each step with clarity and precision, e-commerce businesses can scale effectively and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Fulfillment Model Comparison Table
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | The business itself | Established businesses | Full control over inventory and processes | High operational costs and complexity |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | 3PL provider | Growing businesses | Scalability and reduced overhead costs | Less control over inventory and processes |
| Dropshipping | Supplier | Startups and small businesses | Low upfront investment and risk | Lower profit margins and reliance on suppliers |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment means that a business manages its own warehousing, inventory, and order processing. This model is typically best suited for established businesses that have the resources and infrastructure to handle logistics internally. One of the primary advantages of in-house fulfillment is the level of control it offers; businesses can monitor inventory levels, manage shipping processes, and ensure quality control directly. This can lead to a more personalized customer experience, as businesses can tailor their operations to meet the specific needs of their clientele. However, this model also comes with significant disadvantages, including high operational costs related to warehousing, staffing, and equipment. Moreover, as order volumes grow, the complexity of operations can increase, potentially leading to inefficiencies unless the business invests further in logistics technology and staff training.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) refers to outsourcing logistics and fulfillment operations to a specialized provider. This model is particularly beneficial for growing businesses that need to scale their operations without the burden of managing logistics themselves. The key advantage of 3PL is scalability; as order volumes increase, businesses can easily expand their fulfillment capabilities without needing to invest in additional warehouse space or staff. Furthermore, 3PL providers often have established shipping relationships and expertise in logistics management, which can lead to reduced shipping costs and improved delivery times. However, the reliance on a third party can result in less control over inventory and fulfillment processes. Businesses must ensure that their 3PL partner aligns with their operational goals and maintains the same quality standards they would uphold themselves. Communication and transparency are also critical, as any lapses in service can directly impact customer satisfaction.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where a retailer sells products without holding inventory; instead, the retailer purchases items from a third-party supplier who ships directly to the customer. This model is ideal for startups and small businesses that wish to enter the market with minimal upfront investment and risk. One of the primary advantages of dropshipping is the low barrier to entry; businesses do not need to invest in inventory upfront, which allows for a more agile approach to market demands. Additionally, dropshipping enables retailers to offer a broader range of products without the need for storage space. However, dropshipping also has notable disadvantages, including lower profit margins due to reliance on suppliers for pricing and fulfillment. Furthermore, businesses may face challenges with product quality, shipping times, and inventory availability, as they do not control these aspects of the supply chain. This reliance can lead to customer dissatisfaction if suppliers fail to meet expectations, making it essential for businesses to vet suppliers thoroughly and establish strong relationships.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment model is crucial for the success and scalability of an e-commerce business. Each model—In-House Fulfillment, Third-Party Logistics (3PL), and Dropshipping—offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed against the specific needs and goals of the business. In-house fulfillment provides control but at a higher cost, 3PL offers scalability and expertise but less control, and dropshipping allows for low-risk entry into the market but with challenges related to profitability and supplier reliability. By understanding these dynamics, business owners can make informed decisions that align with their operational strategy and growth ambitions.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a logistics service provided by Amazon that allows sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon takes care of storage, packaging, and shipping, along with customer service and returns. This service enables sellers to leverage Amazon’s vast logistics network and customer base, significantly simplifying the e-commerce operations for businesses of all sizes.
How FBA Works
-
Set Up Your FBA Account: Sellers need to create an Amazon seller account and enroll in FBA. This involves selecting the products they want to fulfill through Amazon.
-
Prepare Your Products: Sellers must package and label their products according to Amazon’s requirements. Proper labeling ensures that products are correctly identified and processed in the fulfillment centers.
-
Ship to Amazon: Once products are ready, sellers ship them to one or more of Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon provides shipping guidelines and can assist with discounted shipping rates.
-
Storage and Inventory Management: Products are stored in Amazon’s warehouses until sold. Sellers can monitor their inventory levels through the Amazon seller dashboard.
-
Order Fulfillment: When a customer orders a product, Amazon handles the entire fulfillment process. This includes picking, packing, and shipping the product directly to the customer.
-
Customer Service and Returns: Amazon also manages customer inquiries and handles returns, allowing sellers to focus on growing their business rather than dealing with operational logistics.
Pros of Using FBA
1. Prime Eligibility
One of the significant advantages of using FBA is that products become eligible for Amazon Prime. This means that Prime members can receive free two-day shipping, making products more attractive to customers who value fast delivery. Increased visibility and attractiveness can lead to higher sales volumes.
2. Customer Trust
Amazon has built a strong reputation for customer service and reliability. By using FBA, sellers can benefit from this trust, as customers are often more willing to purchase items fulfilled by Amazon due to perceived credibility and the ease of returns.
3. Multi-Channel Fulfillment
FBA isn’t limited to Amazon’s marketplace. Sellers can use FBA to fulfill orders from their own websites or other sales channels, allowing for streamlined operations across multiple platforms. This can simplify logistics, as all inventory can be managed from a single location.
4. Scalability
FBA allows sellers to scale their business without needing to invest heavily in warehousing or logistics. As demand grows, sellers can easily send more inventory to Amazon’s warehouses without worrying about the complexities of storage and order fulfillment.
5. Access to Amazon’s Global Market
By using FBA, sellers can tap into Amazon’s extensive customer base and global marketplace, allowing for potential growth in international sales without the logistical headaches typically associated with cross-border shipping.
Cons of Using FBA
1. High Fees
While FBA offers numerous advantages, it also comes with costs. Sellers must pay for storage space, fulfillment fees, and additional charges for long-term storage. These fees can accumulate, especially for products that do not sell quickly, eroding profit margins.
2. Strict Inventory Rules
Amazon has stringent inventory management rules. Sellers must adhere to specific requirements regarding product preparation, labeling, and storage. Failing to comply can lead to additional fees or even restrictions on selling.
3. Commingling Risks
FBA allows for commingled inventory, where products from different sellers are stored together. This can lead to challenges if a seller’s product is damaged or if there are quality concerns, as returns may not always be directed back to the original seller.
4. Less Control Over Fulfillment
Using FBA means relinquishing control over the fulfillment process. Sellers must trust Amazon to manage their inventory and customer interactions, which can be a concern for those who prefer to maintain direct oversight of their operations.
5. Potential for Account Suspension
Amazon’s policies are strict, and sellers risk having their accounts suspended if they do not comply with guidelines. This can be a significant concern for sellers who rely heavily on FBA for their business operations.
Who is FBA Best For?
Fulfillment by Amazon is particularly beneficial for:
-
Small to Medium-Sized Businesses: Businesses that lack the resources to manage their logistics can benefit from Amazon’s robust infrastructure, allowing them to focus on product development and marketing.
-
E-commerce Entrepreneurs: Those looking to scale quickly without investing heavily in logistics can find FBA a valuable asset in their growth strategy.
-
Retailers with Seasonal Products: Businesses that experience fluctuating demand can utilize FBA to manage inventory without the need for long-term storage commitments.
-
Sellers with Established Brands: Brands that already have a customer base and are looking to expand their reach can leverage FBA to tap into Amazon’s customer trust and fast shipping capabilities.
In conclusion, while Fulfillment by Amazon offers a myriad of advantages that can significantly streamline e-commerce operations, it is crucial for sellers to carefully consider the associated costs and operational dynamics. By weighing the pros and cons, businesses can make informed decisions about whether FBA aligns with their overall growth strategy.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Inventory management and warehousing are foundational services provided by fulfillment centers. This service involves the systematic tracking of inventory levels, orders, sales, and deliveries, ensuring that businesses have the right amount of stock on hand at all times. Fulfillment centers utilize advanced inventory management software to monitor stock levels in real-time, allowing e-commerce businesses to minimize excess inventory while ensuring product availability.
The benefits of effective inventory management are multifaceted. First, it prevents stockouts and backorders, which can lead to lost sales and dissatisfied customers. By maintaining optimal inventory levels, businesses can enhance their customer experience and build loyalty. Moreover, efficient warehousing practices reduce holding costs associated with excess stock, thereby improving overall cash flow. Businesses can also benefit from improved forecasting, which allows them to make informed purchasing decisions based on historical data and market trends.
Pick and Pack Services
Pick and pack services involve the process of selecting products from inventory (picking) and packaging them for shipment (packing). Fulfillment centers employ trained staff and sophisticated technology to ensure that orders are accurately picked according to customer specifications and efficiently packed to prevent damage during transit.
The primary advantage of pick and pack services is the significant time savings they offer e-commerce businesses. With a dedicated team handling order fulfillment, businesses can focus on core activities such as marketing, product development, and customer service. Additionally, fulfillment centers often employ quality control measures to minimize errors in order fulfillment, which enhances customer satisfaction and reduces the costs associated with returns and exchanges. This service is particularly valuable during peak seasons or promotional events, where order volumes can surge unexpectedly.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services involve the grouping of various products into ready-to-ship kits or the assembly of components into a final product. This service is particularly beneficial for businesses that sell items that are often bundled together or require assembly before they can be sold.
The benefits of kitting and assembly are twofold. First, it simplifies the shipping process by allowing businesses to send out complete kits rather than individual components, thereby streamlining logistics and reducing shipping costs. Second, it enhances the customer experience by delivering a ready-to-use product, which can be particularly appealing in gift-giving scenarios or when offering subscription boxes. By outsourcing this service to a fulfillment center, businesses can also reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency, as the fulfillment center can leverage economies of scale and expertise in assembly processes.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, refers to the process of handling returned products from customers. Fulfillment centers play a critical role in managing this aspect of the supply chain by processing returns efficiently and determining the best course of action for returned items—whether to restock, refurbish, or recycle.
The benefits of effective returns management are substantial for e-commerce businesses. A streamlined returns process can significantly enhance customer satisfaction, as consumers are more likely to make a purchase if they know they can easily return items if necessary. Additionally, efficient handling of returns minimizes financial losses associated with unsold or damaged products. By analyzing return data, businesses can also gain insights into customer behavior and product quality, allowing them to make informed decisions about inventory and product offerings. This service not only mitigates the negative impacts of returns but can also transform a potentially frustrating process into an opportunity for customer engagement and retention.
In conclusion, the core services offered by fulfillment centers—inventory management and warehousing, pick and pack services, kitting and assembly, and returns management—are essential for e-commerce businesses looking to scale efficiently. By leveraging these services, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive growth in a competitive marketplace.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
Choosing the right location for your fulfillment partner’s warehouses is crucial for optimizing shipping times and costs. The closer the warehouses are to your customer base, the faster and cheaper you can fulfill orders.
Key Questions:
– Where are your warehouses located, and how do they align with my primary customer demographics?
– What is your shipping network, and do you have partnerships with carriers that provide competitive rates and reliable service?
– Can you provide a map of your distribution network?
Technology & Integrations
In today’s e-commerce landscape, technology is a game-changer. A fulfillment partner’s technology stack should seamlessly integrate with your existing systems, enabling real-time inventory management, order tracking, and data analytics.
Key Questions:
– What technology platforms do you use for order management and inventory tracking?
– Are your systems compatible with my e-commerce platform (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce, Magento)?
– Can you provide API access for custom integrations, and how frequently do you update your systems?
Specializations (e.g., Cold Storage, Oversized Items)
Depending on the nature of your products, you may require specialized services. If you sell perishable goods, for instance, a partner with cold storage capabilities is essential. Similarly, if you deal with oversized or fragile items, ensure that the partner has the necessary expertise.
Key Questions:
– What types of products do you specialize in handling, and do you have the necessary equipment and expertise?
– Can you accommodate unique shipping requirements, such as temperature control or special packaging?
– What safety measures do you have in place for handling fragile or oversized items?
Scalability & Capacity
As your business grows, your fulfillment needs will evolve. It is vital to partner with a fulfillment provider that can scale with you, whether that means increasing storage capacity, order processing speeds, or additional services.
Key Questions:
– How do you handle seasonal spikes in order volume?
– What is your current storage capacity, and how can it be expanded if needed?
– Can you provide examples of how you’ve supported businesses through periods of rapid growth?
Pricing and Contracts
Understanding the pricing structure of your fulfillment partner is critical to maintaining your profit margins. Be clear about all potential costs, including storage fees, pick-and-pack fees, and shipping rates. Contracts should be transparent and flexible enough to accommodate changes in your business.
Key Questions:
– What is your pricing structure, and what factors can affect my overall costs?
– Are there any hidden fees I should be aware of, such as for returns or special handling?
– How flexible are your contracts, and what is the process for renegotiating terms as my business grows?
Customer Support & Reviews
Reliable customer support can make or break your relationship with a fulfillment partner. Look for a provider with a dedicated support team that can address your concerns swiftly. Additionally, researching reviews and testimonials from other clients can provide insight into the partner’s reliability and service quality.
Key Questions:
– What levels of customer support do you offer (e.g., dedicated account manager, 24/7 support)?
– Can you provide references or case studies from businesses similar to mine?
– How do you handle disputes or issues that may arise during the fulfillment process?
Conclusion
Selecting the right fulfillment partner is a critical decision that can significantly impact your e-commerce business’s success. By using this checklist, you can ensure that you are making an informed choice that aligns with your operational needs and growth objectives. Each of these points serves as a foundation for building a partnership based on efficiency, reliability, and scalability, ultimately allowing you to focus on what you do best—growing your business.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
Initial setup fees are typically one-time charges incurred when you begin using a fulfillment service. These fees cover the costs associated with onboarding your business into the fulfillment center’s system. Setup may include account creation, integration with your e-commerce platform, and initial inventory processing.
The calculation of initial setup fees can vary widely based on the complexity of your operations. For instance, if your business requires custom software integrations or specialized handling of products (such as fragile items), you may face higher fees. Generally, you can expect to pay anywhere from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on the fulfillment provider and the specific services you require.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged each time a shipment of inventory arrives at the fulfillment center. These fees cover the labor and handling costs associated with unloading, inspecting, and entering your products into inventory.
Typically, receiving fees are calculated based on the number of pallets or boxes received, or the total weight of the shipment. For example, a fulfillment center might charge a flat fee per pallet, ranging from $20 to $50, or a fee based on weight that could be around $0.50 to $1.00 per pound. Understanding how these fees are structured will help you better manage your incoming inventory costs.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are charged for the space your inventory occupies within the fulfillment center. These fees can be billed monthly or quarterly and are usually calculated on a per-pallet or per-bin basis.
The cost of storage typically varies depending on the location of the warehouse and the type of products stored. For instance, standard storage fees might range from $10 to $30 per pallet per month. If you have smaller items that can be stored in bins, the fees might be calculated at a lower rate, such as $5 to $15 per bin. Understanding seasonal fluctuations in storage needs, especially during peak sales periods, can help you optimize your costs.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are charged for the labor involved in retrieving items from inventory and preparing them for shipment. This includes picking the items, packing them securely, and labeling them for delivery.
These fees can be structured in various ways, often based on the number of items picked or the number of orders processed. A common model is a flat fee per order (e.g., $1 to $5) plus an additional fee for each item picked (e.g., $0.25 to $1.00). If your business has a high volume of orders but fewer items per order, it may benefit from a fulfillment center that offers a more favorable pricing structure based on orders rather than items.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are incurred for the actual transportation of your products to customers. These fees can be the most variable and are influenced by factors such as shipping methods (standard, expedited, international), package weight, dimensions, and destination.
Fulfillment centers often negotiate rates with carriers and can provide you with various shipping options. Fees are typically calculated based on weight and distance, and may include surcharges for residential delivery or fuel costs. Businesses should also consider the impact of shipping fees on customer satisfaction, as high shipping costs can lead to cart abandonment.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
-
Provide Detailed Information: When requesting a quote, be specific about your product types, average order size, and expected order volume. This information helps fulfillment centers provide tailored pricing.
-
Ask About Hidden Fees: Inquire about any potential hidden costs that may arise during the fulfillment process, such as returns processing or special handling fees.
-
Negotiate Rates: Don’t hesitate to negotiate rates with fulfillment providers, especially if you anticipate high order volumes or long-term partnerships. Many providers are open to adjusting their fees based on your business potential.
-
Request a Breakdown: Ensure you receive a detailed breakdown of all fees included in the quote. This transparency will help you understand the cost structure and identify areas where you might save.
-
Consider Flexibility: As your business grows, your needs may change. Look for fulfillment providers that offer scalable pricing models that can adapt to your evolving requirements.
By understanding these common fulfillment pricing models and how they are calculated, e-commerce business owners can make informed decisions that align with their operational strategies and financial goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What does “love is the fulfillment of the law” mean in a business context?
The phrase emphasizes that ethical and compassionate behavior towards others—employees, customers, and partners—is paramount. In a business context, this means prioritizing customer satisfaction, fair treatment of employees, and ethical dealings over merely following rules or regulations.
2. How can love guide my business operations?
Incorporating love into business operations involves fostering a culture of respect, empathy, and support. This can manifest through transparent communication, fair labor practices, and prioritizing customer needs, ensuring that all actions align with a commitment to do no harm.
3. What is the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse primarily serves as a storage facility for goods, while a fulfillment center is designed to process and ship orders. Fulfillment centers typically handle inventory management, order processing, packing, and shipping, making them essential for e-commerce businesses aiming to scale efficiently.
4. What is a 3PL (Third-Party Logistics)?
A 3PL provider offers outsourced logistics services, including warehousing, inventory management, and transportation. Businesses utilize 3PLs to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and focus on core competencies while relying on experts for logistics and supply chain management.
5. How much do fulfillment services cost?
Fulfillment service costs vary based on factors like order volume, storage space, and specific services required (e.g., packing, shipping). On average, businesses can expect to pay between $2 to $5 per order plus additional fees for storage and handling. It’s crucial to obtain quotes from multiple providers to find the best fit for your budget and needs.
6. How can I ensure my fulfillment process aligns with the principle of love?
To align your fulfillment process with love, ensure that your policies and practices prioritize customer satisfaction and employee well-being. This could include timely communication about order status, fair labor practices, and actively seeking feedback to improve services.
7. What role does customer service play in fulfillment?
Customer service is integral to fulfillment as it directly impacts customer satisfaction and loyalty. A responsive and empathetic customer service team can resolve issues quickly, enhancing the overall fulfillment experience and reinforcing a culture of care and support.
8. How can I create a culture of love in my supply chain?
Creating a culture of love in your supply chain involves fostering partnerships based on trust, transparency, and mutual respect. This can include fair negotiation practices, honoring commitments to suppliers, and encouraging open communication to address challenges collaboratively.
9. What are the benefits of ethical fulfillment practices?
Ethical fulfillment practices can lead to increased customer loyalty, enhanced brand reputation, and improved employee morale. Businesses that prioritize love and ethics in their fulfillment processes are often viewed more favorably by consumers, leading to higher sales and long-term success.
10. How can I measure the effectiveness of love in my fulfillment strategy?
To measure the effectiveness of love in your fulfillment strategy, track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer satisfaction scores, employee engagement levels, and retention rates. Regular feedback from customers and employees can also provide insights into how well your practices align with the principle of love.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
Evaluating the Benefits of Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a game-changer for e-commerce businesses aiming to scale operations effectively. By leveraging a fulfillment service, businesses can save valuable time and resources, allowing owners and managers to focus on core activities such as marketing and product development. This shift not only enhances operational efficiency but also improves customer satisfaction, as fulfillment partners often provide faster shipping and streamlined order processing.
Scalability is another key advantage of utilizing a fulfillment service. As your business grows, so does the complexity of managing inventory, shipping, and returns. A fulfillment partner is equipped to handle fluctuations in demand, ensuring that you can scale operations without the burden of investing in additional warehouse space or staff. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial during peak seasons or promotional events when order volumes can surge unexpectedly.
Moreover, partnering with a fulfillment expert brings invaluable industry knowledge and technology. These providers typically use advanced logistics solutions, which can lead to improved accuracy and efficiency in your supply chain. Their expertise in navigating shipping logistics, compliance, and inventory management can be a significant asset, helping you avoid common pitfalls and optimize your operations.
However, the importance of choosing the right fulfillment partner cannot be overstated. Not all providers are created equal, and the wrong choice can hinder your growth rather than support it. Conducting a thorough audit of your current shipping processes can help you identify inefficiencies and determine whether a fulfillment partner is the right next step for your business.
Call to Action
Take the time to evaluate your current fulfillment strategy. Are you experiencing delays, high shipping costs, or customer complaints? Consider whether outsourcing fulfillment could provide the operational support you need to foster growth and enhance customer satisfaction.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.