What Is A Fulfillment Center? A Complete Guide (2025)
What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
Navigating the E-commerce Fulfillment Landscape
As your online business begins to grow, one of the most common challenges you may face is managing the overwhelming task of packing and shipping orders. The excitement of increasing sales can quickly turn into stress when you’re confronted with the logistical complexities of fulfilling customer orders efficiently and accurately. This is where the concept of e-commerce fulfillment comes into play.
E-commerce fulfillment refers to the entire process of getting a product from your inventory to your customer’s doorstep. It encompasses everything from receiving and storing inventory to picking, packing, and shipping orders. For many growing businesses, understanding the nuances of fulfillment is crucial for scaling operations without sacrificing customer satisfaction.
In this guide, we will explore various fulfillment models that can cater to your business’s unique needs. We’ll discuss Third-Party Logistics (3PL) providers, which can handle logistics on your behalf, and Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), a popular choice that leverages Amazon’s extensive network for storage and shipping. Each model has its own set of advantages and challenges, and understanding them will help you make informed decisions.
We will also delve into the core services offered by fulfillment partners. These services typically include inventory management, order processing, packaging, and shipping. Knowing what to expect from a fulfillment provider will enable you to streamline your operations and enhance your customers’ experience.
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is another critical aspect we’ll cover. Factors such as location, scalability, technology integration, and pricing should all influence your decision. Selecting a partner that aligns with your business goals can lead to improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Finally, we will address the various pricing structures associated with fulfillment services. Understanding the costs involved will help you budget appropriately and maximize your profit margins.
The goal of this guide is to empower you, as a business owner or operations manager, to make smart decisions about your logistics strategy. By equipping you with the knowledge of e-commerce fulfillment, we hope to alleviate some of the stress associated with scaling your operations and ultimately help your business thrive in the competitive online marketplace.
What You’ll Learn In This Guide
- What is E-commerce Fulfillment? An Introduction for Growing Businesses
- The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
- Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
- A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
- Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
- How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
- Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
- Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
- Important Disclaimer
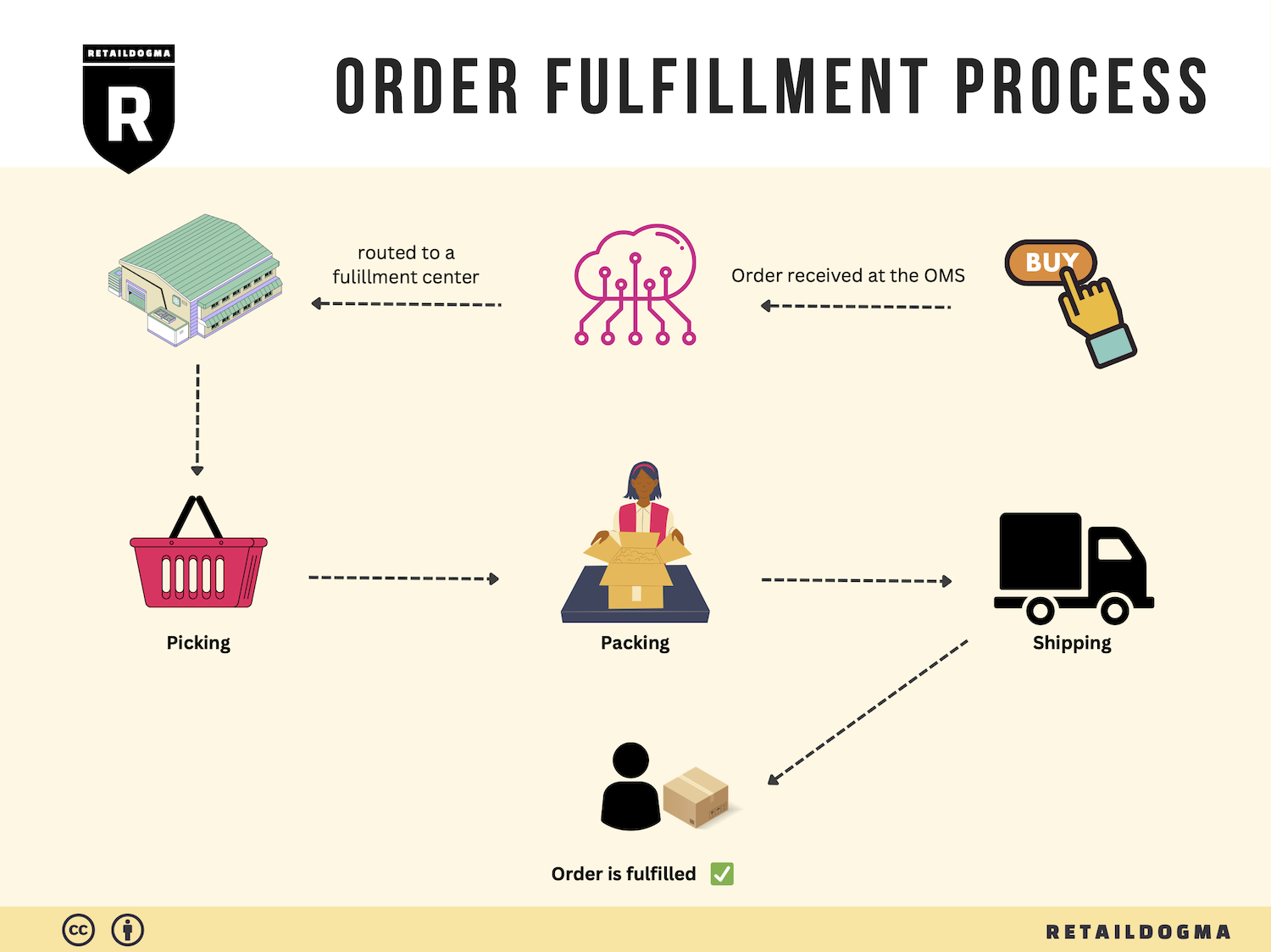
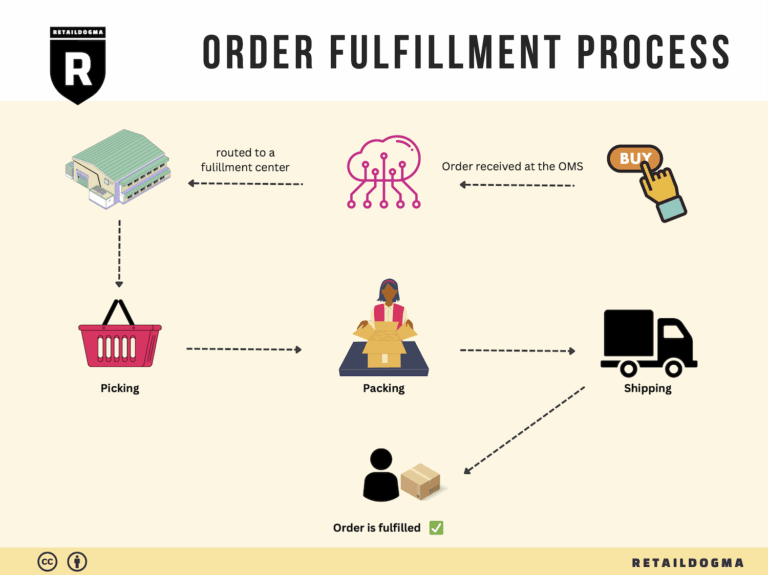
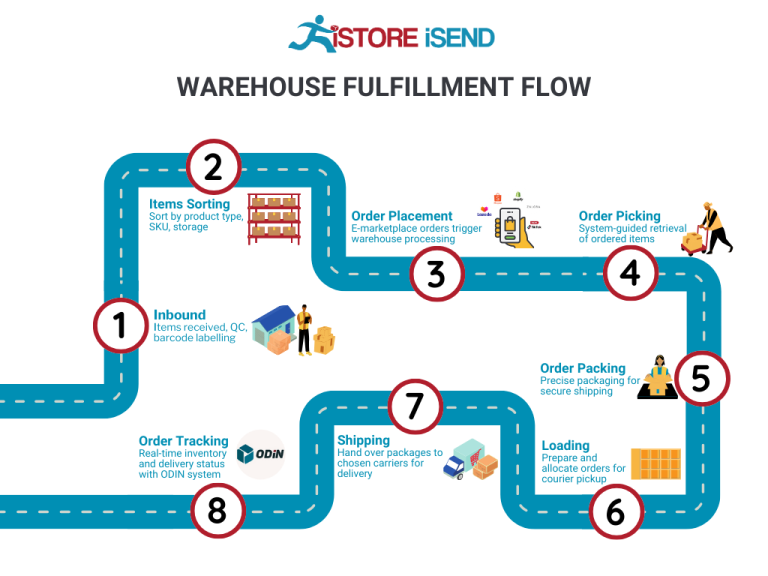
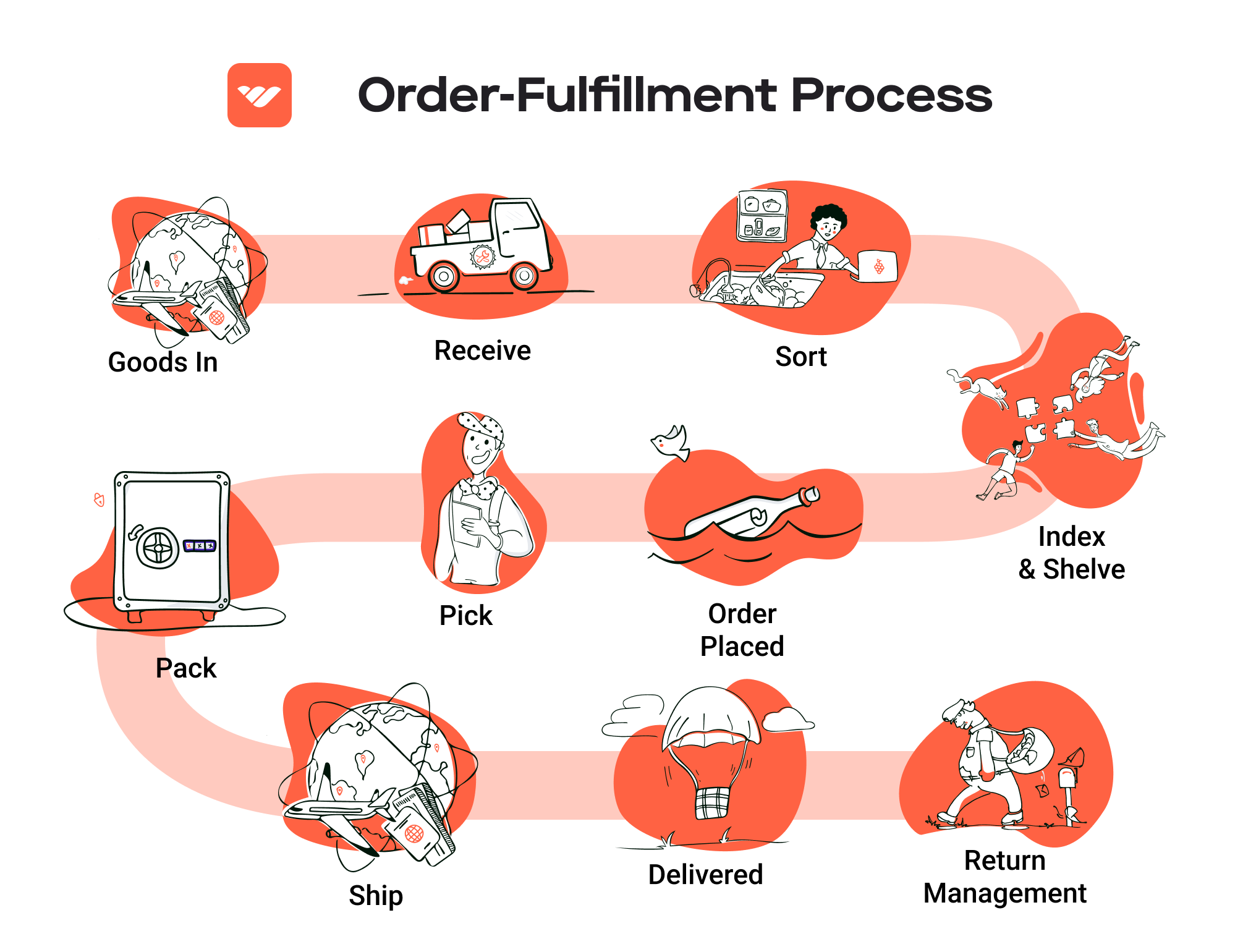
The Order Fulfillment Process: From ‘Buy’ Button to Customer’s Door
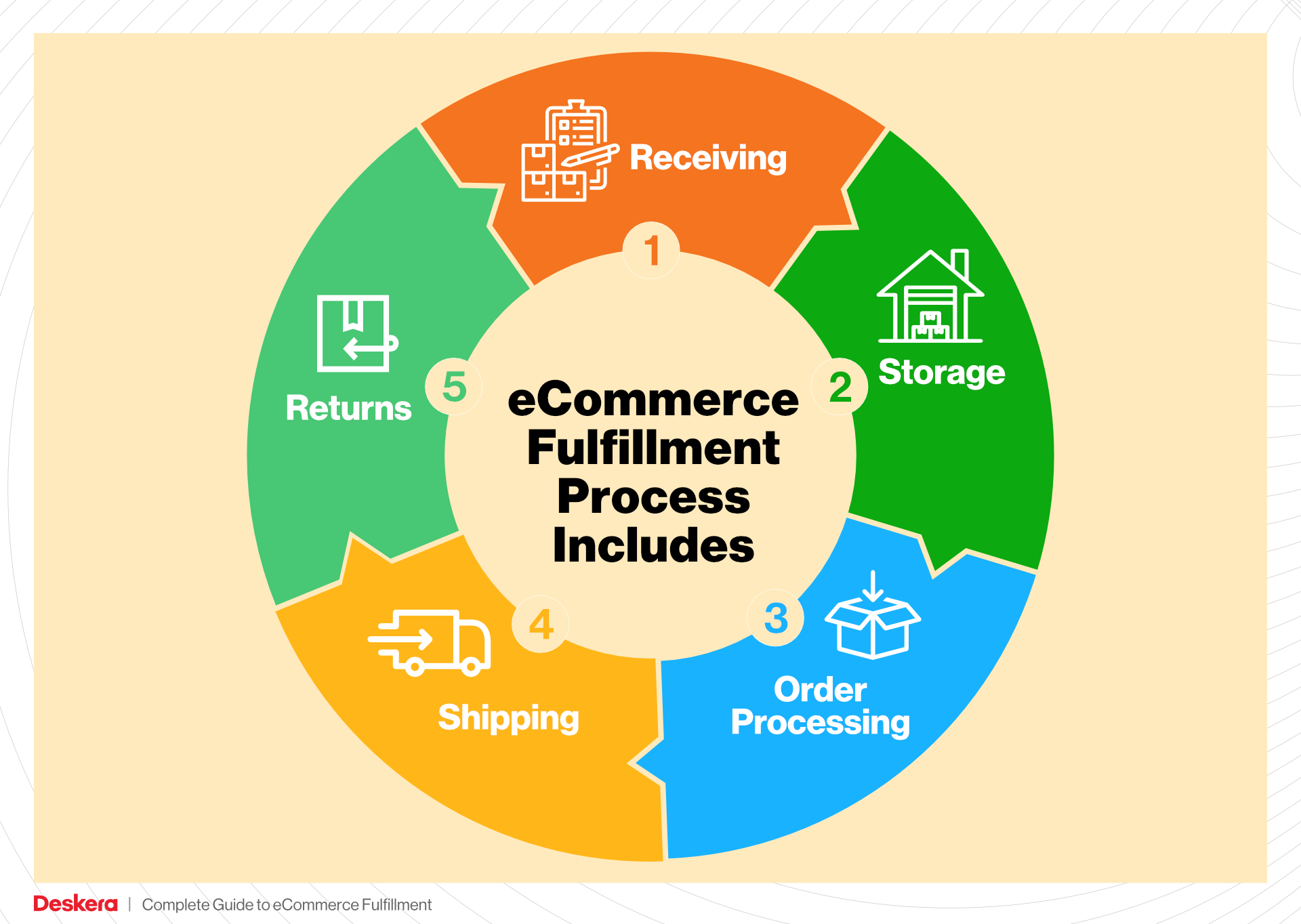
1. Receiving Inventory
The first step in the order fulfillment process is receiving inventory at the fulfillment center. This is where products are delivered from suppliers or manufacturers and checked against purchase orders to ensure accuracy. Each item is assigned a Stock Keeping Unit (SKU), a unique identifier that helps track inventory levels and sales.
Importance: Proper receiving procedures are crucial as they set the foundation for effective inventory management. Accurate receiving ensures that all products are accounted for, reducing the risk of stock discrepancies that can lead to order fulfillment errors.
Key Term: SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) – A unique identifier for each product, essential for tracking inventory and managing stock levels.
2. Warehouse Storage
Once inventory is received and verified, it is stored in the fulfillment center. Items are organized strategically to maximize space and efficiency, often using a combination of shelving, bins, and pallets. The layout is designed to facilitate easy access and quick retrieval of products.
Importance: Efficient warehouse storage minimizes the time spent searching for items, which is critical for maintaining fast order fulfillment times. A well-organized storage system also helps prevent damage and loss of inventory, ensuring that products remain in optimal condition for shipping.
Key Term: Bin Location – A designated area within the warehouse for storing specific items, aiding in quick retrieval during the picking process.
3. Order Picking
When a customer places an order, the next step is order picking. This involves retrieving the selected items from their storage locations based on the order details. Fulfillment centers often utilize pick lists, which provide a detailed overview of the items to be gathered, including quantities and locations.
Importance: Efficient order picking is vital for minimizing errors and speeding up the fulfillment process. The faster and more accurately items can be picked, the quicker the order can be processed and shipped, which is essential for customer satisfaction.
Key Term: Pick List – A document or digital tool that outlines the items to be picked for an order, including their locations and quantities, streamlining the picking process.
4. Order Packing
After items are picked, they are taken to the packing station, where they are carefully packed for shipment. This step involves selecting the appropriate packaging materials, ensuring that items are protected during transit, and generating shipping labels. The packing process may also include quality checks to confirm that the correct items are included.
Importance: Proper packing is essential to prevent damage during shipping and to ensure that the order arrives in excellent condition. Additionally, efficient packing helps optimize shipping costs and speed, as it can influence the choice of carrier and delivery speed.
Key Term: Packaging Materials – Various materials such as boxes, bubble wrap, and tape used to protect items during shipping and ensure they arrive safely at their destination.
5. Shipping & Delivery
The final step in the order fulfillment process is shipping and delivery. Once the order is packed, it is handed over to a carrier (such as UPS, FedEx, or USPS) for delivery to the customer. Fulfillment centers often have partnerships with multiple carriers to optimize shipping costs and delivery times.
Importance: Timely shipping is a critical aspect of customer satisfaction. Efficient logistics and the ability to offer various shipping options can enhance the customer experience and encourage repeat business. Additionally, tracking systems allow customers to monitor their orders in real-time, providing transparency and reassurance.
Key Term: Carrier – A company responsible for transporting goods from the fulfillment center to the customer, playing a crucial role in the overall logistics of the fulfillment process.
By understanding and optimizing each step of the order fulfillment process, e-commerce businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and significantly improve customer satisfaction. Each phase is interconnected, and attention to detail at every step can lead to a seamless experience from the moment a customer clicks the ‘Buy’ button to the moment they receive their order at their door.
Comparing Fulfillment Models: In-House vs. 3PL vs. Dropshipping
Comparison of Fulfillment Models
| Model | Who Handles Inventory | Best For (Business Stage) | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Fulfillment | Business itself | Startups, established businesses | Full control over inventory and operations | High overhead costs and resource requirements |
| Third-Party Logistics (3PL) | Third-party provider | Growing businesses | Scalability and flexibility in operations | Less control over inventory and potential communication issues |
| Dropshipping | Supplier | New entrepreneurs, niche markets | Low upfront costs and minimal risk | Lower profit margins and reliance on suppliers’ reliability |
In-House Fulfillment
In-house fulfillment involves a business managing its entire inventory and shipping process internally. This model is often adopted by startups or established businesses looking to maintain control over their logistics. The key advantage of in-house fulfillment is that it allows a company to oversee every aspect of its operations, from inventory management to packaging and shipping. This control can lead to improved quality assurance and the ability to customize the fulfillment process to meet specific business needs. Additionally, businesses can build a strong brand experience by handling customer interactions directly.
However, the in-house model comes with significant disadvantages. It requires substantial investment in warehousing space, staff, and technology, leading to high overhead costs. As a business scales, managing logistics internally can become increasingly complex and resource-intensive. This model may not be sustainable for companies looking to expand rapidly or those that experience fluctuating demand, as the costs associated with maintaining a large operational infrastructure can outweigh the benefits.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Third-party logistics (3PL) involves outsourcing fulfillment operations to a specialized logistics provider. This model is ideal for growing businesses that want to scale their operations without the burden of managing logistics themselves. A key advantage of using a 3PL is the scalability it offers; businesses can easily adjust their logistics operations based on demand fluctuations without having to invest in additional infrastructure. 3PL providers typically have established networks, technology, and expertise in logistics, which can enhance efficiency and reduce shipping times.
However, the reliance on a third-party provider can pose challenges. Businesses may experience a lack of control over their inventory and fulfillment processes, which can lead to inconsistencies in service quality and potential communication breakdowns. Additionally, integrating systems with a 3PL can require time and resources, especially if the business has unique operational requirements. It’s crucial for businesses to thoroughly vet potential 3PL partners to ensure they align with their operational goals and customer service standards.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a fulfillment model where businesses sell products without holding any inventory. Instead, when a customer makes a purchase, the product is shipped directly from the supplier to the customer. This model is particularly attractive for new entrepreneurs or those operating in niche markets, as it significantly lowers upfront costs and reduces financial risk. With dropshipping, businesses do not need to invest in inventory, warehousing, or shipping logistics, allowing them to focus on marketing and customer acquisition.
Despite its advantages, dropshipping has notable drawbacks. One of the main challenges is lower profit margins, as suppliers often take a significant cut of the sales price. Moreover, businesses are heavily reliant on suppliers for order fulfillment, which can lead to inconsistencies in product quality and shipping times. Any delays or issues on the supplier’s end can directly impact customer satisfaction and the business’s reputation. Additionally, with many businesses adopting dropshipping, competition can be fierce, making it essential for entrepreneurs to differentiate their offerings and provide exceptional customer service.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment model is crucial for e-commerce businesses looking to scale efficiently. Each model—In-House Fulfillment, 3PL, and Dropshipping—has its unique advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice depends on the specific needs, resources, and growth stage of the business. In-house fulfillment offers control but at a high cost, 3PL provides scalability with some loss of control, and dropshipping minimizes risk but can limit profitability. Business owners should evaluate their operational goals, customer expectations, and market conditions to determine the most suitable fulfillment strategy for their growth journey.
A Deep Dive into Amazon FBA: Pros, Cons, and Who It’s For
Understanding Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a service offered by Amazon that allows e-commerce sellers to store their products in Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Amazon then takes care of storage, packaging, shipping, and customer service for these products. This service has grown significantly since its inception in 2006, allowing businesses of all sizes to leverage Amazon’s vast logistics network and customer base.
How FBA Works
When a seller enrolls in FBA, they send their products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. Once the products are stored, they become part of Amazon’s inventory. When a customer places an order for an FBA product, Amazon handles the entire fulfillment process, including:
- Storage: Products are stored in Amazon’s warehouses, strategically located across various regions to ensure fast delivery.
- Order Processing: When an order is placed, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the product to the customer.
- Customer Service: Amazon manages customer service inquiries and returns, providing a seamless experience for both sellers and buyers.
- Prime Eligibility: Products fulfilled through FBA are eligible for Amazon Prime, attracting more customers who prefer fast shipping.
This model allows sellers to focus on their business strategy and marketing while benefiting from Amazon’s robust infrastructure.
Pros of Using FBA
1. Prime Eligibility
One of the most significant advantages of using FBA is that your products become eligible for Amazon Prime. This means that Prime members can receive their orders with free two-day shipping, making your products more appealing to a broader audience.
2. Increased Customer Trust
Products fulfilled by Amazon come with the assurance of Amazon’s customer service and return policies. This trust can lead to higher conversion rates, as customers are more likely to purchase items from sellers who utilize FBA.
3. Multi-Channel Fulfillment
FBA allows sellers to fulfill orders from other sales channels, such as their own website or other e-commerce platforms, using Amazon’s logistics. This multi-channel fulfillment capability simplifies inventory management and logistics, making it easier for businesses to scale.
4. Reduced Workload
By outsourcing the logistics to Amazon, sellers can significantly reduce their workload. This includes not only shipping but also handling returns and customer inquiries, freeing up time to focus on other critical areas of their business.
5. Access to Advanced Logistics
Amazon has invested heavily in its logistics capabilities, which can be challenging for smaller businesses to replicate. By using FBA, sellers gain access to a sophisticated system that can handle complex shipping and inventory management.
Cons of Using FBA
1. High Fees
While FBA can simplify operations, it comes with various fees that can add up quickly. Sellers must pay for storage, fulfillment, and additional services, which can eat into profit margins, particularly for low-cost items.
2. Strict Inventory Management Rules
Amazon has stringent inventory management policies that sellers must adhere to. This includes limits on the number of units that can be stored, particularly for new sellers. Failure to comply can result in penalties or removal of inventory.
3. Commingling Risks
Amazon may commingle inventory from different sellers, meaning that your products could be shipped alongside those from other sellers. This poses a risk if another seller’s product is defective or of low quality, potentially affecting your seller rating and customer satisfaction.
4. Less Control Over Shipping
When using FBA, sellers relinquish control over the shipping process. While Amazon’s logistics are generally reliable, any issues that arise, such as delays or errors, can reflect poorly on your business.
5. Long-Term Storage Fees
If inventory remains unsold for an extended period, sellers incur long-term storage fees, which can significantly impact profitability. This incentivizes sellers to manage their inventory carefully, but it can also lead to pressure to discount products or run promotions.
Who is FBA Best For?
Fulfillment by Amazon can be an excellent option for a variety of sellers, but it is particularly beneficial for:
- Small to Medium-Sized Businesses: FBA allows smaller businesses to leverage Amazon’s vast logistics network without the need for significant upfront investment in warehousing and shipping.
- E-commerce Entrepreneurs: New entrepreneurs looking to enter the market can benefit from Amazon’s established customer base and logistics infrastructure, making it easier to scale their operations.
- Sellers with High Sales Volume: Businesses that can sell a high volume of products can absorb the fees associated with FBA more easily, making it a cost-effective solution.
- Multi-Channel Sellers: Businesses that sell across multiple platforms can streamline their logistics through FBA, simplifying inventory management and fulfillment processes.
In conclusion, Fulfillment by Amazon can provide significant advantages for e-commerce sellers, particularly in terms of logistics and customer trust. However, it is essential to weigh these benefits against the potential downsides, such as fees and inventory management challenges. Understanding your business model and customer base will help you determine whether FBA is the right fit for your operations.
Core Services Offered by Fulfillment Centers
Inventory Management & Warehousing
Fulfillment centers provide essential inventory management and warehousing services that enable e-commerce businesses to optimize their stock levels and storage efficiency. These facilities are equipped with sophisticated inventory management systems that track stock quantities, monitor product conditions, and forecast demand based on sales data.
By utilizing these services, e-commerce businesses can benefit from reduced overhead costs associated with maintaining their own warehouse space. They can store products in strategically located fulfillment centers, which are often placed near major transportation hubs. This not only minimizes shipping times but also allows businesses to respond more effectively to fluctuations in demand. With real-time inventory tracking, businesses can avoid stockouts or overstock situations, ensuring they meet customer expectations without tying up unnecessary capital in inventory.
Pick and Pack Services
One of the primary functions of fulfillment centers is their pick and pack services. This process involves selecting items from the warehouse (picking) and preparing them for shipment (packing). Fulfillment centers employ efficient systems and trained staff to ensure that orders are processed quickly and accurately.
For e-commerce businesses, this service translates into faster order fulfillment times and higher customer satisfaction rates. When customers place orders, the fulfillment center can quickly retrieve the items, package them appropriately, and ship them out—often within the same day. This agility is particularly beneficial for businesses utilizing Amazon’s Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) service, where timely deliveries are critical to maintaining positive seller ratings and customer loyalty. The accuracy in picking and packing also reduces returns due to order errors, further streamlining operations.
Kitting and Assembly
Kitting and assembly services offered by fulfillment centers allow e-commerce businesses to streamline their product offerings. Kitting involves bundling multiple products into a single package, while assembly refers to the process of putting together components to create a finished product. For instance, a business selling a DIY furniture kit can have the fulfillment center assemble the parts before shipping them to customers.
This service provides several advantages. First, it simplifies the order process for customers by offering them bundled products at a competitive price. Second, it allows businesses to reduce shipping costs by consolidating items into one package, which can also lead to enhanced customer satisfaction through a more organized delivery experience. Additionally, kitting can facilitate promotional campaigns, where businesses can create special bundles to encourage higher sales volumes.
Returns Management (Reverse Logistics)
Returns management, or reverse logistics, is a critical service provided by fulfillment centers that helps e-commerce businesses efficiently process returned products. This involves receiving, inspecting, restocking, or disposing of items that customers send back. Given that returns are a natural part of e-commerce, having a robust returns management system is vital for maintaining customer trust and loyalty.
Fulfillment centers streamline this process by implementing clear protocols for handling returns. They assess the condition of returned items, determine whether they can be restocked or need to be repaired, and manage inventory adjustments accordingly. For businesses, this means less time and resources spent managing returns in-house, allowing them to focus on core operations. Efficient returns management also enhances customer satisfaction, as customers appreciate straightforward return processes and prompt resolutions. By analyzing return data, businesses can also identify trends or issues with specific products, informing future purchasing and product development decisions.
Conclusion
In summary, the core services offered by fulfillment centers—inventory management and warehousing, pick and pack services, kitting and assembly, and returns management—are essential for e-commerce businesses looking to scale efficiently. By leveraging these services, businesses can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and ultimately drive sales growth. Understanding and utilizing these services effectively allows e-commerce businesses to remain competitive in a fast-paced market, making fulfillment centers a valuable partner in their growth journey.
How to Choose a Fulfillment Partner: A 6-Point Checklist
Location & Warehouse Network
When selecting a fulfillment partner, the location of their warehouses is critical. Proximity to your customer base can significantly impact shipping times and costs, enhancing customer satisfaction and retention.
- Questions to Ask:
- What are the locations of your warehouses, and how do they align with our customer distribution?
- How do you handle shipping logistics to ensure timely deliveries?
- Are your facilities located near major transportation hubs or highways?
A well-distributed warehouse network allows for faster shipping and reduced transportation costs, which can be a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced e-commerce environment.
Technology & Integrations
In the digital age, the technology stack of your fulfillment partner is as important as their physical capabilities. A robust technology platform can streamline operations, improve inventory management, and enhance order processing.
- Questions to Ask:
- What fulfillment management software do you use, and how does it integrate with our existing systems (e.g., e-commerce platforms, ERPs)?
- Can you provide real-time inventory tracking and order status updates?
- How do you ensure data security and compliance with privacy regulations?
Effective technology integration can lead to operational efficiencies and better customer experiences through real-time updates and accurate inventory management.
Specializations (e.g., Cold Storage, Oversized Items)
Different businesses have unique product requirements. Understanding your potential partner’s specializations can help ensure they can meet your specific needs, whether you deal with perishable items, oversized products, or hazardous materials.
- Questions to Ask:
- Do you have specialized storage capabilities, such as cold storage or climate-controlled environments?
- How do you handle products that require special handling or packaging?
- Can you manage returns effectively for specialized products?
Choosing a partner with the right specializations can prevent costly mistakes and ensure compliance with industry regulations while catering to your product’s unique needs.
Scalability & Capacity
As your business grows, your fulfillment partner must have the capacity to scale alongside you. Understanding their scalability options can help you avoid disruptions in service as you expand.
- Questions to Ask:
- How do you handle seasonal fluctuations in demand?
- What is your current capacity, and how do you plan to expand in the future?
- Can you accommodate increases in order volume without impacting service quality?
A partner that can scale effectively will help you maintain service levels and customer satisfaction during peak seasons or rapid growth periods.
Pricing and Contracts
Cost is a significant factor in choosing a fulfillment partner. Understanding the pricing structure and contract terms is essential to avoid unexpected expenses that could affect your bottom line.
- Questions to Ask:
- Can you provide a detailed breakdown of your pricing structure, including storage, shipping, and handling fees?
- Are there any hidden fees or minimum order requirements?
- What is the length of the contract, and what are the terms for renewal or termination?
Transparent pricing and flexible contract terms can help you manage your budget effectively and ensure a good return on your investment.
Customer Support & Reviews
The level of customer support provided by your fulfillment partner can significantly impact your operations. Responsive and knowledgeable support can help you resolve issues quickly, ensuring minimal disruption to your business.
- Questions to Ask:
- What customer support channels do you offer (e.g., phone, email, live chat)?
- How quickly can we expect a response to inquiries or issues?
- Can you provide references or case studies from current clients?
Evaluating customer support and reviews can give you insights into how well the fulfillment partner operates and how they treat their clients, which is crucial for a long-term partnership.
Conclusion
Choosing the right fulfillment partner is a strategic decision that can influence your business’s operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By utilizing this checklist, you can assess potential partners thoroughly and ensure you select one that aligns with your business goals and can adapt as your needs evolve. Prioritize your requirements based on your specific business model, and don’t hesitate to negotiate terms that work best for you.
Understanding Fulfillment Pricing: A Breakdown of Common Fees
Initial Setup Fees
When starting to use a fulfillment center, businesses often encounter initial setup fees. These costs may include account setup, integration with your e-commerce platform, and any necessary software customization. Typically, fulfillment centers charge a one-time fee that varies based on the complexity of your requirements.
To calculate initial setup fees, consider the following factors:
– Account Management: Some fulfillment centers may charge for onboarding assistance, which can include training and support.
– Software Integration: Fees may arise if you need custom software solutions to integrate your inventory management with the fulfillment center’s systems.
– Initial Inventory Processing: If you are sending a large volume of products to the fulfillment center, there may be fees associated with processing and cataloging that inventory.
Receiving Fees
Receiving fees are charged when your products arrive at the fulfillment center. This fee covers the labor and resources needed to unload, inspect, and store your inventory. These fees can be calculated per pallet or per item, depending on the fulfillment center’s pricing structure.
Key elements that impact receiving fees include:
– Volume of Inventory: Larger shipments may incur lower per-item costs due to economies of scale.
– Condition of Items: If items require special handling or inspection, additional fees may be applied.
– Complexity of Inventory: If your inventory includes a variety of SKUs, the receiving process may be more labor-intensive, leading to higher fees.
Storage Fees (per pallet/bin)
Storage fees are recurring charges for keeping your inventory in the fulfillment center. These fees can be structured per pallet or per bin and are typically assessed monthly. The cost will vary based on the size and weight of the products stored.
When evaluating storage fees, consider the following factors:
– Storage Duration: Many fulfillment centers offer tiered pricing based on how long items are stored. For example, long-term storage fees may apply if products remain in storage for over a certain period (e.g., six months).
– Volume of Storage: The more space your inventory occupies, the higher the storage fee. It’s essential to calculate how many pallets or bins you will need based on your inventory turnover rate.
– Seasonal Demand: Businesses may experience fluctuations in storage needs based on seasonal demand, which can affect the total monthly storage fees.
Pick & Pack Fees (per item/order)
Pick and pack fees are charged for the process of selecting items from inventory and packing them for shipment. This fee is typically calculated on a per-item or per-order basis.
Factors influencing pick and pack fees include:
– Order Complexity: Orders with multiple items may incur higher fees due to the increased labor required to pick and pack.
– Packaging Requirements: If your products require special packaging materials or methods, these costs can be passed along as part of the pick and pack fee.
– Order Frequency: Some fulfillment centers may offer discounts for businesses that ship a high volume of orders, reducing the per-order pick and pack fee.
Shipping Fees
Shipping fees are the costs associated with delivering orders to customers. These fees can vary significantly based on the shipping method, destination, and weight of the packages. Fulfillment centers typically charge shipping fees based on the negotiated rates with carriers, which can be passed on to businesses.
Key aspects of shipping fees include:
– Carrier Selection: Different carriers (e.g., UPS, FedEx, USPS) may have varying rates. Businesses should consider which carriers offer the best pricing for their shipping needs.
– Shipping Zones: Costs can vary based on the distance from the fulfillment center to the customer. Shipping to far-off destinations will typically incur higher fees.
– Weight and Dimensions: Heavier and larger packages will usually result in higher shipping fees. It’s essential to accurately weigh and measure products to avoid unexpected costs.
Tips for Getting an Accurate Quote
-
Provide Detailed Inventory Information: Be clear about the types of products you’ll be shipping, including dimensions and weights. This information helps fulfillment centers provide more accurate quotes.
-
Consider Your Volume: If you anticipate high shipping volumes, discuss potential volume discounts with fulfillment centers.
-
Ask About Hidden Fees: Always inquire about any additional charges that may not be included in the initial quote, such as long-term storage fees or extra pick and pack costs.
-
Compare Multiple Fulfillment Centers: Don’t settle on the first quote you receive. Compare several fulfillment centers to find the best balance of price and service.
-
Review Contracts Carefully: Before signing, ensure you understand all terms related to pricing, including how fees are calculated and any potential increases.
By understanding these common fulfillment pricing models and carefully evaluating your options, you can make informed decisions that support your e-commerce business’s growth and efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Fulfillment
1. What is the KRB2 Amazon Fulfillment Center?
The KRB2 Amazon Fulfillment Center is one of Amazon’s large-scale facilities located in San Bernardino, California. It specializes in storing, packing, and shipping a wide variety of products for e-commerce, enabling efficient order fulfillment for businesses utilizing Amazon’s infrastructure.
2. How does the KRB2 fulfillment center operate?
The KRB2 center operates by receiving products from sellers, storing them in its warehouse, and processing orders for shipment. Once an order is placed, items are picked, packed, and shipped, often using Amazon’s logistics network, which includes partnerships with major carriers for timely delivery.
3. What is the difference between a warehouse and a fulfillment center?
A warehouse is primarily used for storage, while a fulfillment center focuses on the entire order fulfillment process, including inventory management, order processing, packing, and shipping. Fulfillment centers are designed for efficiency in getting products to customers quickly.
4. How can my business benefit from using the KRB2 fulfillment center?
Utilizing the KRB2 fulfillment center allows businesses to leverage Amazon’s extensive logistics network, ensuring faster delivery times and access to Prime shipping. This can enhance customer satisfaction and help businesses scale without needing to manage their own warehousing and shipping operations.
5. What is a 3PL (Third-Party Logistics)?
A 3PL provider offers outsourced logistics services, which can include transportation, warehousing, inventory management, and order fulfillment. Using a 3PL like Amazon’s fulfillment centers allows businesses to focus on their core operations while relying on experts for logistics.
6. How much do fulfillment services cost?
Fulfillment service costs can vary based on several factors, including storage fees, order processing fees, and shipping costs. At Amazon fulfillment centers, fees are typically based on the size and weight of products, as well as the volume of orders processed. It’s important to review Amazon’s FBA pricing structure for specific details.
7. Can I manage my inventory remotely at the KRB2 fulfillment center?
Yes, Amazon provides a comprehensive dashboard for sellers to manage their inventory remotely. You can track inventory levels, view sales data, and manage shipments directly through your Amazon Seller Central account.
8. What types of products can be stored at the KRB2 fulfillment center?
The KRB2 fulfillment center can store a wide range of products, from electronics to household goods. However, there are restrictions on certain items, such as hazardous materials or perishables. It’s essential to check Amazon’s guidelines for specific product categories.
9. How does Amazon ensure the security of inventory at the KRB2 center?
Amazon employs advanced security measures at its fulfillment centers, including surveillance cameras, controlled access points, and regular security audits. These protocols are designed to protect inventory and ensure the safety of the facility.
10. What should I do if I have issues with my orders fulfilled by the KRB2 center?
If you encounter issues with orders fulfilled by the KRB2 center, such as shipping errors or damaged items, you can resolve these through your Amazon Seller Central account. Amazon provides support for sellers to address any fulfillment-related concerns, ensuring that issues are handled promptly.
Conclusion: Is Outsourcing Fulfillment the Right Move for Your Business?
The Case for Outsourcing Fulfillment
Outsourcing fulfillment can be a game-changer for e-commerce businesses seeking to scale. By leveraging a fulfillment service, companies can significantly save time, allowing them to focus on core business activities such as marketing and product development. This operational efficiency is crucial in today’s fast-paced market, where timely delivery can make or break customer satisfaction.
Another compelling benefit is scalability. As your business grows, so do the complexities of managing inventory, shipping logistics, and customer service. A dedicated fulfillment partner can seamlessly adapt to your changing needs, whether you’re experiencing seasonal spikes in demand or expanding your product line. This flexibility ensures that you can meet customer expectations without overextending your resources.
Furthermore, partnering with an experienced fulfillment provider brings expertise that can enhance your operational capabilities. From optimizing shipping routes to implementing advanced inventory management systems, a knowledgeable partner can help you navigate the intricacies of logistics, ultimately improving your bottom line.
However, it’s vital to choose the right fulfillment partner. Not all providers offer the same level of service, and aligning your business goals with their capabilities is essential for sustainable growth. Conducting thorough research and due diligence will ensure you select a partner that not only meets your current needs but can also support your future ambitions.
In conclusion, if you’re contemplating whether outsourcing fulfillment is the right move, start by auditing your current shipping processes. Assess where inefficiencies lie and consider how a fulfillment partner could alleviate those challenges. This proactive step could be the catalyst for significant growth in your e-commerce journey. Don’t hesitate—take the first step toward streamlining your operations and enhancing your customer experience today.
Important Disclaimer
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information in this guide is for educational purposes. Fulfillment services, pricing, and platform features change frequently. Always conduct your own due diligence and consult with providers directly before making business decisions.